Abstract
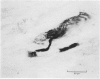
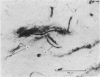
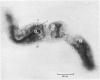
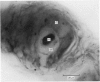
The posterior attachments of the dog knee joint lateral menisci have been studied to identify and characterize their mechanoreceptor innervation. Two basic types of mechanoreceptor were identified that appeared to be similar to the Type III and Type II endings described by Freeman & Wyke (1967) in cat knee periarticular tissues. Significantly, two distinct forms of Type II corpuscles were identified in this study, referred to as Types IIa and IIb, respectively. Endings were usually identified either at the point where the posterior meniscotibial ligament merged with the main body of the meniscus and the meniscofemoral ligament, or within the inner aspect of the meniscofemoral ligament where it joined the meniscal 'body'. The presence of encapsulated mechanoreceptors within the attachments of dog knee lateral menisci means that the central nervous system is being appraised of the mechanical state of these structures. A mechanism is suggested by which the tension of meniscal attachments could be varied according to knee joint position. A possible relationship between the morphology of the receptors identified in this study and the physiological responses of similar cat knee joint receptors is discussed.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxendale R. H., Ferrell W. R. Modulation of transmission in flexion reflex pathways by knee joint afferent discharge in the decerebrate cat. Brain Res. 1980 Dec 8;202(2):497–500. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxendale R. H., Ferrell W. R. The effect of elbow joint afferent discharge on transmission in forelimb flexion reflex pathways to biceps and triceps brachii in decerebrate cats. Brain Res. 1982 Sep 9;247(1):57–63. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxendale R. H., Ferrell W. R. The effect of knee joint afferent discharge on transmission in flexion reflex pathways in decerebrate cats. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:231–242. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess P. R., Clark F. J. Characteristics of knee joint receptors in the cat. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):317–335. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell W. R. The adequacy of stretch receptors in the cat knee joint for signalling joint angle throughout a full range of movement. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:85–99. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman M. A., Wyke B. The innervation of the knee joint. An anatomical and histological study in the cat. J Anat. 1967 Jun;101(Pt 3):505–532. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigg A., Hoffman A. H., Fogarty K. E. Properties of Golgi-Mazzoni afferents in cat knee joint capsule, as revealed by mechanical studies of isolated joint capsule. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Jan;47(1):31–40. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.47.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halata Z. The ultrastructure of the sensory nerve endings in the articular capsule of the knee joint of the domestic cat (Ruffini corpuscles and Pacinian corpuscles). J Anat. 1977 Dec;124(Pt 3):717–729. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor B. L., Gonzales J. Mechanoreceptors of the medial collateral ligament of the cat knee joint. J Anat. 1979 Dec;129(Pt 4):719–729. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor B. L., McConnaughey J. S. The structure and innervation of cat knee menisci, and their relation to a "sensory hypothesis" of meniscal function. Am J Anat. 1978 Nov;153(3):431–442. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001530306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor B. L. The histological structure of dog knee menisci with comments on its possible significance. Am J Anat. 1976 Dec;147(4):407–417. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001470402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi A., Grigg P. Characteristics of hip joint mechanoreceptors in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Jun;47(6):1029–1042. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.47.6.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOGLUND S. Anatomical and physiological studies of knee joint innervation in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1956;36(124):1–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoultz T. W., Swett J. E. The fine structure of the Golgi tendon organ. J Neurocytol. 1972 Jul;1(1):1–26. doi: 10.1007/BF01098642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoultz T. W., Swett J. E. Ultrastructural organization of the sensory fibers innervating the Golgi tendon organ. Anat Rec. 1974 Jun;179(2):147–162. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091790202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]