Abstract
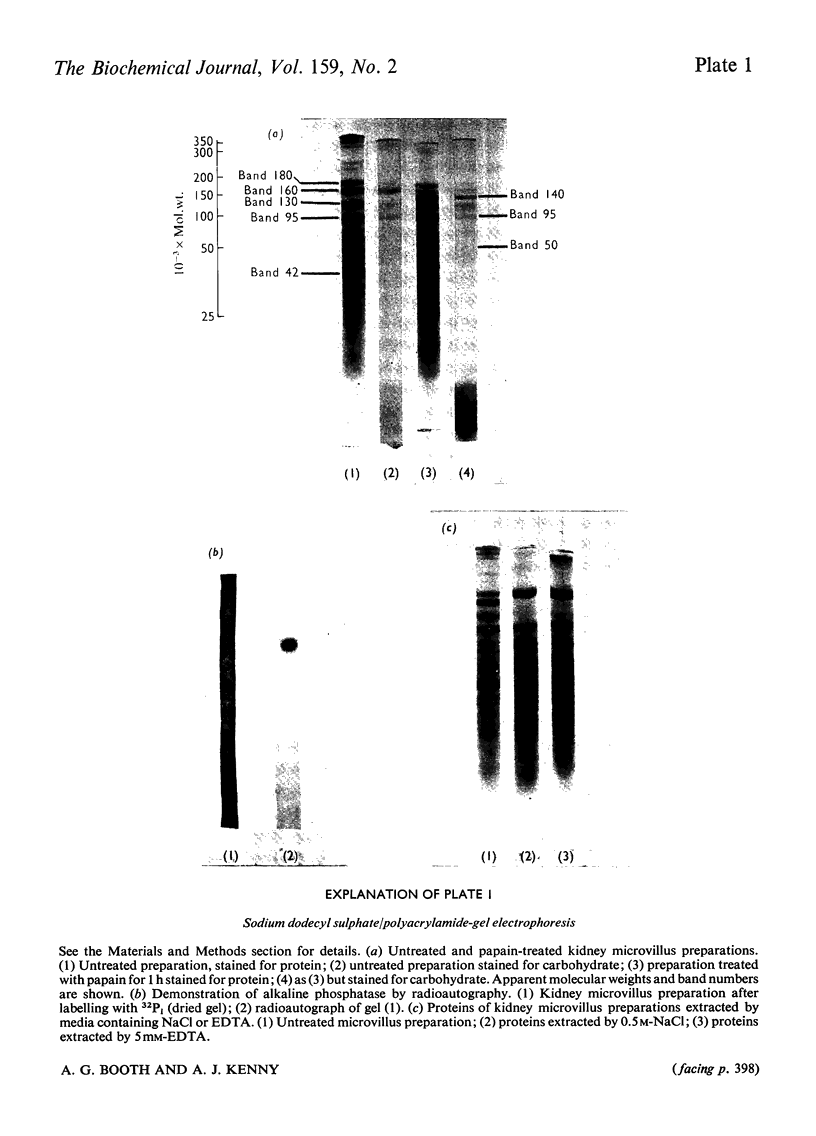
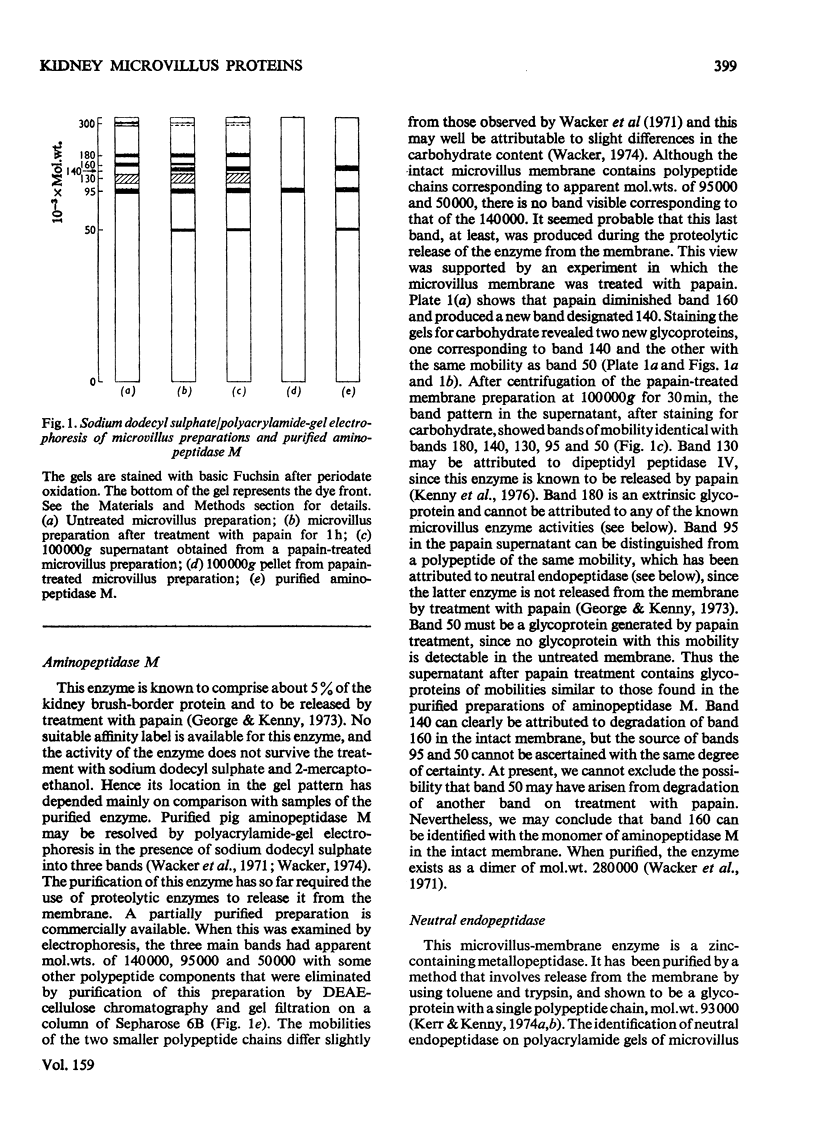
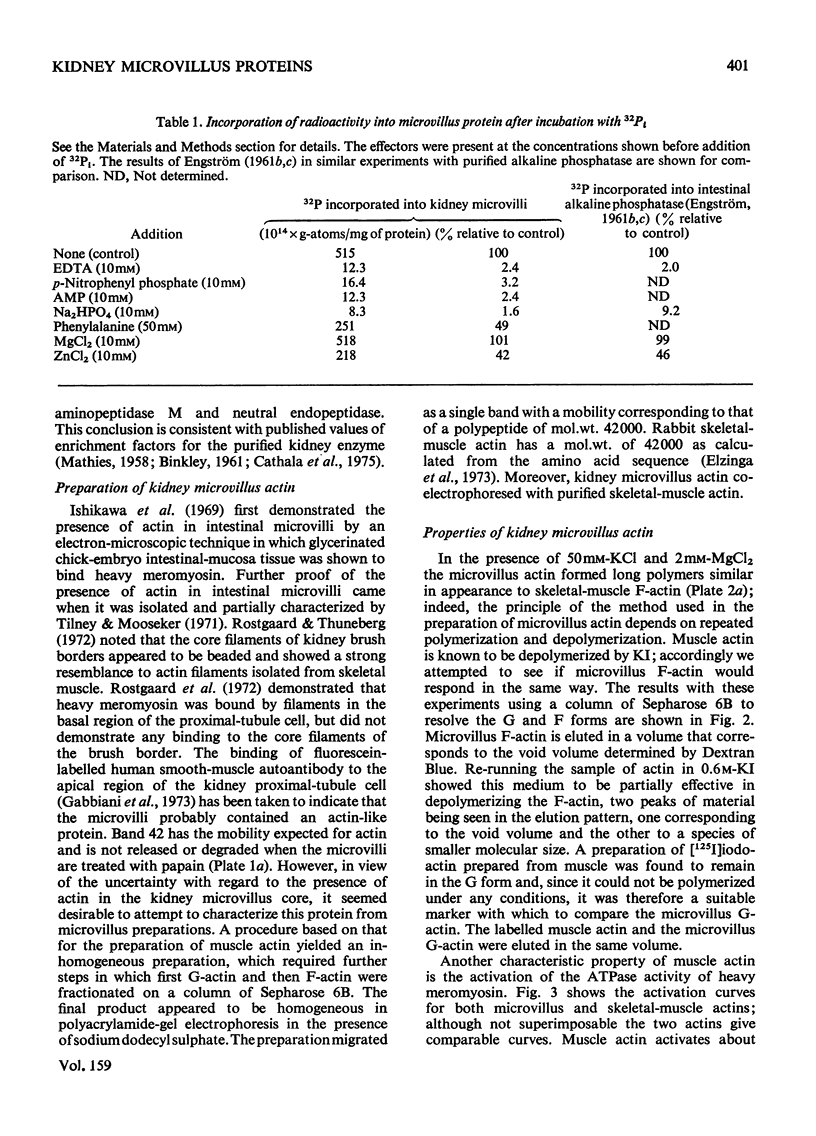
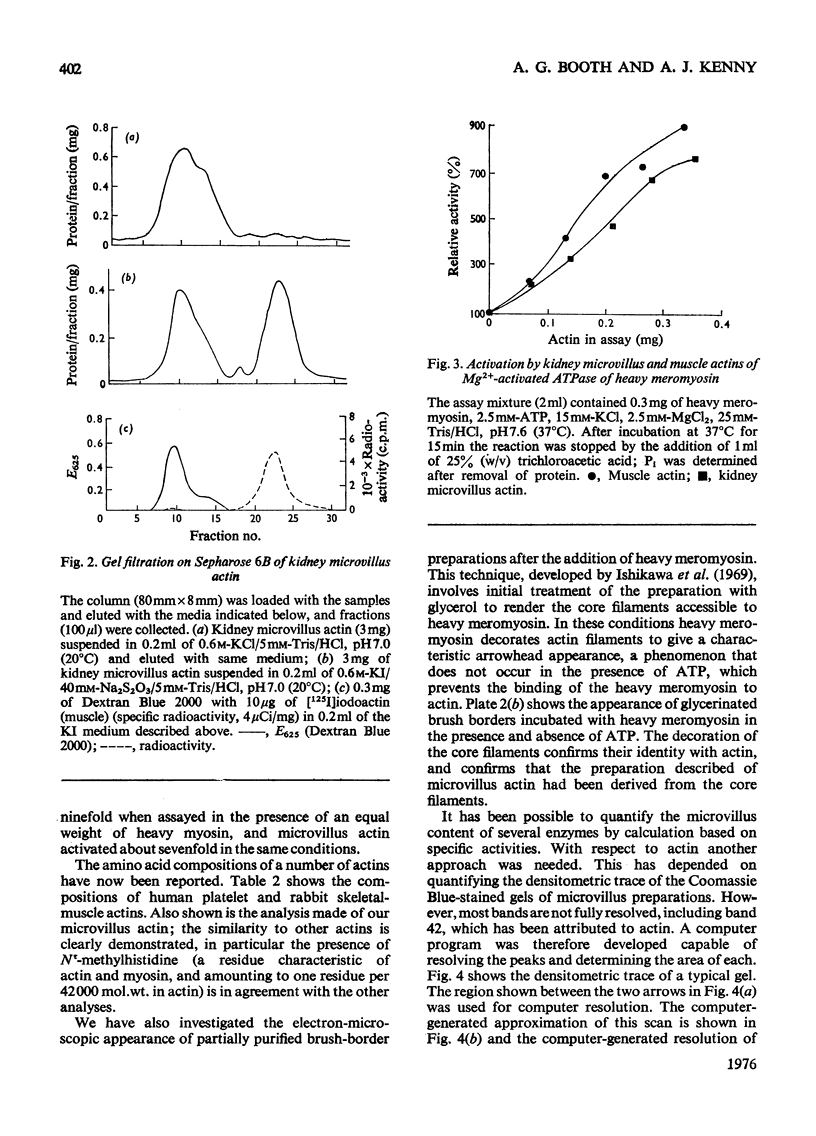
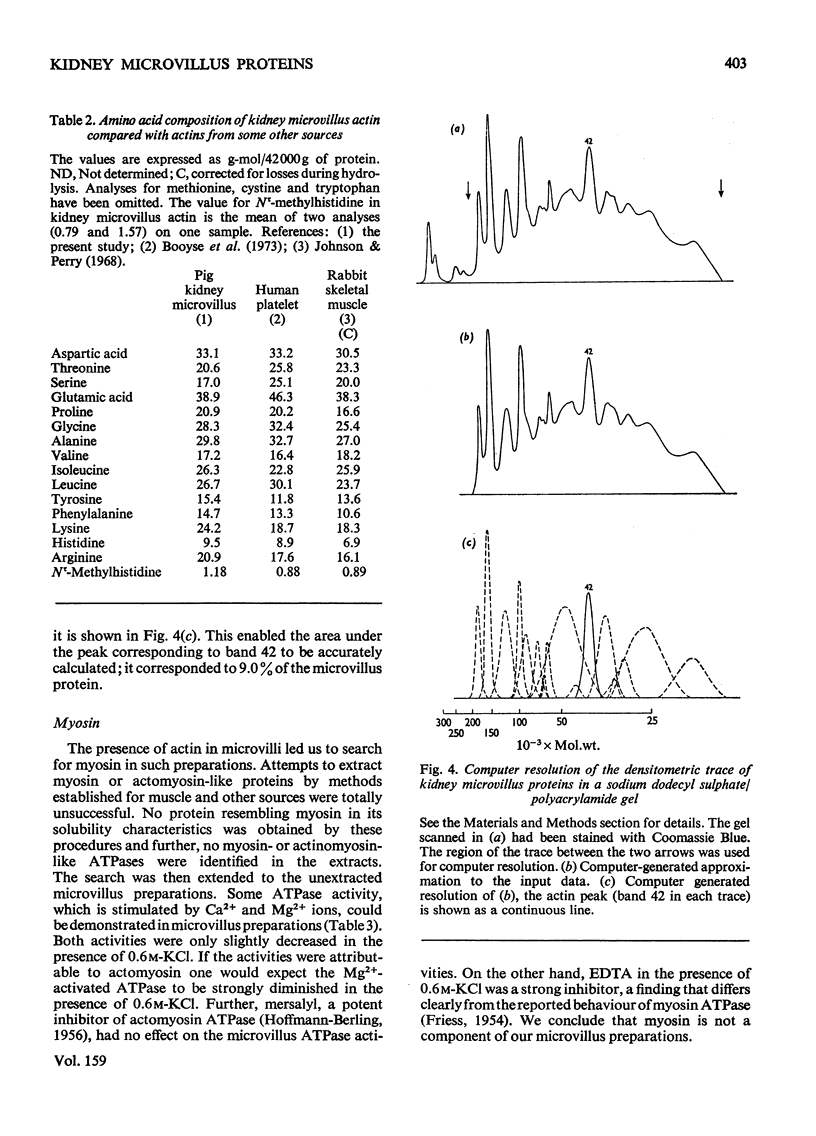
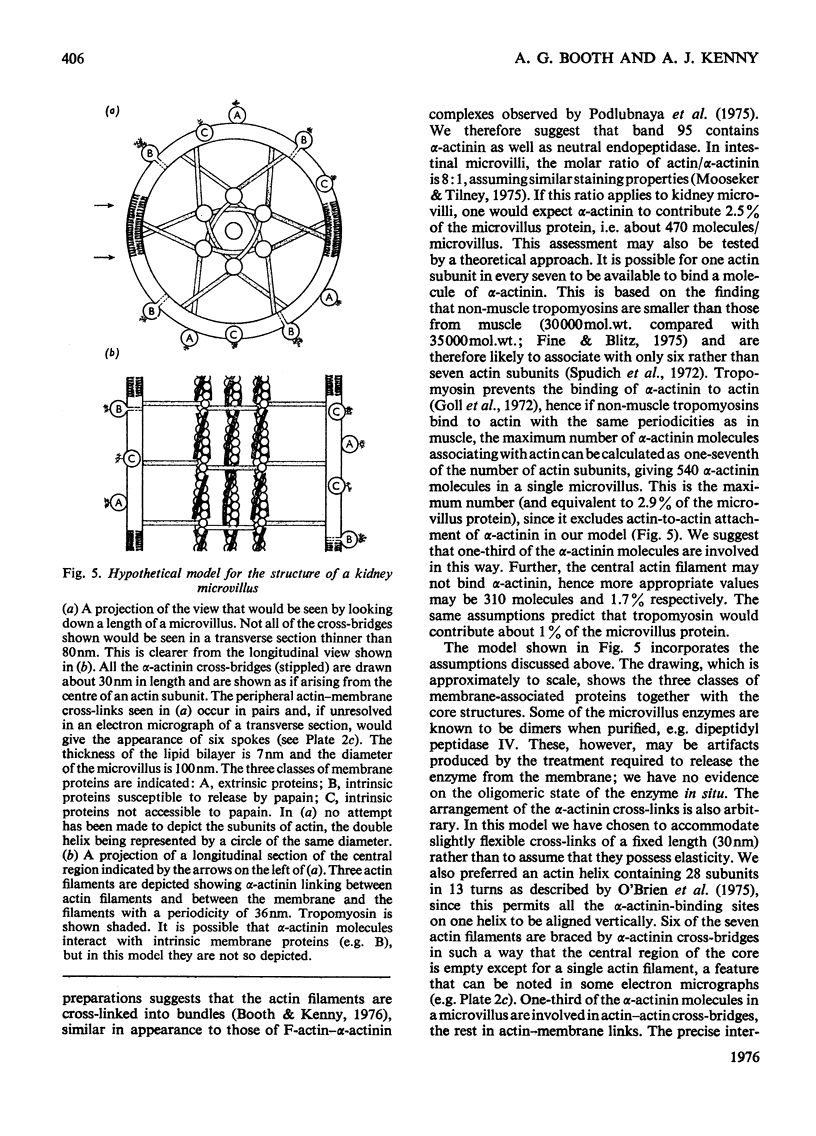
The proteins of microvilli prepared from pig kidney were analysed by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate. The typical pattern stained for protein revealed five major bands, four of which also stained for carbohydrate, and about 15 minor bands. For descriptive purposes the bands were designated numerically by their apparent molecular weights (X10(-3). Well-characterized proteins were identified with four of the five major bands. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV, a serine proteinase that may be specifically labelled with di-isopropyl [32P]phosphorofluoridate, was assigned to band 130. Aminopeptidase M was assigned to band 160, though when released from the membrane by a proteinase, this protein comprises three polypeptides each of lower apparent molecular weight than the native enzyme. Neutral endopeptidase can be assigned to band 95 and actin to band 42. The fifth major band (180) is an extrinsic glycoprotein that has not been identified with any microvillus enzyme activity. These four proteins contribute 21% of the microvillus-membrane protein. Kidney microvillus actin was characterized by a variety of properties and was similar to muscle actin. A computer analysis of the gel pattern indicates that it comprises 9.0% of the microvillus protein. Myosin is not present in the microvillus, but another protein associated with band 95, with properties that distinguish it from neutral endopeptidase, was tentatively identified as alpha-actinin. Alkaline phosphatase was identified as a monomeric polypeptide with an apparent molecular weight of 80000; it is a minor protein of the microvillus and is not discernible as a discrete band in the gel pattern. These and other results permit a model of the organization of the microvillus protein to be suggested. The computer program used has been deposited as Supplementary Publication SUP 50070 (12 pages) at the British Library Lending Division, Boston Spa. Wetherby, West Yorkshire LS23 7BQ, U.K., from whom copies can be obtained on the terms given in Biochem. J. (1976) 153,5.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson N. N., Jr, Touster O. Isolation of rat liver plasma membrane fragments in isotonic sucrose. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:90–102. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth A. G., Kenny A. J. A rapid method for the preparation of microvilli from rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):575–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1420575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth A. G., Kenny J. A morphometric and biochemical investigation of the vesiculation of kidney microvilli. J Cell Sci. 1976 Aug;21(3):449–463. doi: 10.1242/jcs.21.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booyse F. M., Hoveke T. P., Rafelson M. E., Jr Human platelet actin. Isolation and properties. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):4083–4091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D., Thomas C. The actin content of fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1975 May;147(2):221–228. doi: 10.1042/bj1470221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Brunel C. Bovine kidney alkaline phosphatase. Purification, subunit structure, and metalloenzyme properties. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6040–6045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley D. R., Howell K. E., Eichholz A. Solubilization of brush borders of hamster small intestine and fractionation of some of the components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 3;394(3):361–376. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGSTROM L. Isolation of 32P-labeled phosphorylserine from a highly purified preparation of calif intestinal alkaline phosphatase incubated with radioactive inorganic phosphate. A preliminary report. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1959;64:214–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGSTROM L. Studies on calf-intestinal alkaline phosphatase. I. Chromatographic purification, microheterogeneity and some other properties of the purified enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 2;52:36–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90901-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGSTROM L. Studies on calf-intestinal alkaline phosphatase. II. Incorporation of inorganic phosphate into a highly purified enzyme preparation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 2;52:49–59. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90902-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elzinga M., Collins J. H., Kuehl W. M., Adelstein R. S. Complete amino-acid sequence of actin of rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2687–2691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIESS E. T. The effect of a chelating agent on myosin ATPase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Jul;51(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90448-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine R. E., Blitz A. L. A chemical comparison of tropomyosins from muscle and non-muscle tissues. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 5;95(3):447–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Ryan G. B., Lamelin J. P., Vassalli P., Majno G., Bouvier C. A., Cruchaud A., Lüscher E. F. Human smooth muscle autoantibody. Its identification as antiactin antibody and a study of its binding to "nonmuscular" cells. Am J Pathol. 1973 Sep;72(3):473–488. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George S. G., Kenny J. Studies on the enzymology of purified preparations of brush border from rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1973 May;134(1):43–57. doi: 10.1042/bj1340043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Neville D. M., Jr Glycoproteins of cell surfaces. A comparative study of three different cell surfaces of the rat. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6339–6346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover J. S., Salter D. N., Shepherd B. P. A study of some factors that influence the iodination of ox insulin. Biochem J. 1967 Apr;103(1):120–128. doi: 10.1042/bj1030120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goli D. E., Suzuki A., Temple J., Holmes G. R. Studies on purified -actinin. I. Effect of temperature and tropomyosin on the -actinin-F-actin interaction. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):469–488. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90464-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMANN-BERLING H. Das kontraktile Eiweiss undifferenzierter Zellen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Mar;19(3):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90468-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Bischoff R., Holtzer H. Formation of arrowhead complexes with heavy meromyosin in a variety of cell types. J Cell Biol. 1969 Nov;43(2):312–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P., Perry S. V. Chemical studies on the cysteine and terminal peptides in tryptic digests of actin. Biochem J. 1968 Nov;110(2):207–216. doi: 10.1042/bj1100207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Booth A. G., George S. G., Ingram J., Kershaw D., Wood E. J., Young A. R. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV, a kidney brush-border serine peptidase. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):169–182. doi: 10.1042/bj1570169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A., Kenny A. J. The molecular weight and properties of a neutral metallo-endopeptidase from rabbit kidney brush border. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;137(3):489–495. doi: 10.1042/bj1370489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A., Kenny A. J. The purification and specificity of a neutral endopeptidase from rabbit kidney brush border. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;137(3):477–488. doi: 10.1042/bj1370477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Actin, alpha-actinin, and tropomyosin interaction in the structural organization of actin filaments in nonmuscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1976 Feb;68(2):202–219. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.2.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Burridge K. Alpha-actinin: immunofluorescent localization of a muscle structural protein in nonmuscle cells. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):289–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90180-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Slayter H. S., Weeds A. G., Baker H. Substructure of the myosin molecule. I. Subfragments of myosin by enzymic degradation. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 28;42(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATHIES J. C. Preparation and properties of highly purified alkaline phosphatase from swine kidneys. J Biol Chem. 1958 Nov;233(5):1121–1127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maestracci D., Preiser H., Hedges T., Schmitz J., Crane R. K. Enzymes of the human intestinal brush border membrane. Identification after gel electrophoretic separation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 13;382(2):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Steers E., Jr Selective solubilization of a protein component of the red cell membrane. Science. 1968 Jan 12;159(3811):203–204. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3811.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaki T., Endo M., Ebashi S. Localization of 6S component of a alpha-actinin at Z-band. J Biochem. 1967 Nov;62(5):630–632. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell C. D., Hanahan D. J. Solubilization of certain proteins from the human erythrocyte stroma. Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):51–57. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B., Huxley H. E., DeRosier D. J. Three-dimensional reconstruction of F-actin, thin filaments and decorated thin filaments. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 14;50(2):279–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S., Tilney L. G. Organization of an actin filament-membrane complex. Filament polarity and membrane attachment in the microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):725–743. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien E. J., Gillis J. M., Couch J. Symmetry and molecular arrangement in paracrystals of reconstituted muscle thin filaments. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 15;99(3):461–475. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLOWSKI M., MEISTER A. ISOLATION OF GAMMA-GLUTAMYL TRANSPEPTIDASE FROM HOG KIDNEY. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:338–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palevitz B. A., Ash J. F., Hepler P. K. Actin in the green alga, Nitella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):363–366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podlubnaya Z. A., Tskhovrebova L. A., Zaalishtsbvili M. M., Stefanenko G. A. Electron microscopic study of alpha-actinin. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 25;92(2):357–359. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90234-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirk S. J., Robinson G. B. Isolation and characterization of rabbit kidney brush borders. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1319–1328. doi: 10.1042/bj1281319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostgaard J. Electron microscopy of filaments in the basal part of rat kidney tubule cells, and their in situ interaction with heavy meromyosin. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;132(4):497–521. doi: 10.1007/BF00306638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostgaard J., Thuneberg L. Electron microscopical observations on the brush border of proximal tubule cells of mammalian kidney. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;132(4):473–496. doi: 10.1007/BF00306637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZEWCZUK A., BARANOWSKI T. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF GAMMA-GLUTAMYL TRANSPEPTIDASE FROM BEEF KIDNEY. Biochem Z. 1963;338:317–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Huxley H. E., Finch J. T. Regulation of skeletal muscle contraction. II. Structural studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):619–632. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. A review. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stromer M. H., Goll D. E. Studies on purified -actinin. II. Electron microscopic studies on the competitive binding of -actinin and tropomyosin to Z-line extracted myofibrils. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):489–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90465-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L. Demonstration of glucose inhibitable phlorizin binding to renal brushborder proteins separated by gel electrophoresis. FEBS Lett. 1972 Sep 15;25(2):245–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80495-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L. Isolation of N-ethylmaleimide-labelled phlorizin sensitive D-glucose binding protein of brush border membrane from rat kidney cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 26;291(2):454–464. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90497-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Mooseker M. Actin in the brush-border of epithelial cells of the chicken intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2611–2615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonomura Y., Appel P., Morales M. On the molecular weight of myosin. II. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):515–521. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wacker H., Lehky P., Fischer E. H., Stein E. A. Physical and chemical characterization of pig kidney particulate aminopeptidase. Helv Chim Acta. 1971;54(2):473–485. doi: 10.1002/hlca.19710540206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]