Abstract
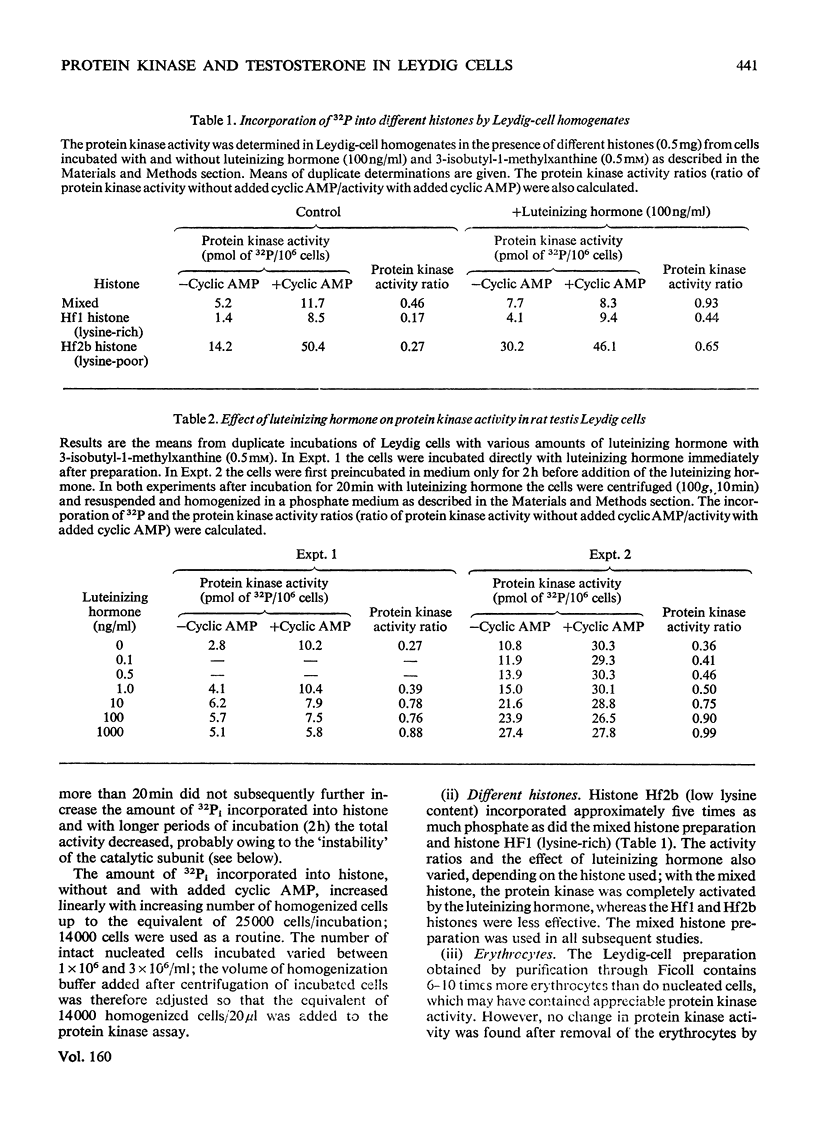
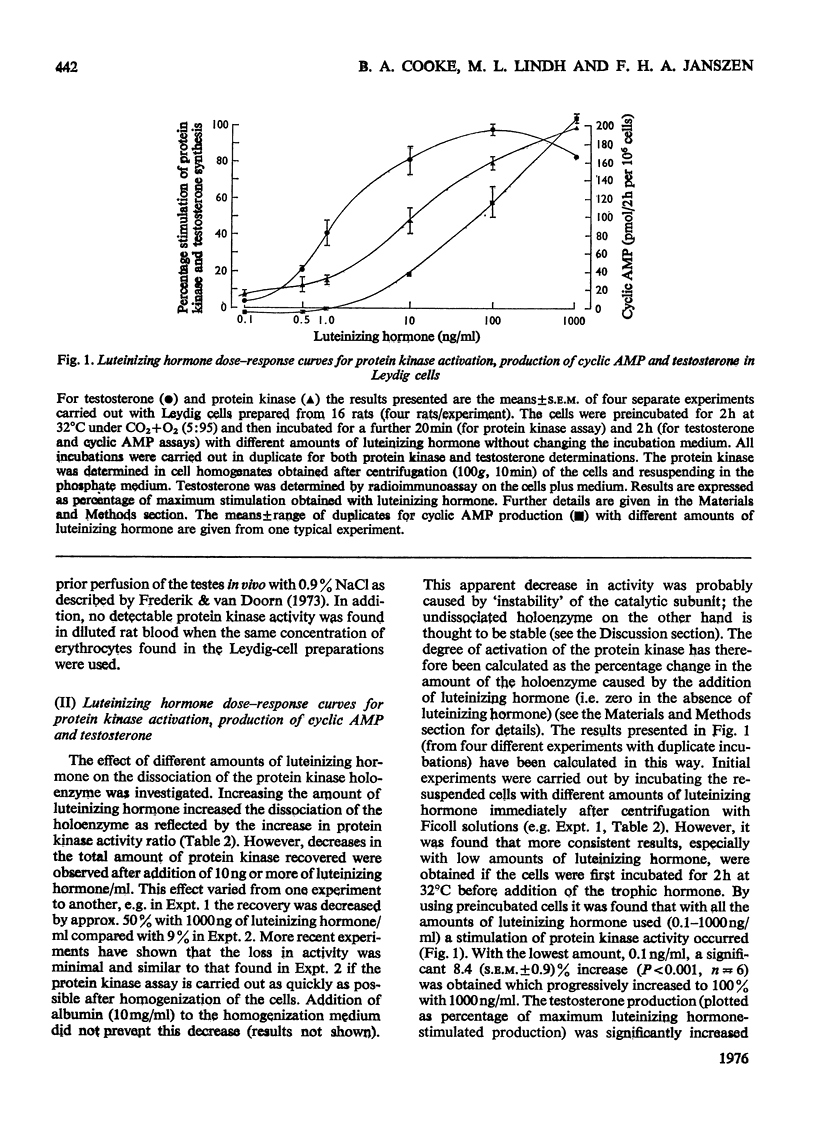
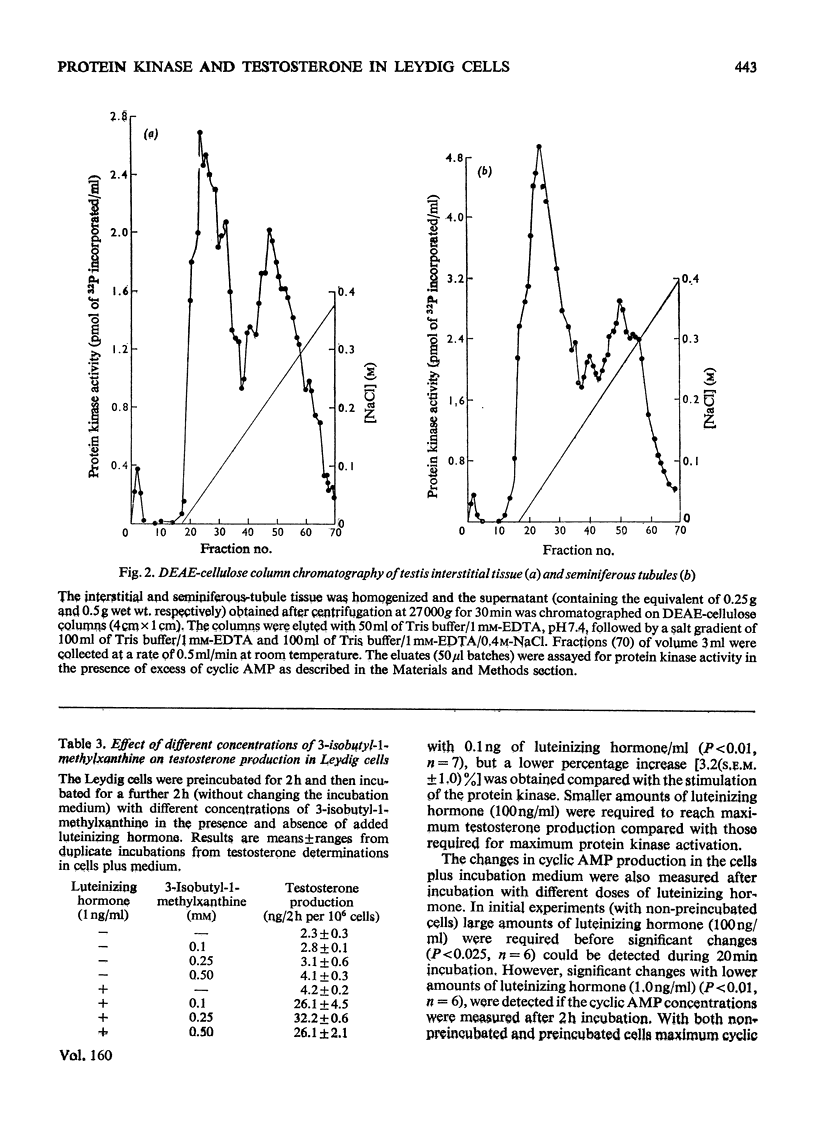
The effect of different doses of luteinizing hormone on activation of protein kinases, cyclic AMP and testosterone production was studied in purified rat testis Leydig-cell preparations in the presence of 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (a phosphodiesterase inhibitor). In addition, the nature of the protein kinases present in these cells and other tissues was investigated. The following results were obtained. 1. With all the amounts of luteinizing hormone used (0.1-1000 ng/ml), both activation of protein kinase and stimulation of testosterone production were demonstrated. With the lowest amount of luteinizing hormone (0.1 ng/ml), an 8.4+/-0.9% (S.E.M.,n=6) stimulation of protein kinase activation occurred, increasing to 100% with 1000 ng/ml, compared with 3.2+/-1.0%(S.E.M.,n=7) and 100% stimulation of testosterone production with 0.1 and 100 ng/ml respectively. 2. With amounts of luteinizing hormone up to 1 ng/ml (which gave half-maximal stimulation of testosterone production) no detectable increases in net cyclic AMP production were obtained. With higher amounts of luteinizing hormone, cyclic AMP production increased, but maximal production was not reached with 1000 ng/ml. 3. Two isoenzymic forms of protein kinase were present in Leydig cells and seminiferous tubules; type I was eluted with 0.075 M-and type II with 0.22-0.25 m-NaCl from DEAE-cellulose columns. 4. The protein kinase activity was not affected by the presence of erythrocytes in the Leydig-cell preparation, but varied depending on the type of histone used as substrate (histone F2b greater than mixed greater than histone F1).
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Catt K. J., Dufau M. L. Spare gonadotrophin receptors in rat testis. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 15;244(137):219–221. doi: 10.1038/newbio244219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. J., Walsh D. A. Multiple forms of hepatic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1971 Sep 14;10(19):3614–3621. doi: 10.1021/bi00795a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke B. A., van der Kemp A. J. Protein kinase activity in rat testis interstitial tissue. Effect of luteinizing hormone and other factors. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 15;154(2):371–378. doi: 10.1042/bj1540371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Keely S. L., Park C. R. The distribution and dissociation of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases in adipose, cardiac, and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):218–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Soderling T. R., Park C. R. Regulation of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. I. Preliminary characterization of the adipose tissue enzyme in crude extracts. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 10;248(5):1813–1821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederik P. M., van Doorn L. G. A technique for perfusion of rat testes in situ through the internal spermatic arteries. J Reprod Fertil. 1973 Oct;35(1):117–121. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0350117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungmann R. A., Hiestand P. C., Schweppe J. S. Mechanism of action of gonadotropin. IV. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent translocation of ovarian cytoplasmic cyclic adenosine monophosphate-binding protein and protein kinase to nuclear acceptor sites. Endocrinology. 1974 Jan;94(1):168–183. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-1-168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keely S. L., Jr, Corbin J. D., Park C. R. On the question of translocation of heart cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1501–1504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenman S. G., Bhalla R. C., Sanborn B. M., Stevens R. H. Protein kinase translocation as an early event in the hormonal control of uterine contraction. Science. 1974 Feb 1;183(4123):430–432. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4123.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. R., Fakunding J. L., Tindall D. J. Follicle stimulating hormone regulation of protein kinase activity and protein synthesis in testis. Biol Reprod. 1976 Feb;14(1):54–63. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod14.1.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson C., Dufau M., Catt K. Gonadotropin binding and stimulation of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and testosterone production in isolated Leydig cells. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8818–8823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle W. R., Ramachandran J. Effect of LH on steroidogenesis and cyclic AMP accumulation in rat Leydig cell preparations and mouse tumor Leydig cells. Endocrinology. 1973 Jul;93(1):127–134. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer W. K., Castagna M., Walsh D. A. Nuclear protein kinase activity in glucagon-stimulated perfused rat livers. Biochem J. 1974 Nov;143(2):469–471. doi: 10.1042/bj1430469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson M. C., Schulster D. The role of protein kinase activation in the control of steroidogenesis by adrenocorticotrophic hormone in the adrenal cortex. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;136(4):993–998. doi: 10.1042/bj1360993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Protein phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:831–887. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas O., Walaas E., Gronnerod O. Hormonal regulation of cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase of rat diaphragm by epinephrine and insulin. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Dec 17;40(2):465–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


