Abstract
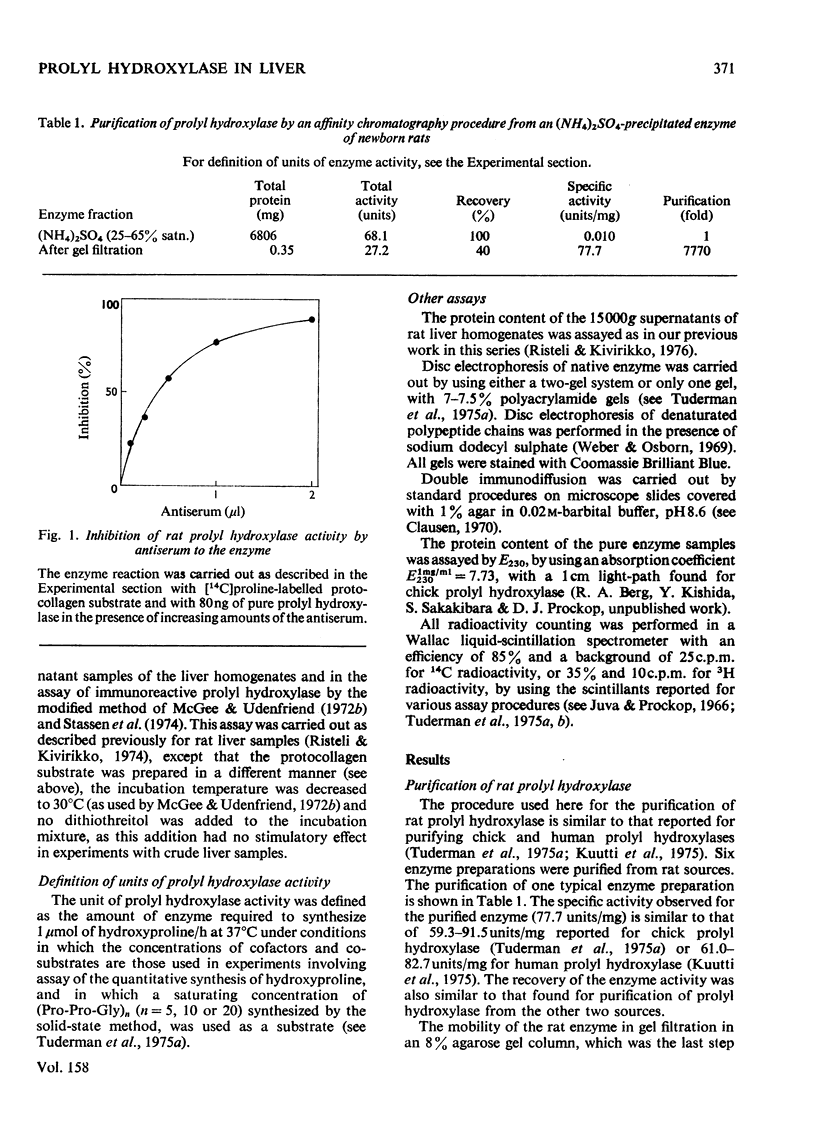
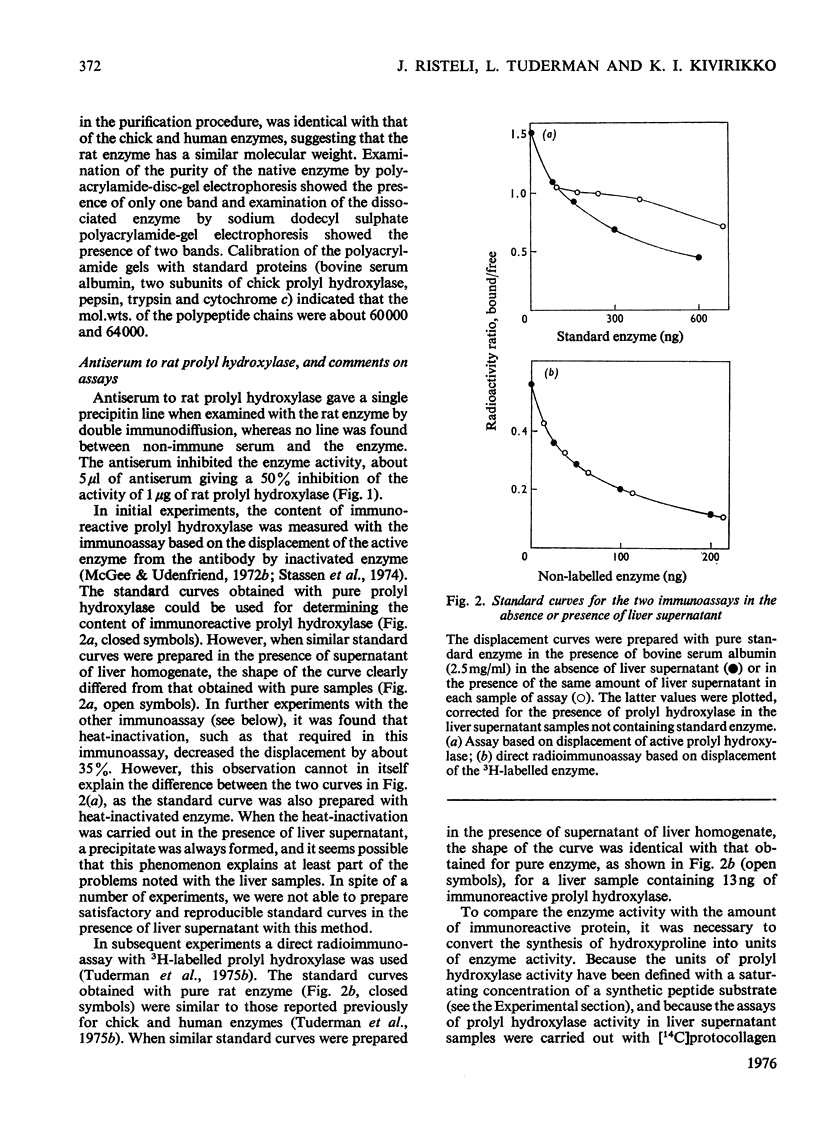
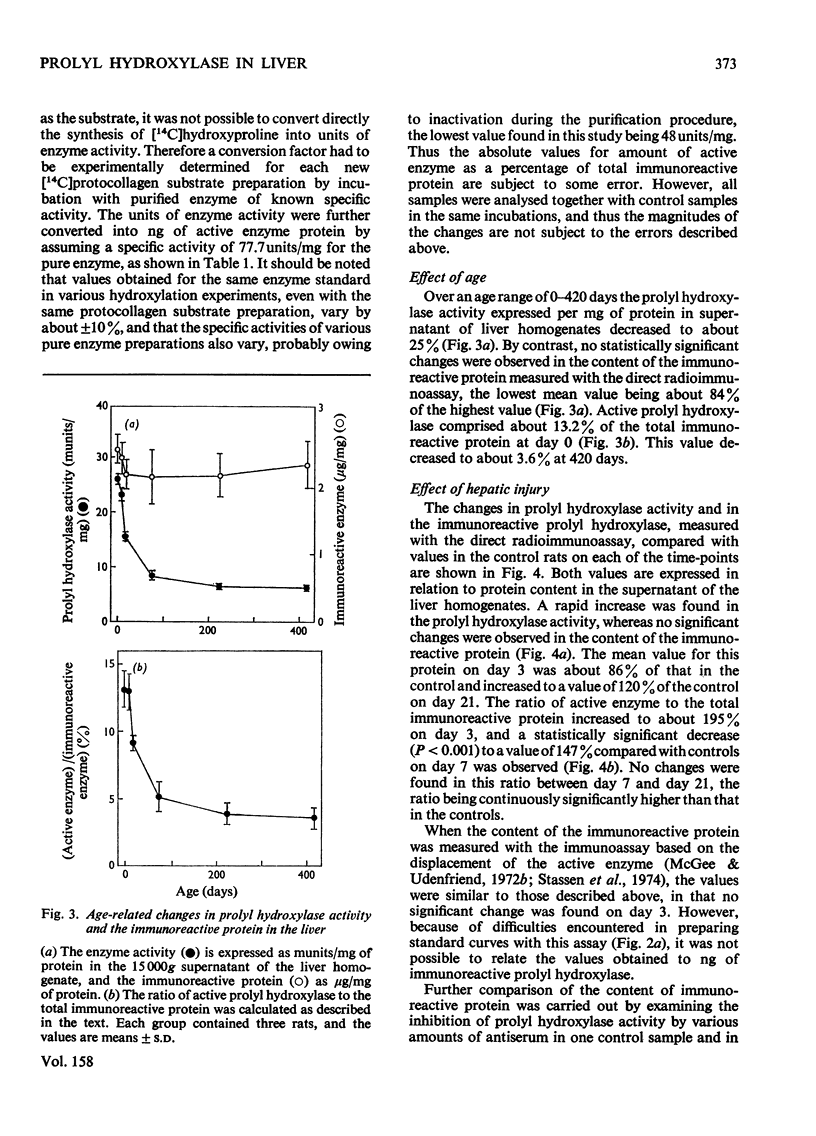
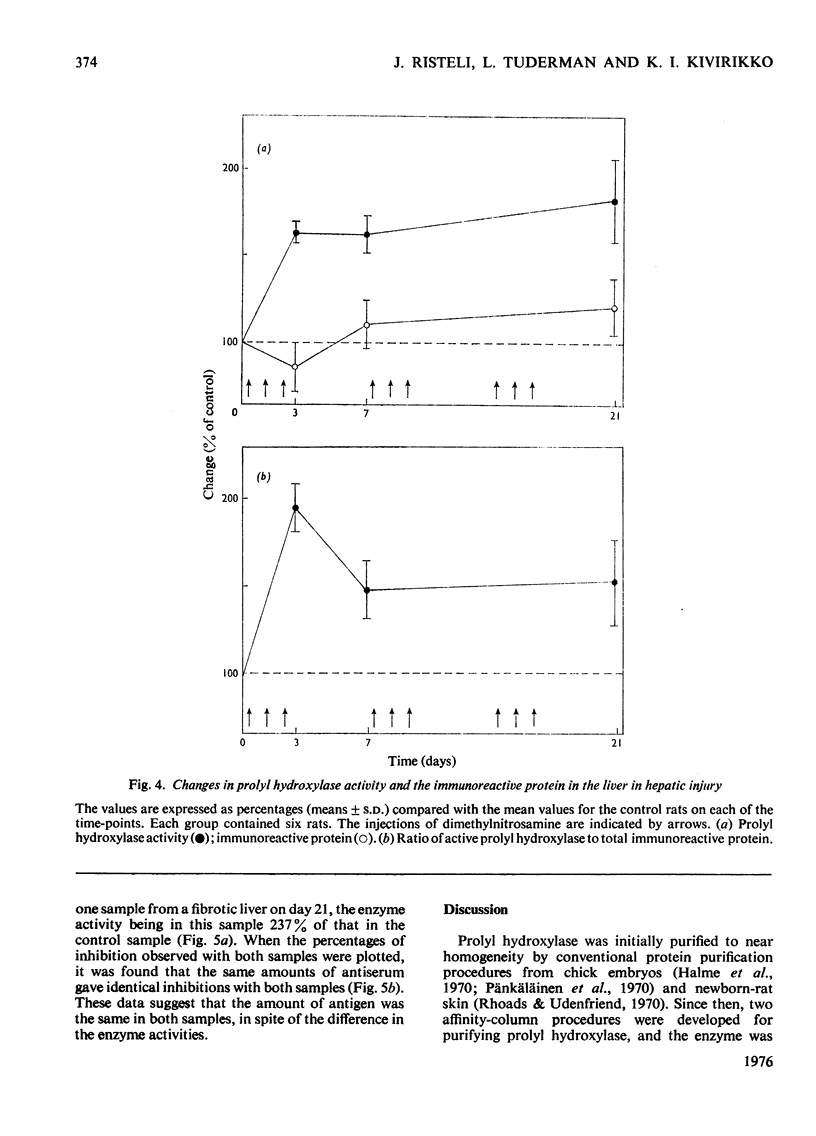
Prolyl hydroxylase was purified from newborn rats by affinity chromatography using poly(L-proline), and antiserum to the enzyme was prepared in rabbits. The rat prolyl hydroxylase was similar to the chick and human enzymes with respect to specific activity, molecular weight and molecular weights of the polypeptide chains. The activity of prolyl hydroxylase and the content of immunoreactive enzyme were measured in rat liver as a function of age in experimental hepatic injury. Active prolyl hydroxylase comprised about 13.2% of the total immunoreactive protein in the liver of newborn rats and the value decreased to about 3.6% at the age of 420 days. This decrease was due to a decrease in the enzyme activity, whereas only minor changes were found in the content of the immunoreactive protein. In hepatic injury, a significant increase was found in the ratio of active enzyme to total immunoreactive protein, owing to an increase in the enzyme activity. The data indicate that prolyl hydroxylase activity in rat liver is controlled in part by a mechanism which does not involve changes in the content of the total immunoreactive protein.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg R. A., Prockop D. J. Affinity column purification of protocollagen proline hydroxylase from chick embryos and further characterization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 25;248(4):1175–1182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. A., Prockop D. J. Purification of (14C) protocollagen and its hydroxylation by prolyl-hydroxylase. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3395–3401. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanck T. J., Peterkofsky B. The stimulation of collagen secretion by ascorbate as a result of increased proline hydroxylation in chick embryo fibroblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Nov;171(1):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P. The biosynthesis of collagen. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):567–603. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger H. G., Lee V. W., Rennie G. C. A generalized computer program for the treatment of data from competitive protein-binding assays including radioimmunoassays. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Aug;80(2):302–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardinale G. J., Udenfriend S. Prolyl hydroxylase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974;41(0):245–300. doi: 10.1002/9780470122860.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehm P., Prockop D. J. Time lag in the secretion of collagen by matrix-free tendon cells and inhibition of the secretory process by colchicine and vinblastine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 21;264(2):375–382. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90302-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinman L., Lieber C. S. Hepatic collagen metabolism: effect of alcohol consumption in rats and baboons. Science. 1972 May 19;176(4036):795–795. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4036.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halme J., Kivirikko K. I., Simons K. Isolation and partial characterization of highly purified protocollagen proline hydroxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 18;198(3):460–470. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood R., Grant M. E., Jackson D. S. Collagen biosynthesis. Characterization of subcellular fractions from embyonic chick fibroblasts and the intracellular localization of protocollagen prolyl and protocollagen lysyl hydroxylases. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;144(1):123–130. doi: 10.1042/bj1440123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juva K., Prockop D. J. Modified procedure for the assay of H-3-or C-14-labeled hydroxyproline. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90249-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao W. W., Berg R. A., Prockop D. J. Ascorbate increases the synthesis of procollagen hydroxyproline by cultured fibroblasts from chick embryo tendons without activation of prolyl hydroxyla. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 5;411(2):202–215. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90300-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivirikko K. I., Laitinen O., Prockop D. J. Modifications of a specific assay for hydroxyproline in urine. Anal Biochem. 1967 May;19(2):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90160-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuttan R., Cardinale G. J., Udenfriend S. An activatable form of prolyl hydroxylase in fibrobalast extracts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 2;64(3):947–954. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90139-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuutti E. R., Tuderman L., Kivirikko K. I. Human prolyl hydroxylase. Purification, partial characterization and preparation of antiserum to the enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):181–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis F. L. Solid-phase radioimmune assay. Using 3 H-labeled antigen for the mouse olfactory bulb specific protein. Anal Biochem. 1972 Dec;50(2):602–607. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90071-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee J. O., Langness U., Udenfriend S. Immunological evidence for an inactive precursor of collagen proline hydroxylase in cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1585–1589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee J. O., Udenfriend S. A general method for the rapid measurement of enzyme precursors by the displacement of enzyme from antibody: the measurement of collagen proline hydroxylase precursor in cultured fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Feb 25;46(4):1646–1653. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90798-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee J. O., Udenfriend S. Partial purification and characterization of peptidyl proline hydroxylase precursor from mouse fibroblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Sep;152(1):216–221. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90209-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pänkäläinen M., Aro H., Simons K., Kivirikko K. I. Protocollagen proline hydroxylase: molecular weight, subunits and isoelectric point. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 22;221(3):559–565. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90227-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E., Udenfriend S. Decarboxylation of alpha-ketoglutarate coupled to collagen proline hydroxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1473–1478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E., Udenfriend S. Purification and properties of collagen proline hydroxylase from newborn rat skin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Aug;139(2):329–339. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90485-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice R. H., Means G. E. Radioactive labeling of proteins in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):831–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risteli J., Kivirikko K. I. Activities of prolyl hydroxylase, lysyl hydroxylase, collagen galactosyltransferase and collagen glucosyltransferase in the liver of rats with hepatic injury. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;144(1):115–122. doi: 10.1042/bj1440115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risteli J., Kivirikko K. I. Intracellular enzymes of collagen biosynthesis in rat liver as a function of age and in hepatic injury induced by dimethylnitrosamine. Changes in prolyl hydroxylase, lysyl hydroxylase, collagen galactosyltransferase and collagen glucosyltransferase activities. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 15;158(2):361–367. doi: 10.1042/bj1580361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stassen F. L., Cardinale G. J., McGee J. O., Udenfriend S. Prolyl hydroxylase and an immunologically related protein in mammalian tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jan;160(1):340–345. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(74)80042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi T., Kivirikko K. I., Prockop D. J. Increased protocollagen hydroxylase activity in the livers of rats with hepatic fibrosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 27;28(6):940–944. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi T., Prockop D. J. Protocollagen proline hydroxylase in normal liver and in hepatic fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 1969 Apr;56(4):744–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuderman L., Kuutti E. R., Kivirikko K. I. An affinity-column procedure using poly(L-proline) for the purification of prolyl hydroxylase. Purification of the enzyme from chick embryos. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Mar 3;52(1):9–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuderman L., Kuutti E. R., Kivirikko K. I. Radiommunoassay for human and chick prolyl hydroxylases. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 15;60(2):399–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb21016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



