Abstract
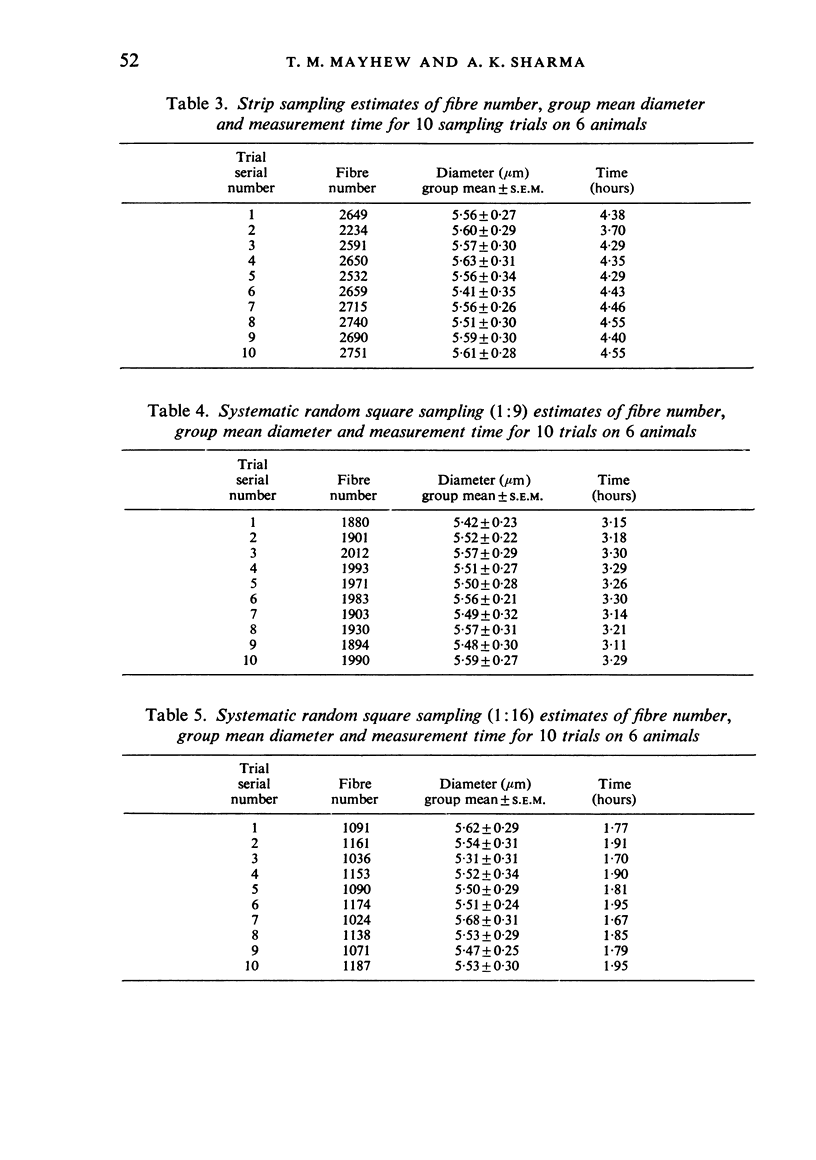
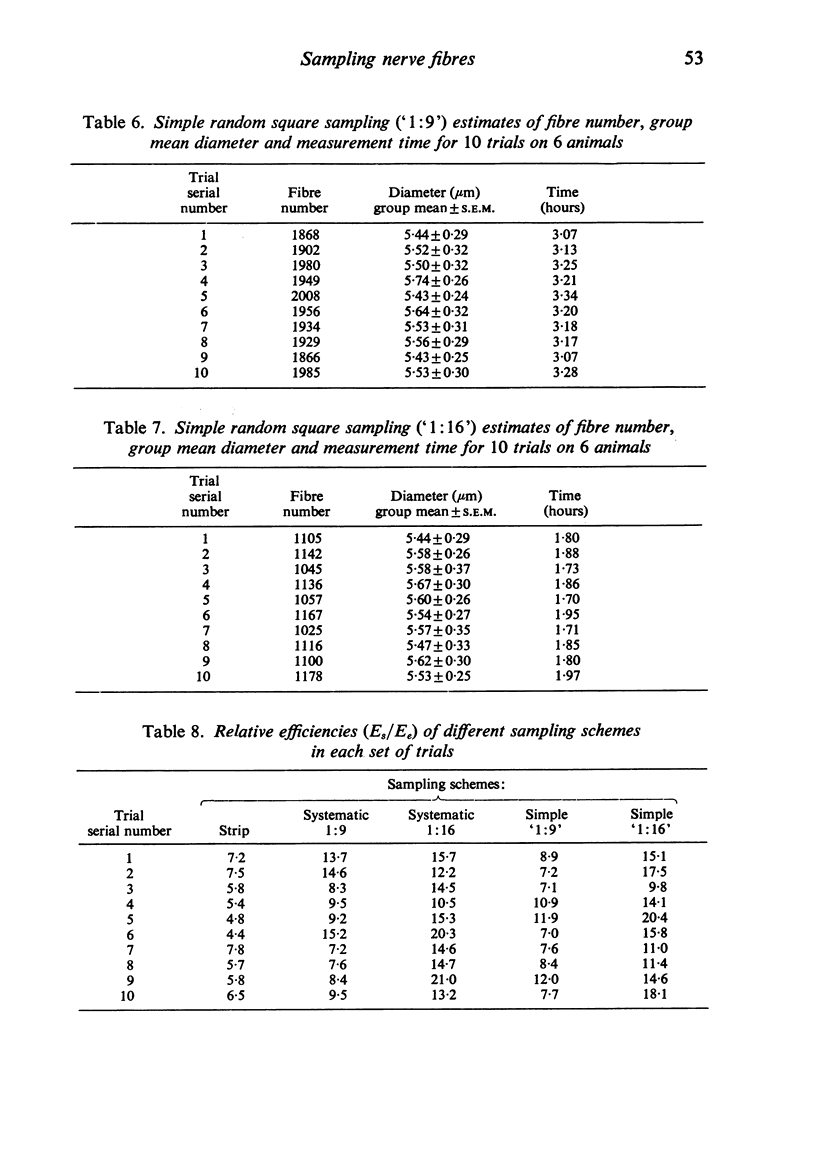
Using the tibial nerves of diabetic rats, alternative sampling schemes have been compared for estimating the sizes of fibres in nerve trunks of mixed fascicularity. The merits of each scheme were evaluated by comparing their reliability, precision, cost in time, and efficiency with 'absolute' values obtained by first measuring every fibre. The external diameter of all myelinated fibres was measured in each of six nerves (c. 2900 fibres/nerve). Total measurement time was about 29 hours. All sampling schemes produced group means within +/-4% of the absolute value of 5.52 micron. The most efficient schemes were those in which only 6% of all fibres were selected for measurement. For these the measurement time was 2 hours or less. Results are discussed in the general context of measurement of the sizes of nerve fibres. It is concluded that future studies should place more emphasis on sampling fewer fibres from more animals rather than on measuring all fibres very precisely. These considerations are likely to be of special concern to those wanting to analyse specimens with large fibre complements and those screening large numbers of specimens.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biedenbach M. A., Beuerman R. W., Brown A. C. Graphic-digitizer analysis of axon spectra in ethmoidal and lingual branches of the trigeminal nerve. Cell Tissue Res. 1975;157(3):341–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00225525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. J., Sumner A. J., Greene D. A., Diamond S. M., Asbury A. K. Distal neuropathy in experimental diabetes mellitus. Ann Neurol. 1980 Aug;8(2):168–178. doi: 10.1002/ana.410080207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotran R. S., Karnovsky M. J. Ultrastructural studies on the permeability of the mesothelium to horseradish peroxidase. J Cell Biol. 1968 Apr;37(1):123–137. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diani A. R., Davis D. E., Fix J. D., Swartzman J., Gerritsen G. C. Morphometric analysis of autonomic neuropathology in the abdominal sympathetic trunk of the ketonuric diabetic Chinese hamster. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;53(4):293–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00690371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan A. The nerve fibre composition of the cat optic nerve. J Anat. 1967 Jan;101(Pt 1):1–11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn R. F., O'Leary D. P., Kumley W. E. Quantitative analysis of micrographs by computer graphics. J Microsc. 1975 Nov;105(2):205–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1975.tb04051.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis T. J., Rosen D., Cavanagh J. B. Automated measurement of peripheral nerve fibres in transverse section. J Biomed Eng. 1980 Oct;2(4):272–280. doi: 10.1016/0141-5425(80)90120-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERNAND V. S. V., YOUNG J. Z. The sizes of the nerve fibres of muscle nerves. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1951 Dec 31;139(894):38–58. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1951.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraher J. P. On methods of measuring nerve fibres. J Anat. 1980 Jan;130(Pt 1):139–151. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta M., Mayhew T. M., Bedi K. S., Sharma A. K., White F. H. Inter-animal variation and its influence on the overall precision of morphometric estimates based on nested sampling designs. J Microsc. 1983 Aug;131(Pt 2):147–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1983.tb04241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanker J. S., Ambrose W. W., Yates P. E., Koch G. G., Carson K. A. Peripheral neuropathy in mouse hereditary diabetes mellitus. I. Comparison of neurologic, histologic, and morphometric parameters with dystonic mice. Acta Neuropathol. 1980;51(2):145–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00690457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsen J. Axonal dwindling in early experimental diabetes. I. A study of cross sectioned nerves. Diabetologia. 1976 Dec;12(6):539–546. doi: 10.1007/BF01220629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgen H., Gundersen G., Boysen M., Reith A. Comparison of semiautomatic digitizer-tablet and simple point counting performance in morphometry. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1981;37(3):317–325. doi: 10.1007/BF02892580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupfer C., Chumbley L., Downer J. C. Quantitative histology of optic nerve, optic tract and lateral geniculate nucleus of man. J Anat. 1967 Jun;101(Pt 3):393–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu O., Cruz-Orive L. M., Hoppeler H., Weibel E. R. Measuring error and sampling variation in stereology: comparison of the efficiency of various methods for planar image analysis. J Microsc. 1981 Jan;121(Pt 1):75–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1981.tb01200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew T. M., Sharma A. K. Sampling schemes for estimating nerve fibre size. II. Methods for unifascicular nerve trunks. J Anat. 1984 Aug;139(Pt 1):59–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSHTON W. A. H. A theory of the effects of fibre size in medullated nerve. J Physiol. 1951 Sep;115(1):101–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma A. K., Bajada S., Thomas P. K. Age changes in the tibial and plantar nerves of the rat. J Anat. 1980 Mar;130(Pt 2):417–428. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma A. K., Bajada S., Thomas P. K. Influence of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on myelinated nerve fibre maturation and on body growth in the rat. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;53(4):257–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00690367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma A. K., Thomas P. K., De Molina A. F. Peripheral nerve fiber size in experimental diabetes. Diabetes. 1977 Jul;26(7):689–692. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.7.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sievers J. Basic two-dye stains for epoxy-embedded 0.3-1 sections. Stain Technol. 1971 Jul;46(4):195–199. doi: 10.3109/10520297109067853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanmore A., Bradbury S., Weddell A. G. A quantitative study of peripheral nerve fibres in the mouse following the administration of drugs. 1. Age changes in untreated CBA mice from 3 to 21 months of age. J Anat. 1978 Sep;127(Pt 1):101–115. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimura K., Windebank A. J., Natarajan V., Lambert E. H., Schmid H. H., Dyck P. J. Interstitial hyperosmolarity may cause axis cylinder shrinkage in streptozotocin diabetic nerve. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1980 Nov;39(6):710–721. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198011000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treff W. M., Meyer-König E., Schlote W. Morphometric analysis of a fibre system in the central nervous system. J Microsc. 1972 Apr;95(2):337–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1972.tb03732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. L., Wendell-Smith C. P. Some additional parametric variations between peripheral nerve fibre populations. J Anat. 1971 Sep;109(Pt 3):505–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemp C., Bestetti G., Rossi G. L. Morphological and morphometric study of peripheral nerves from rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;53(2):99–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00689989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


