Abstract
1. Inhibition of endogenous microsomal NADPH oxidase by CO enables membrane-bound glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase (EC 1.8.4.2) to be assayed conveniently by a linked assay involving NADPH and glutathione reductase (EC 1.6.4.2). 2. The specific activity of the enzyme in rat liver microsomal preparations is of the order of 1 nmol of oxidized glutathione formed/min per mg of membrane protein. 3. The specific activity of the enzyme is comparable in rough and smooth microsomal fractions, and the activity is not affected by treatment with EDTA and the removal of ribosomes from rough microsomal fractions. 4. Membrane-bound glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase is not affected by concentrations of deoxycholate up to 0.5%, whereas protein disulphide-isomerase (EC 5.3.4.1) is drastically inhibited. 5. On these grounds it is concluded that, in rat liver microsomal fractions, glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase and protein disulphide-isomerase activities are not both catalysed by a single enzyme species.
Full text
PDF




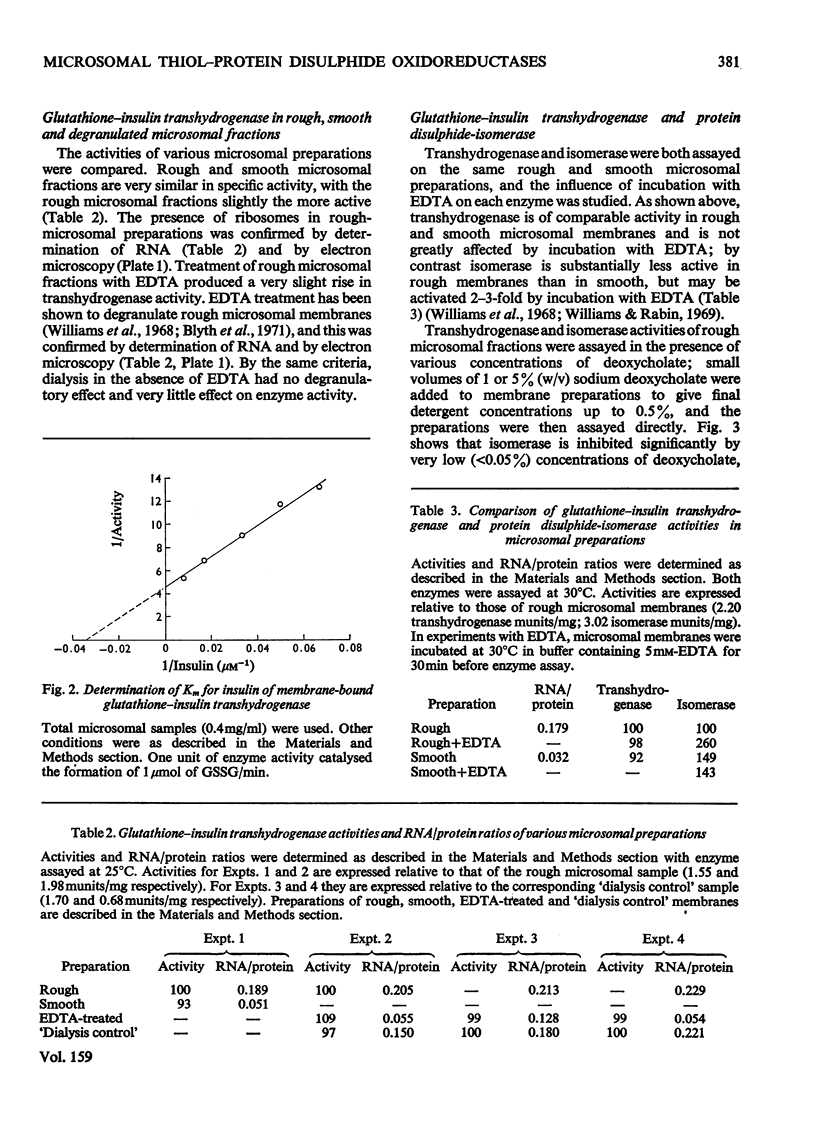
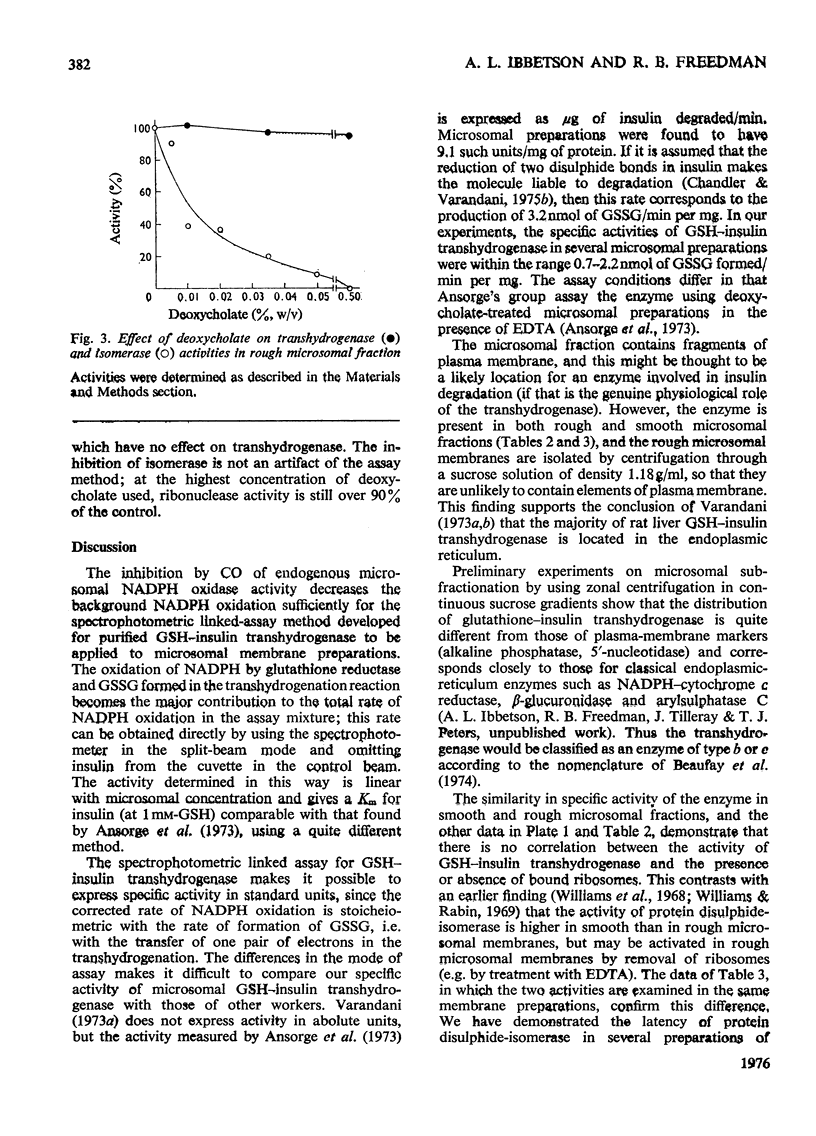


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansorge S., Bohley P., Kirschke H., Langner J., Wiederanders B., Hanson H. Metabolism of insulin and glucagon. Glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase from microsomes of rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jan 3;32(1):27–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaufay H., Amar-Costesec A., Thinès-Sempoux D., Wibo M., Robbi M., Berthet J. Analytical study of microsomes and isolated subcellular membranes from rat liver. 3. Subfractionation of the microsomal fraction by isopycnic and differential centrifugation in density gradients. J Cell Biol. 1974 Apr;61(1):213–231. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Distribution of radioactivity between the acid-soluble pool and the pools of RNA in the nuclear, nonsedimethable and ribosome fractions of rat liver after a single injection of lebaled orotic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug 23;166(1):48–57. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90489-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blyth C. A., Freedman R. B., Rabin B. R. The effects of aflatoxin B1 on the sex-specific binding of steroid hormones to microsomal membranes of rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jun 29;20(4):580–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler M. L., Varandani P. T. Insulin degradation. XV. Use of different assay methods for the study of mechanism of action of glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 26;397(2):307–317. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler M. L., Varandani P. T. Kinetic analysis of the mechanism of insulin degradation by glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase (thiol: protein-disulfide oxidoreductase). Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2107–2115. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lorenzo F., Goldberger R. F., Steers E., Jr, Givol D., Anfinsen B. Purification and properties of an enzyme from beef liver which catalyzes sulfhydryl-disulfide interchange in proteins. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 10;241(7):1562–1567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Corte E., Parkhouse R. M. Biosynthesis of immunoglobulin A (IgA) and immunoglobulin M (IgM). Requirement for J chain and a disulphide-exchanging enzyme for polymerization. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;136(3):597–606. doi: 10.1042/bj1360597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson S., Askelöf P., Axelsson K., Carlberg I., Guthenberg C., Mannervik B. Resolution of glutathione-linked enzymes in rat liver and evaluation of their contribution to disulfide reduction via thiol--disulfide interchange. Acta Chem Scand B. 1974;28(8):922–930. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.28b-0922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIVOL D., DELORENZO F., GOLDBERGER R. F., ANFINSEN C. B. DISULFIDE INTERCHANGE AND THE THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Mar;53:676–684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.3.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERGER R. F., EPSTEIN C. J., ANFINSEN C. B. Acceleration of reactivation of reduced bovine pancreatic ribonuclease by a microsomal system from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:628–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins H. C., Freedman R. B. Fluorescence studies of drug and cation interactions with microsomal membranes. FEBS Lett. 1973 May 1;31(3):301–307. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins H. C., Freedman R. B. Thiol-protein disulphide oxidoreductases. Differences between protein disulphide-isomerase and glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase activities in ox liver. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):385–393. doi: 10.1042/bj1590385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzen H. M., Tietze F. Studies on the specificity and mechanism of action of hepatic glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3561–3570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreibich G., Sabatini D. D. Microsomal membranes and the translational apparatus of eukaryotic cells. Fed Proc. 1973 Nov;32(11):2133–2138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLENHAUER H. H. PLASTIC EMBEDDING MIXTURES FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. Stain Technol. 1964 Mar;39:111–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro H. N. The determination of nucleic acids. Methods Biochem Anal. 1966;14:113–176. doi: 10.1002/9780470110324.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARAHARA H. T., WILLIAMS R. H. Reduction of insulin by extracts of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jan;234(1):71–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACKER E. Glutathione-homocystine transhydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1955 Dec;217(2):867–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner R. F., De Lorenzo F., Anfinsen C. B. Enzymically catalyzed disulfide interchange in randomly cross-linked soybean trypsin inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1965 Dec;240(12):4648–4651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMIZAWA H. H., VARANDANI P. T. GLUTATHIONE-INSULIN TRANSHYDROGENASE OF HUMAN LIVER. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jul;240:3191–3194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. H. The role of 'insulinase' in the degradation of insulin. Postgrad Med J. 1973 Dec;49(Suppl):940–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENETIANER P., STRAUB F. B. The enzymic reactivation of reduced ribonuclease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jan 8;67:166–168. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91812-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T. Insulin degradation. V. Unmasking of glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase in rat liver microsomal membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 28;304(3):642–659. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90210-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T. Insulin degradation. X. Identification of insulin degrading activity of rat liver plasma membrane as glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T. Insulin degradation. XII. The amino acid composition, amino-terminal, and carbohydrate content of beef pancreatic glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 18;371(2):577–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T., Nafz M. A., Chandler M. L. Interaction of insulin analogs, glucagon, growth hormone, vasopressin, oxytocin, and scrambled forms of ribonuclease and lysozyme with glytathione-insulin transhydrogenase (thiol: protein-disulfide oxidoreductase): dependence upon conformation. Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2115–2120. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. J., Gurari D., Rabin B. R. The effects of ribosomes on the activity of a membrane bound enzyme catalysing thiol-disulphide interchange. FEBS Lett. 1968 Dec;2(2):133–135. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(68)80123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. J., Rabin B. R. The effects of aflatoxin B(1) and steroid hormones on polysome binding to microsomal membranes as measured by the activity of an enzyme catalysing disulphide interchange. FEBS Lett. 1969 Jul;4(2):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80207-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]