Abstract
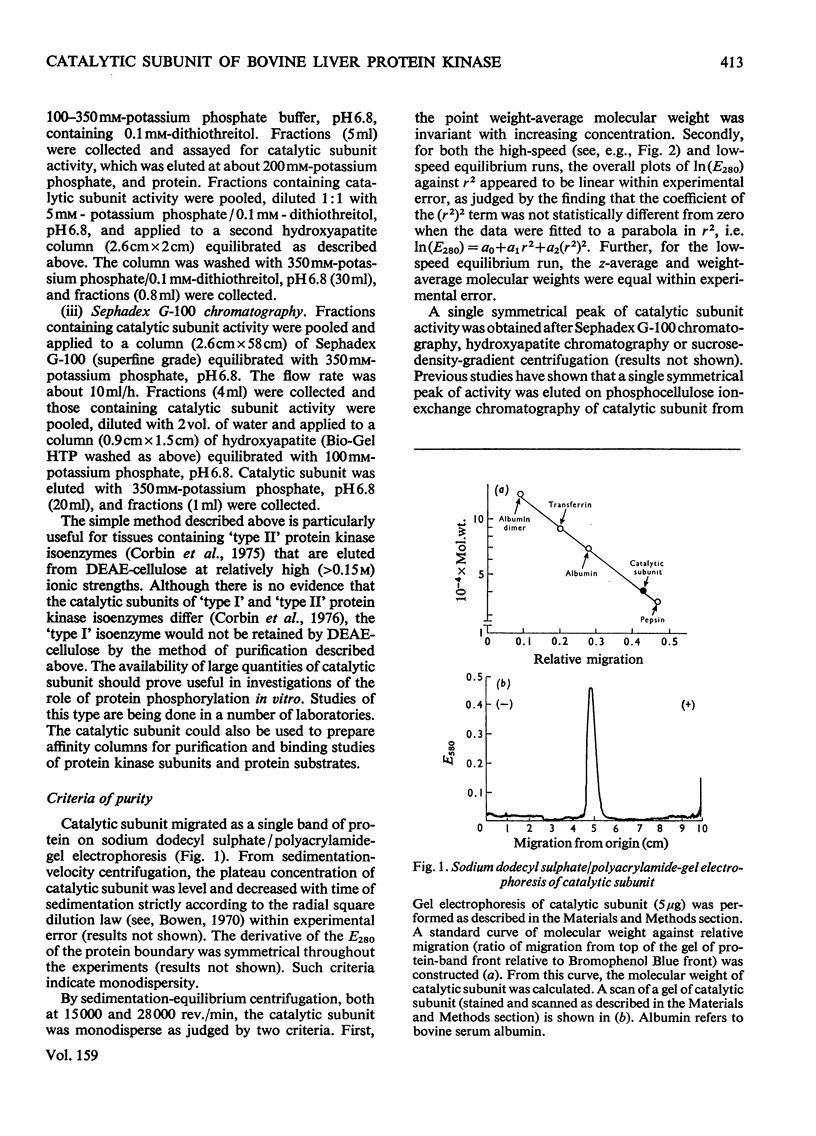
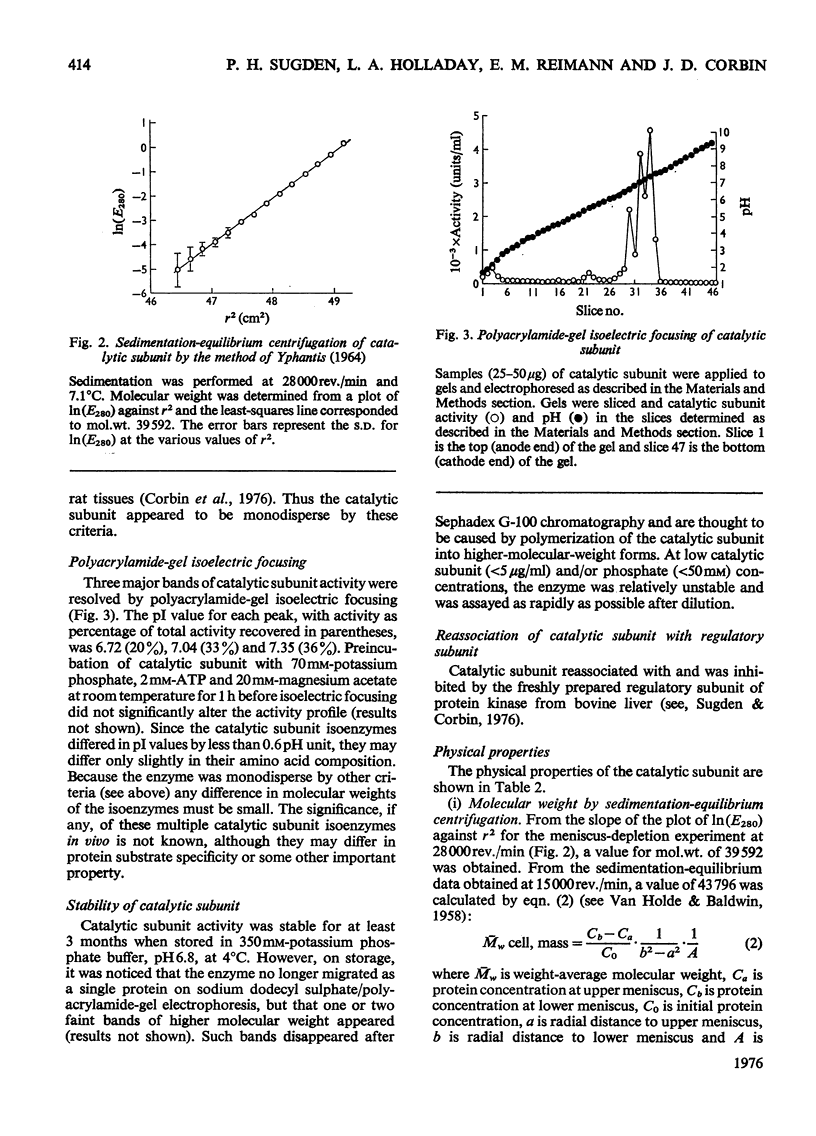
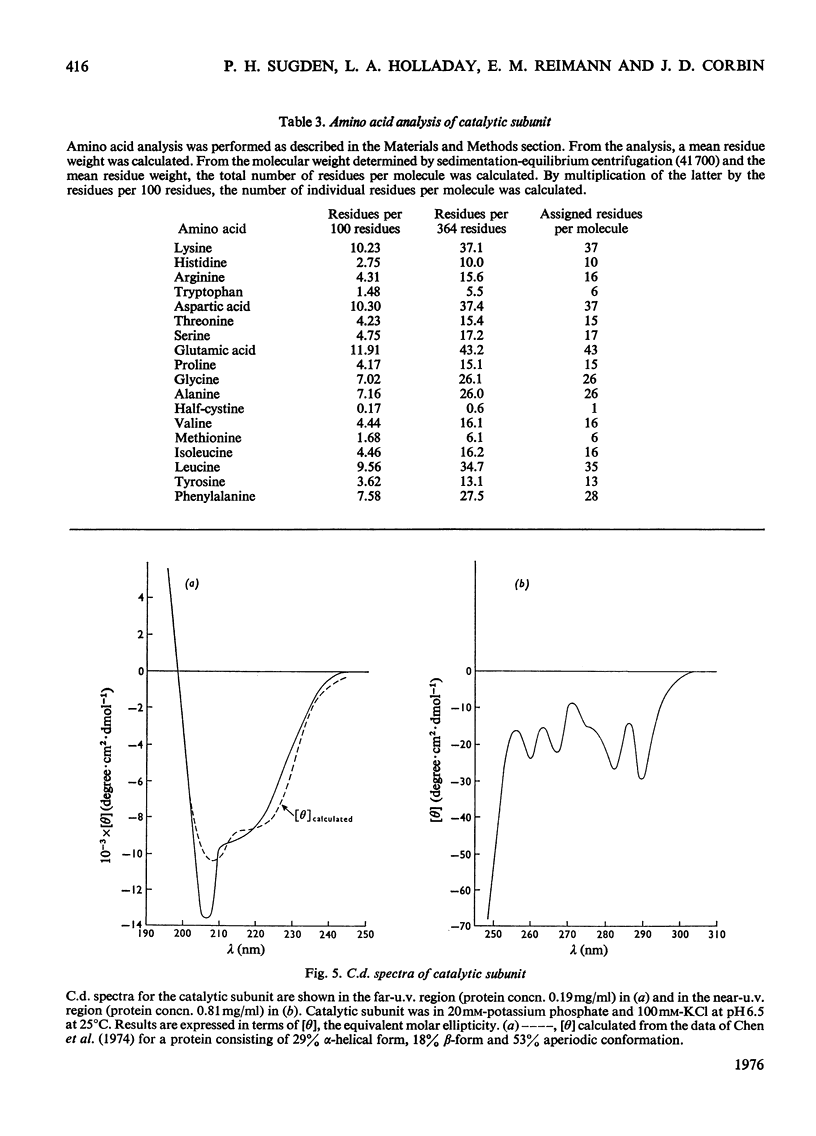
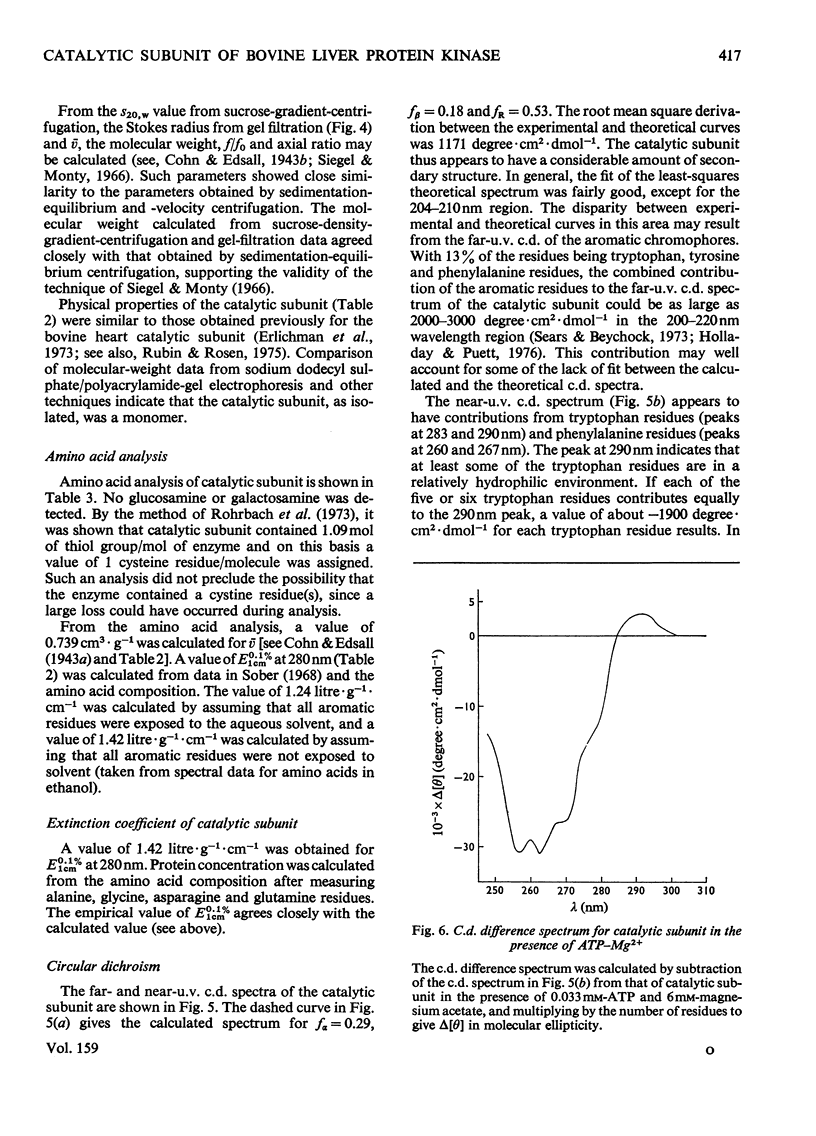
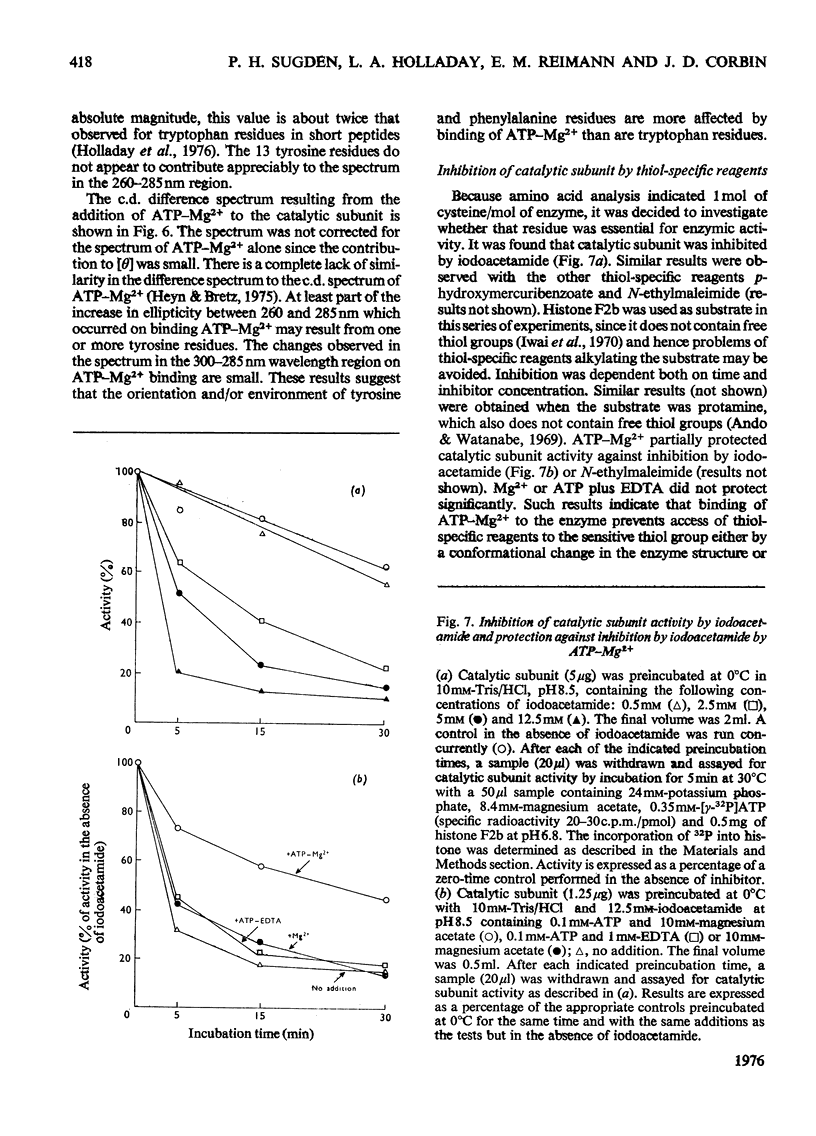
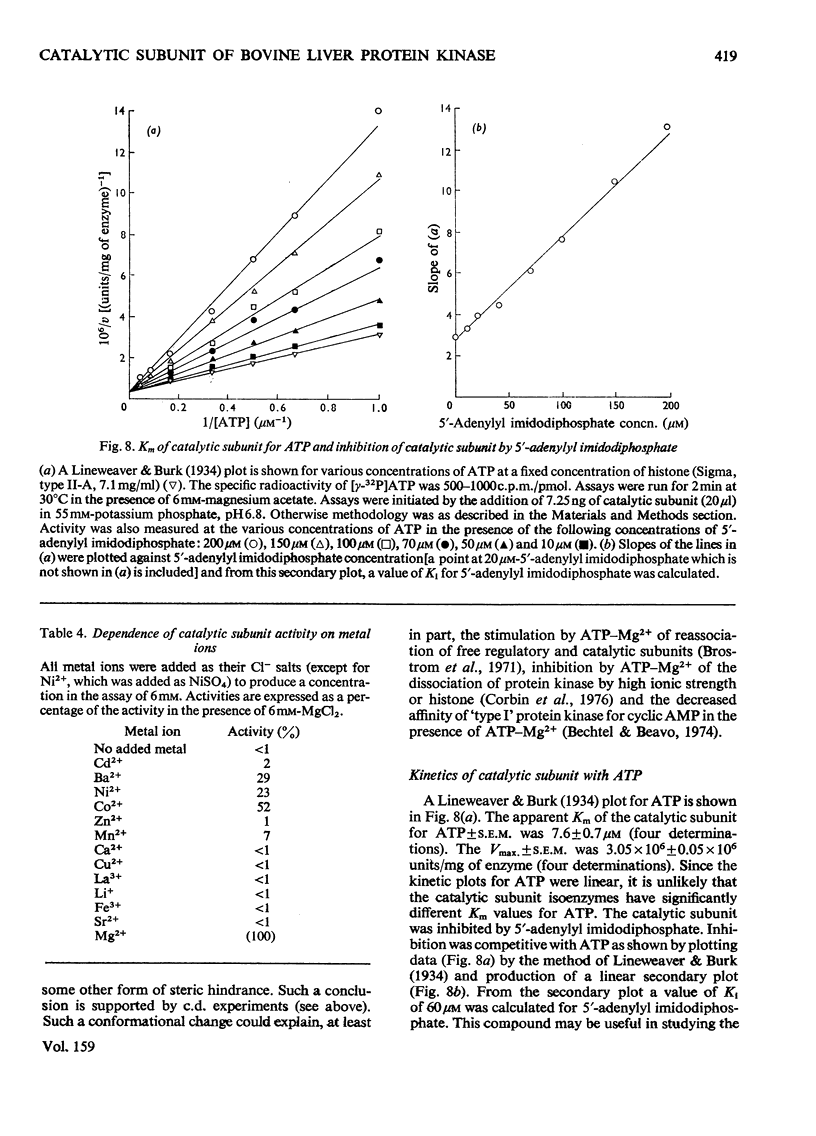
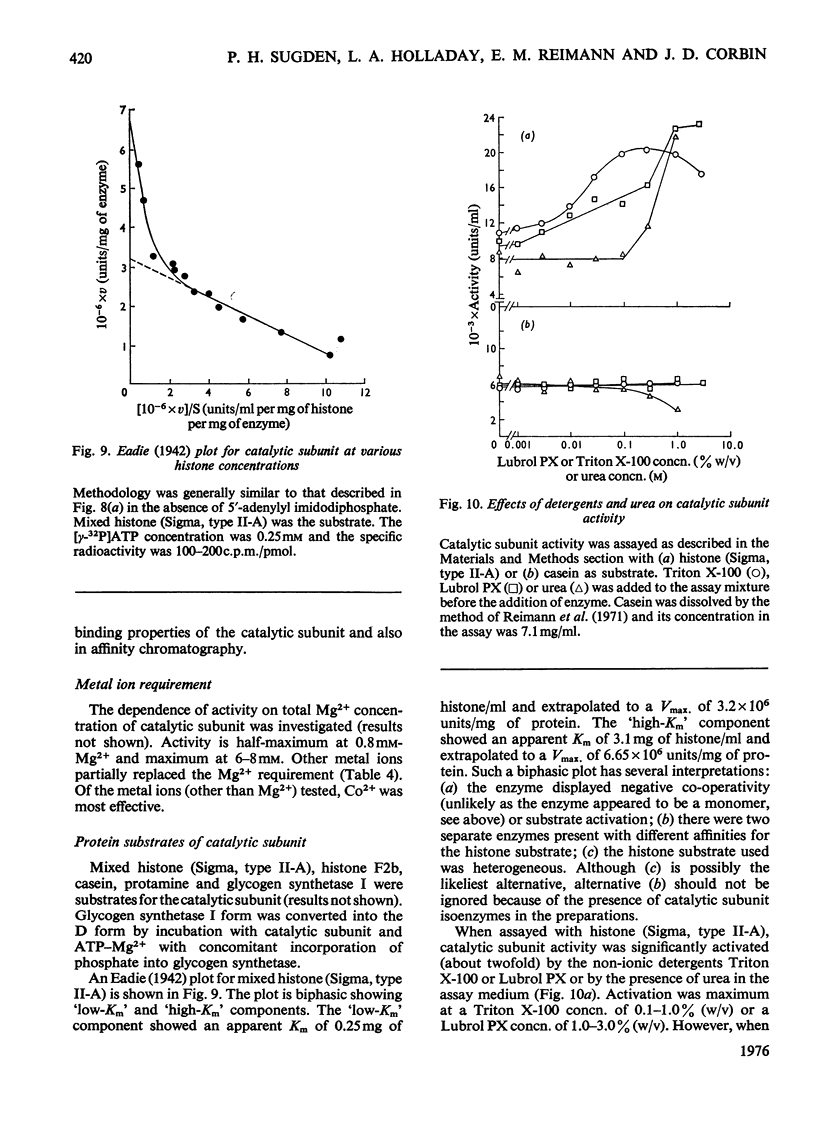
1. The catalytic subunit of bovine liver cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase (EC2.7.1.37) was purified essentially by the method of Reimann & Corbin [(1976) Fed. Proc. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 35, 1384]. 2. Sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis, sedimentation-velocity centrifugation and sedimentation-equilibrium centrifugation showed that the catalytic subunit was monodisperse. Polyacrylamide-gel isoelectric-focusing electrophoresis revealed the presence of at least three isoenzyme forms of catalytic subunit activity with slightly different pI values (6.72, 7.04 and 7.35). 3. Physical properties of the catalytic subunit were determined by several different methods. It had mol.wt. 39000-42000, Stokes radium 2.73-3.08 nm, so20.w 3.14S, f/fo 1.19-1.23 and, assuming a prolate ellipsoid, axial ration 4-5. 4. Amino acid analysis was performed on the catalytic subunit. It had one cysteine residue/molecule which was essential for activity. Inhibition by thiol-specific reagents was partially prevented by the presence of ATP-Mg2+. 5. The circular-dichroic spectrum showed the catalytic subunit contained 29% alpha-helical form, 18% beta-form and 53% aperiodic form. Near-u.v. circular dichroism showed the presence of aromatic residues whose equivalent molar ellipticity was greatly altered by the addition of ATP-Mg2+. 6. Kinetic experiments showed that the catalytic subunit had an apparent Km for ATP of 7 muM. 5'-Adenylyl imidodiphosphate inhibitied competitively with ATP with a Ki of 60 muM. The kinetic plot for histone (Sigma, type II-A) was biphasic showing 'high'-and 'low'-Km segments. Under assay conditions the specific activity of the catalytic subunit was 3 X 10(6) units/mg of protein. Of various metal ions tested, the catalytic subunit was most active with Mg2+.7. When assayed with histone (Sigma, type II-A) as substrate, the activity of the catalytic subunit was increased by non-ionic detergents or urea. No such activation was observed with casein as substrate.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando T., Watanabe S. A new method for fractionation of protamines and the amino acid sequences of salmine and three components of iridine. Int J Protein Res. 1969;1(3):221–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1969.tb01646.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom C. O., Corbin J. D., King C. A., Krebs E. G. Interaction of the subunits of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase of muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2444–2447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREETH J. M. The use of the Gouy diffusiometer with dilute protein solutions; an assessment of the accuracy of the method. Biochem J. 1952 Apr;51(1):10–17. doi: 10.1042/bj0510010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellino F. J., Barker R. Examination of the dissociation of multichain proteins in guanidine hydrochloride by membrane osmometry. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2207–2217. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catsimpoolas N. Micro isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gel columns. Anal Biochem. 1968 Dec;26(3):480–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Yang J. T., Chau K. H. Determination of the helix and beta form of proteins in aqueous solution by circular dichroism. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3350–3359. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Brostrom C. O., Alexander R. L., Krebs E. G. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3736–3743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Keely S. L., Park C. R. The distribution and dissociation of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases in adipose, cardiac, and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):218–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Reimann E. M. Assay of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:287–290. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlichman J., Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Physical properties of a purified cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from bovine heart muscle. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 10;248(21):7607–7609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES W. L., Jr Protein mercaptides. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1950;14:79–84. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1950.014.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyn M. P., Bretz R. The self-association of ATP: thermodynamics and geometry. Biophys Chem. 1975 Feb;3(1):35–45. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(75)80035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holladay L. A., Puett D. Circular dichroism of corticotropin, fragment 1-24, and model compounds. An assessment of the contributions of the peptide chromophore and armoatic residues. Biopolymers. 1976 Jan;15(1):43–59. doi: 10.1002/bip.1976.360150106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holladay L. A., Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S., Puett D. Conformation and unfolding thermodynamics of epidermal growth factor and derivatives. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 15;15(12):2624–2633. doi: 10.1021/bi00657a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwai K., Ishikawa K., Hayashi H. Amino-acid sequence of slightly lysine-rich histone. Nature. 1970 Jun 13;226(5250):1056–1058. doi: 10.1038/2261056b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. W. Studies on histones. 7. Preparative methods for histone fractions from calf thymus. Biochem J. 1964 Jul;92(1):55–59. doi: 10.1042/bj0920055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLER P. J., CORI G. T. Enzymic conversion of phosphorylase a to phosphorylase b. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Sep-Oct;12(1-2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90142-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keely S. L., Corbin J. D., Park C. R. Regulation of adenosine 3:5-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):4832–4840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenman S. G., Bhalla R. C., Sanborn B. M., Stevens R. H. Protein kinase translocation as an early event in the hormonal control of uterine contraction. Science. 1974 Feb 1;183(4123):430–432. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4123.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G. Protein kinases. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1972;5:99–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIASH E., LUSTGARTEN J. Interconversion of horse heart cytochrome C monomer and polymers. J Biol Chem. 1962 Nov;237:3397–3405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACKIS J. J., SASAME H. A., MANN R. K., ANDERSON R. L., SMITH A. K. Soybean trypsin inhibitors: isolation, purification and physical properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Sep;98:471–478. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90213-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann E. M., Walsh D. A., Krebs E. G. Purification and properties of rabbit skeletal muscle adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1986–1995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrbach M. S., Humphries B. A., Yost F. J., Jr, Rhodes W. G., Boatman S., Hiskey R. G., Harrison J. H. The reaction of 4,4'-bis-dimethylaminodiphenylcarbinol with the sulfhydryl group. A new reagent for sulfhydryl analysis. Anal Biochem. 1973 Mar;52(1):127–142. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90338-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Protein phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:831–887. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachman H. K., Edelstein S. J. Ultracentrifuge studies with absorption optics. IV. Molecular weight determinations at the microgram level. Biochemistry. 1966 Aug;5(8):2681–2705. doi: 10.1021/bi00872a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soderling T. R., Corbin J. D., Park C. R. Regulation of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. II. Hormonal regulation of the adipose tissue enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 10;248(5):1822–1829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden P. H., Corbin J. D. Adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-binding proteins in bovine and rat tissues. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):423–437. doi: 10.1042/bj1590423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Perkins J. P., Brosom C. O., Ho E. S., Kreb E. G. Catlysis of the phosphrylaseinase actition reaction. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1968–1976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wastila W. B., Stull J. T., Mayer S. E., Walsh D. A. Measurement of cyclic 3',5'-denosine monophosphate by the activation of skeletal muscle protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1996–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount R. G., Babcock D., Ballantyne W., Ojala D. Adenylyl imidodiphosphate, an adenosine triphosphate analog containing a P--N--P linkage. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2484–2489. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


