Abstract
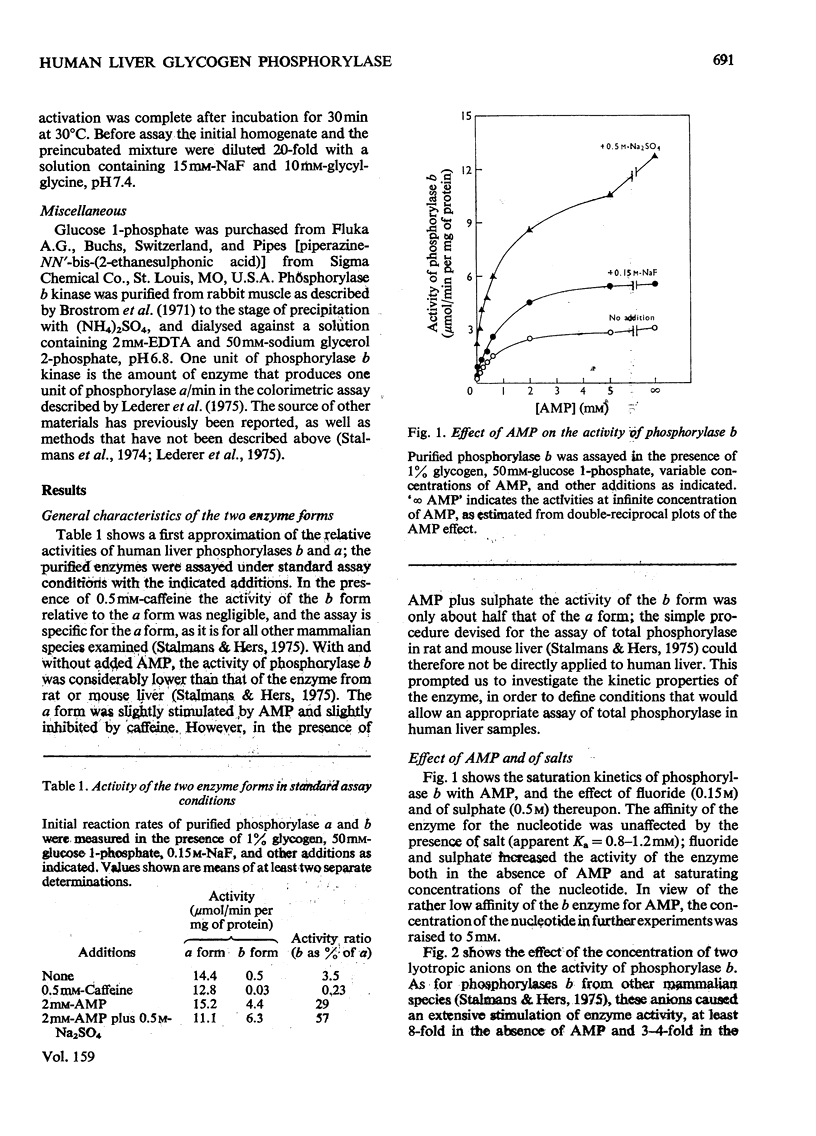
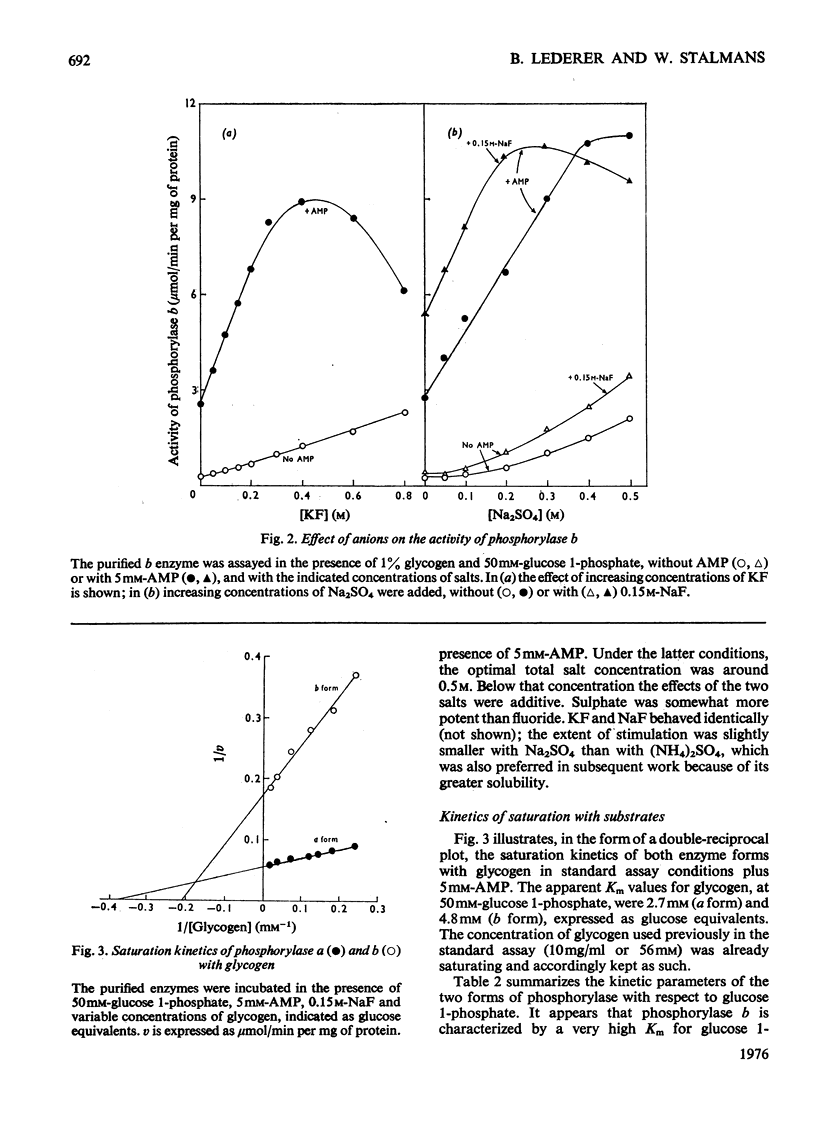
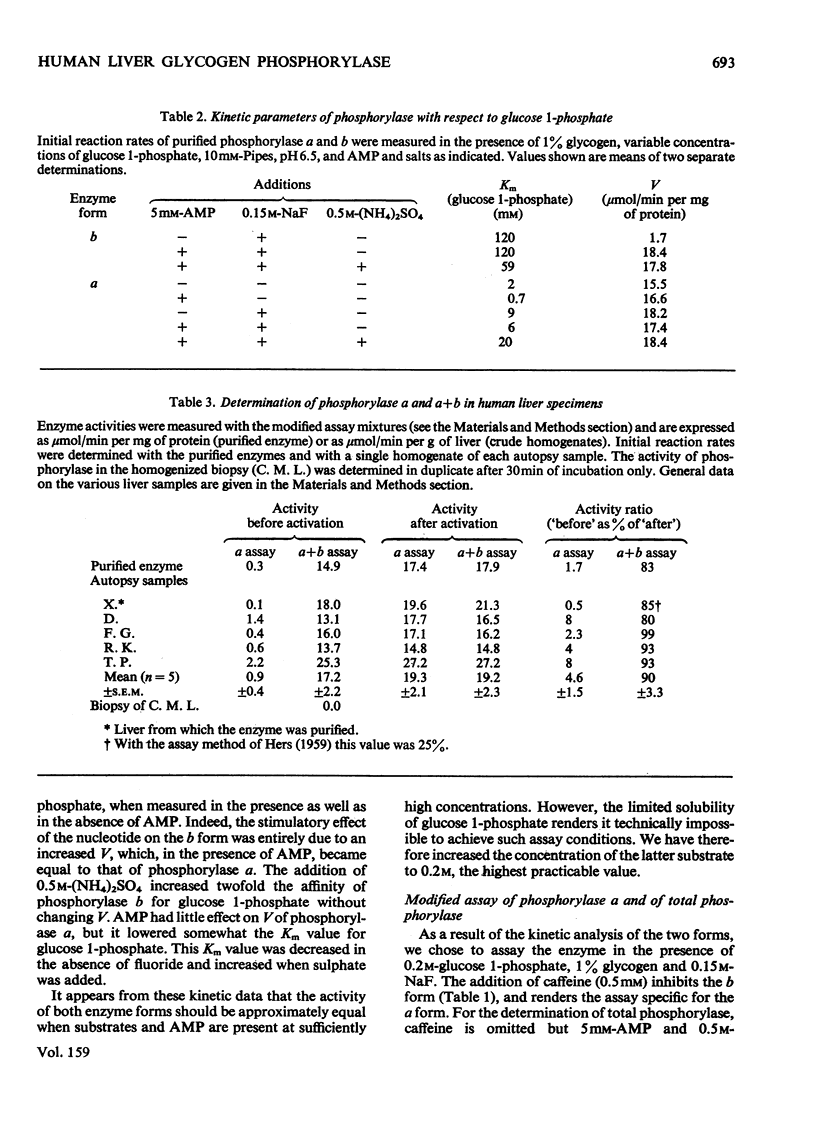
1.The two forms of glycogen phosphorylase were purified from human liver, and some kinetic properties were examined in the direction of glycogen synthesis. The b form has a limited catalytic capacity, resembling that of the rabbit liver enzyme. It is characterized by a low affinity for glucose 1-phosphate, which is unaffected by AMP, and a low V, which becomes equal to that of the a form in the presence of the nucleotide. Lyotropic anions stimulate phosphorylase b and inhibit phosphorylase a by modifying the affinity for glucose 1-phosphate. Both enzyme forms are easily saturated with glycogen. 2. These kinetic properties have allowed us to design a simple assay method for total (a + b) phosphorylase in human liver. It requires only 0.5 mg of tissue, and its average efficiency is 90% when the enzyme is predominantly in the b form. 3. The assay of total phosphorylase allows the unequivocal diagnosis of hepatic glycogen-storage disease caused by phosphorylase deficiency. One patient with a complete deficiency is reported. 4. The assay of human liver phosphorylase a is based on the preferential inhibition of the b form by caffeine. The a form displays the same activity when measured by either of the two assays.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleman M. M., Krebs E. G., Fischer E. H. Purification and properties of inactive liver phosphorylase. Biochemistry. 1966 Jun;5(6):2101–2107. doi: 10.1021/bi00870a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom C. O., Hunkeler F. L., Krebs E. G. The regulation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase by Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1961–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond G. I., Hardwick D. F., Israels S. Liver glycogen phosphorylase deficiency. Can Med Assoc J. 1970 Apr 11;102(7):740–742. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes J., Koster J. F., Grose W. F., Sorgedrager N. Hepatic phosphorylase deficiency. Its differentiation from other hepatic glycogenoses. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Mar;49(3):186–191. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.3.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilboe D. P., Larson K. L., Nuttall F. Q. Radioactive method for the assay of glycogen phosphorylases. Anal Biochem. 1972 May;47(1):20–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guibaud P., Mathieu M. Hétèrogénéite de la glycogénose type VI. Etude de l'activité de la phosphorylase leucocytaire dans deux familles. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1972 Dec;29(10):1043–1057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERS H. G. Etudes enzymatiques sur fragments hépatiques; application à la classification des glycogénoses. Rev Int Hepatol. 1959;9(1):35–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES R. C., YUNIS A. A., KREBS E. G., FISCHER E. H. Comparative studies on glycogen phosphorylase. III. The phosphorylated site in human muscle phosphorylase alpha. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jan;237:40–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hug G., Chuck G., Walling L., Schubert W. K. Liver phosphorylase deficiency in glycogenosis type VI: documentation by biochemical analysis of hepatic biopsy specimens. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Jul;84(1):26–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer B., Van Hoof F., Van den Berghe G., Hers H. Glycogen phosphorylase and its converter enzymes in haemolysates of normal human subjects and of patients with type VI glycogen-storage disease. A study of phosphorylase kinase deficiency. Biochem J. 1975 Apr;147(1):23–35. doi: 10.1042/bj1470023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddaiah V. T., Madsen N. B. Kinetics of purified liver phosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Sep 10;241(17):3873–3881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer-Peet J., Norman M. E., Lake B. D., McNamara J., Patrick A. D. Hepatic glycogen storage disease. Clinical and laboratory findings in 23 cases. Q J Med. 1971 Jan;40(157):95–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalmans W., Hers H. G. The stimulation of liver phosphorylase b by AMP, fluoride and sulfate. A technical note on the specific determination of the a and b forms of liver glycogen phosphorylase. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):341–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalmans W., Laloux M., Hers H. G. The interaction of liver phosphorylase a with glucose and AMP. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Nov 15;49(2):415–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalmans W. The role of the liver in the homeostasis of blood glucose. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1976;11:51–97. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152811-9.50009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan A. W., Nuttall F. Q. Characteristics of the dephosphorylated form of phosphorylase purified from rat liver and measurement of its activity in crude liver preparations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 20;410(1):45–60. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YUNIS A. A., FISCHER E. H., KREBS E. G. Crystallization and properties of human muscle phosphorylases a and b. J Biol Chem. 1960 Nov;235:3163–3168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YUNIS A. A., KREBS E. G. Comparative studies on glycogen phosphorylase. II. Immunological studies on rabbit and human skeletal muscle phosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jan;237:34–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


