Abstract
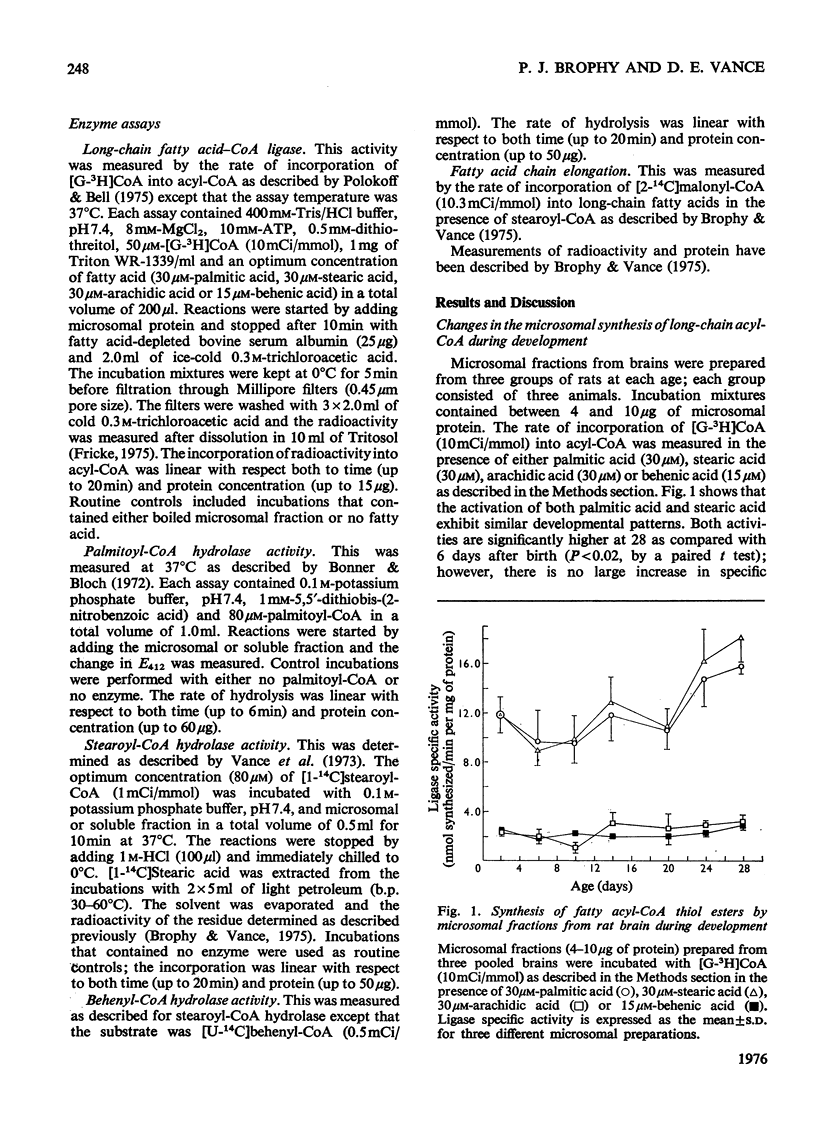
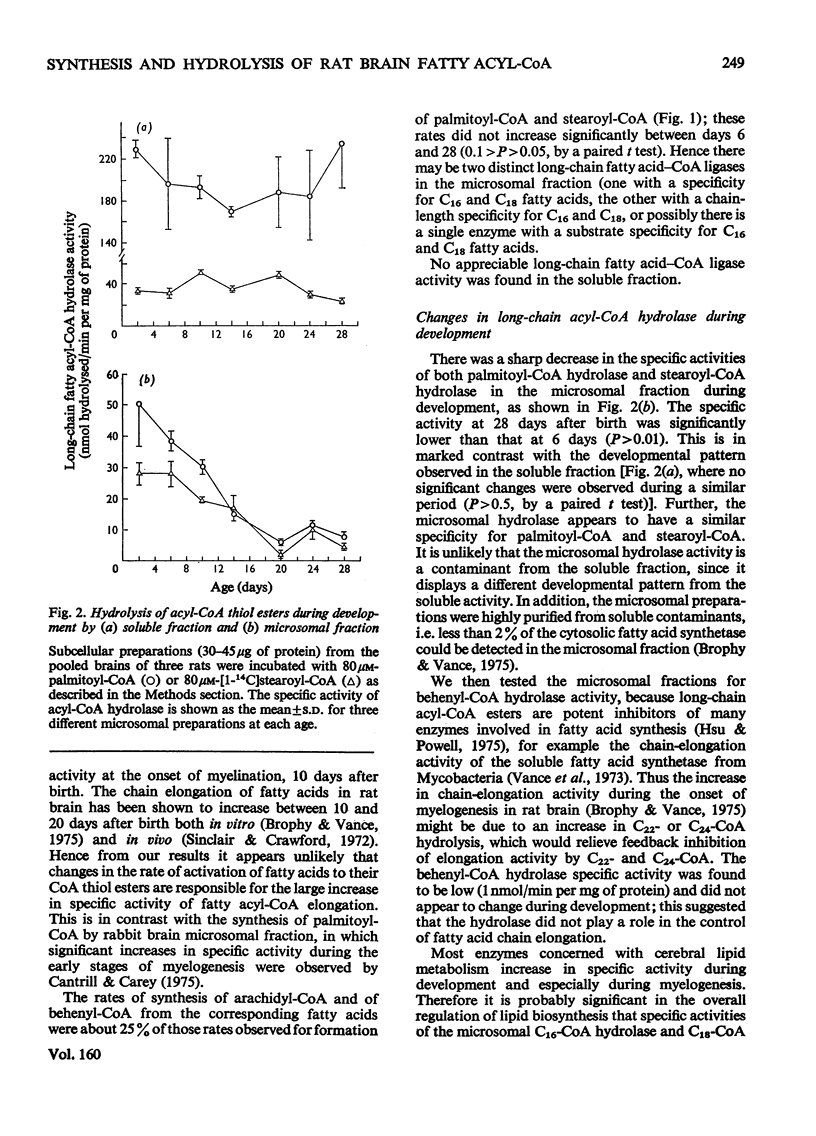
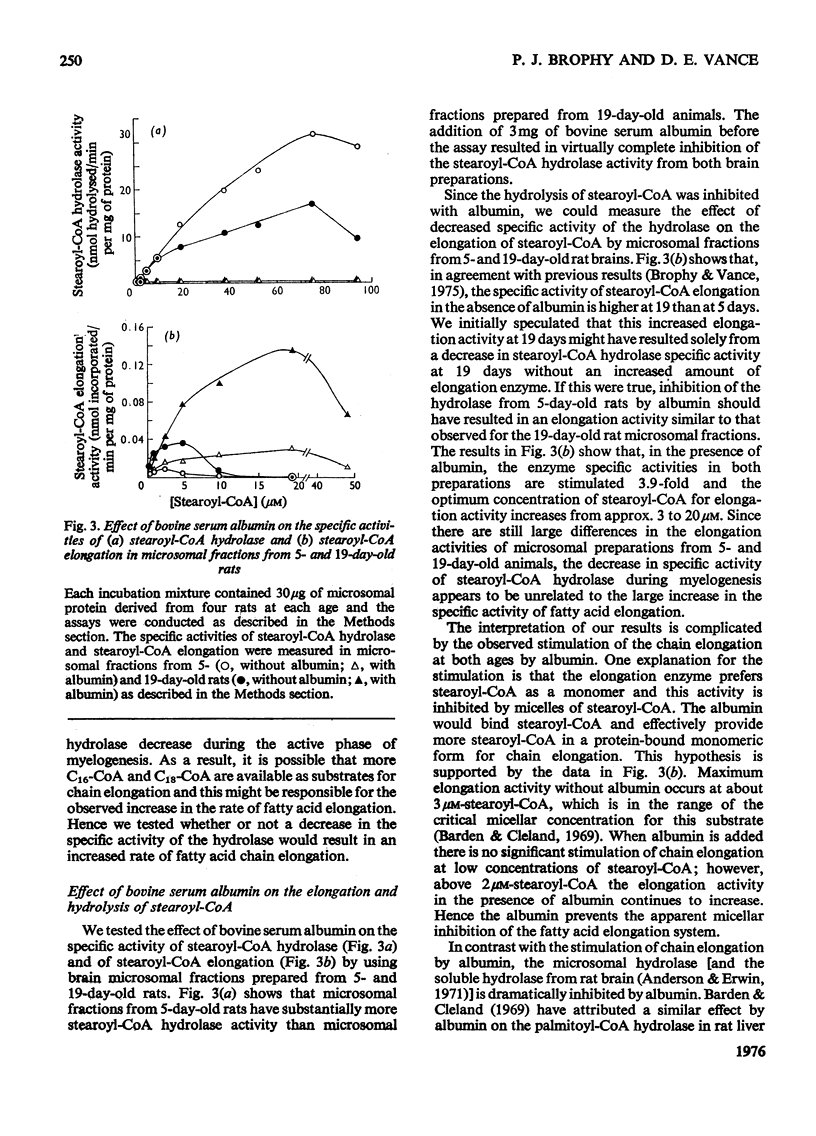
1. The specific activities of long-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase (EC6.2.1.3) and of long-chain fatty acyl-CoA hydrolase (EC3.1.2.2) were measured in soluble and microsomal fractions from rat brain. 2. In the presence of either palmitic acid or stearic acid, the specific activity of the ligase increased during development; the specific activity of this enzyme with arachidic acid or behenic acid was considerably lower. 3. The specific activities of palmitoyl-CoA hydrolase and of stearoyl-CoA hydrolase in the microsomal fraction decreased markedly (75%) between 6 and 20 days after birth; by contrast, the corresponding specific activities in the soluble fraction showed no decline. 4. Stearoyl-CoA hydrolase in the microsomal fraction is inhibited (99%) by bovine serum albumin; this is in contrast with the microsomal fatty acid-chain-elongation system, which is stimulated 3.9-fold by albumin. Inhibition of stearoyl-CoA hydrolase does not stimulate stearoyl-CoA chain elongation. Therefore it does not appear likely that the decline in the specific activity of hydrolase during myelogenesis is responsible for the increased rate of fatty acid chain elongation. 5. It is suggested that the decline in specific activity of the microsomal hydrolase and to a lesser extent the increase in the specific activity of the ligase is directly related to the increased demand for long-chain acyl-CoA esters during myelogenesis as substrates in the biosynthesis of myelin lipids.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Arif A., Blecher M. Synthesis of fatty acyl CoA and other thiol esters using N-hydroxysuccinimide esters of fatty acids. J Lipid Res. 1969 May;10(3):344–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson A. D., Erwin V. G. Brain acyl-coenzyme A hydrolase: distribution, purification and properties. J Neurochem. 1971 Jul;18(7):1179–1186. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barden R. E., Cleland W. W. 1-Acylglycerol 3-phosphate acyltransferase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3677–3684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Bloch K. Purification and properties of fatty acyl thioesterase I from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3123–3133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brophy P. J., Vance D. E. Elongation of fatty acids by microsomal fractions from the brain of the developing rat. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;152(3):495–501. doi: 10.1042/bj1520495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrill R. C., Carey E. M. Changes in the activities of de novo fatty acid synthesis and palmitoyl-CoA synthetase in relation to myelination in rabbit brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 20;380(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricke U. Tritosol: a new scintillation cocktail based on Triton X-100. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):555–558. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90379-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu K. H., Powell G. L. Inhibition of citrate synthase by oleoyl-CoA: a regulatory phenomenon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4729–4733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'BRIEN J. S. STABILITY OF THE MYELIN MEMBRANE. Science. 1965 Mar 5;147(3662):1099–1107. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3662.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polokoff M. A., Bell R. M. Millipore filter assay for long-chain fatty acid:CoASH ligase activity using 3H-labeled coenzyme A. J Lipid Res. 1975 Sep;16(5):397–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair A. J., Crawford M. A. The accumulation of arachidonate and docosahexaenoate in the developing rat brain. J Neurochem. 1972 Jul;19(7):1753–1758. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb06219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance D. E., Esders T. W., Bloch K. On the role of a palmityl thioesterase in fatty acid elongation. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2310–2316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


