Abstract
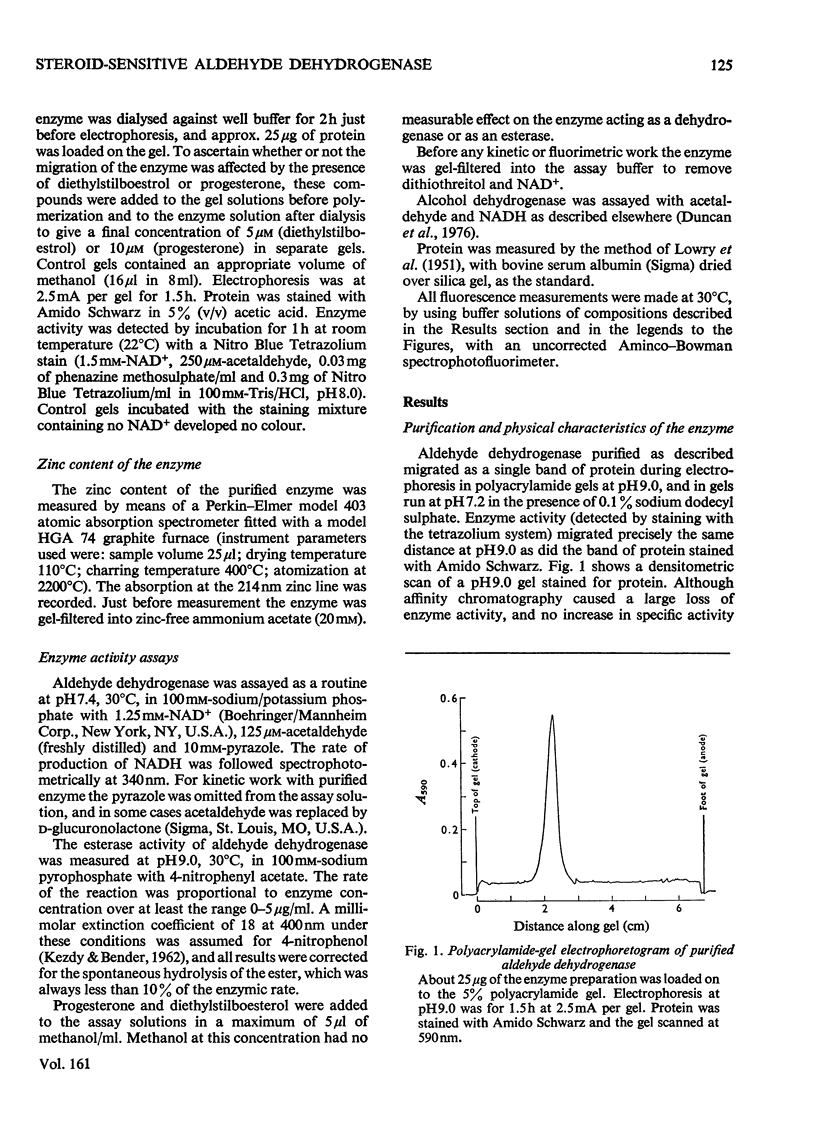
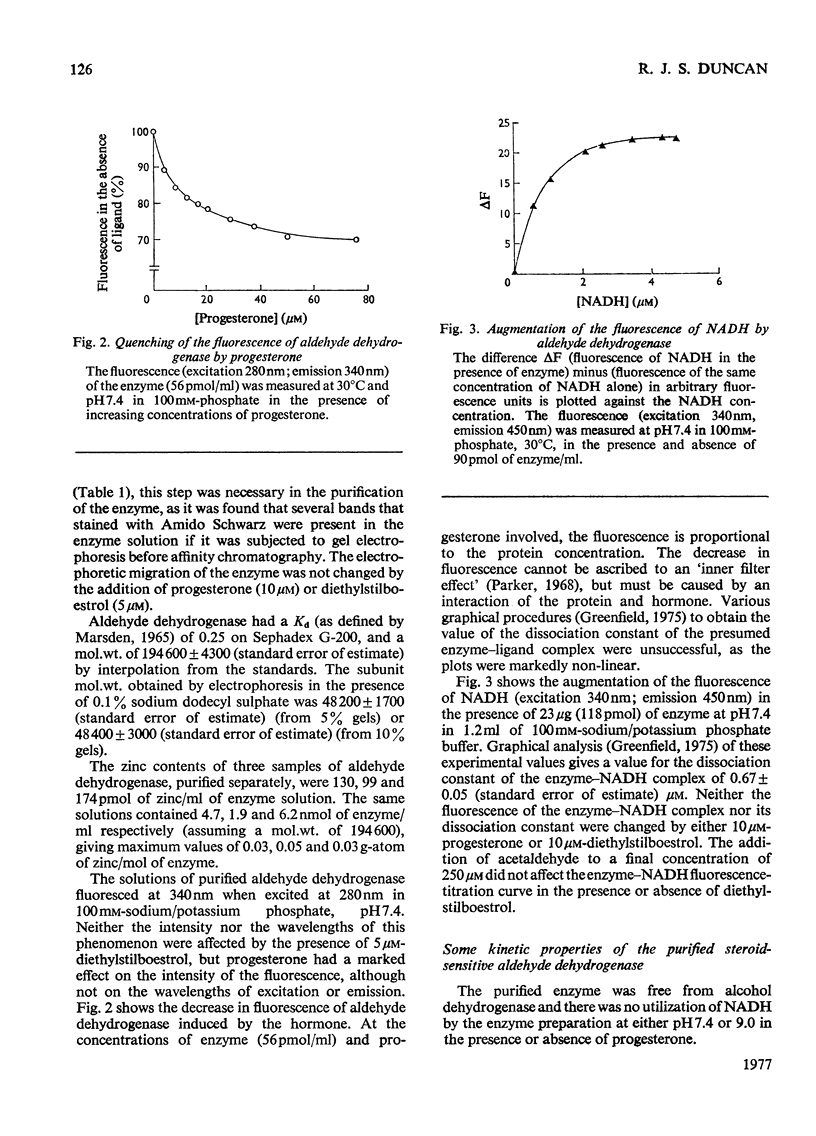
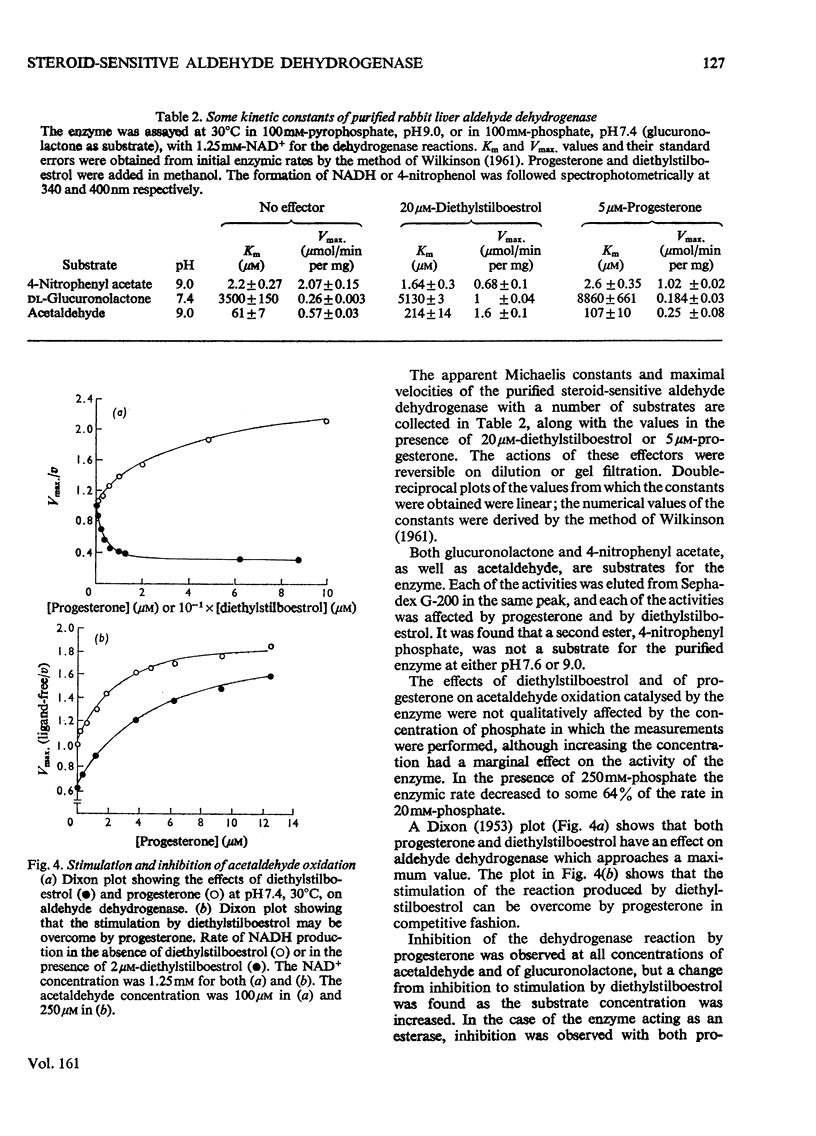
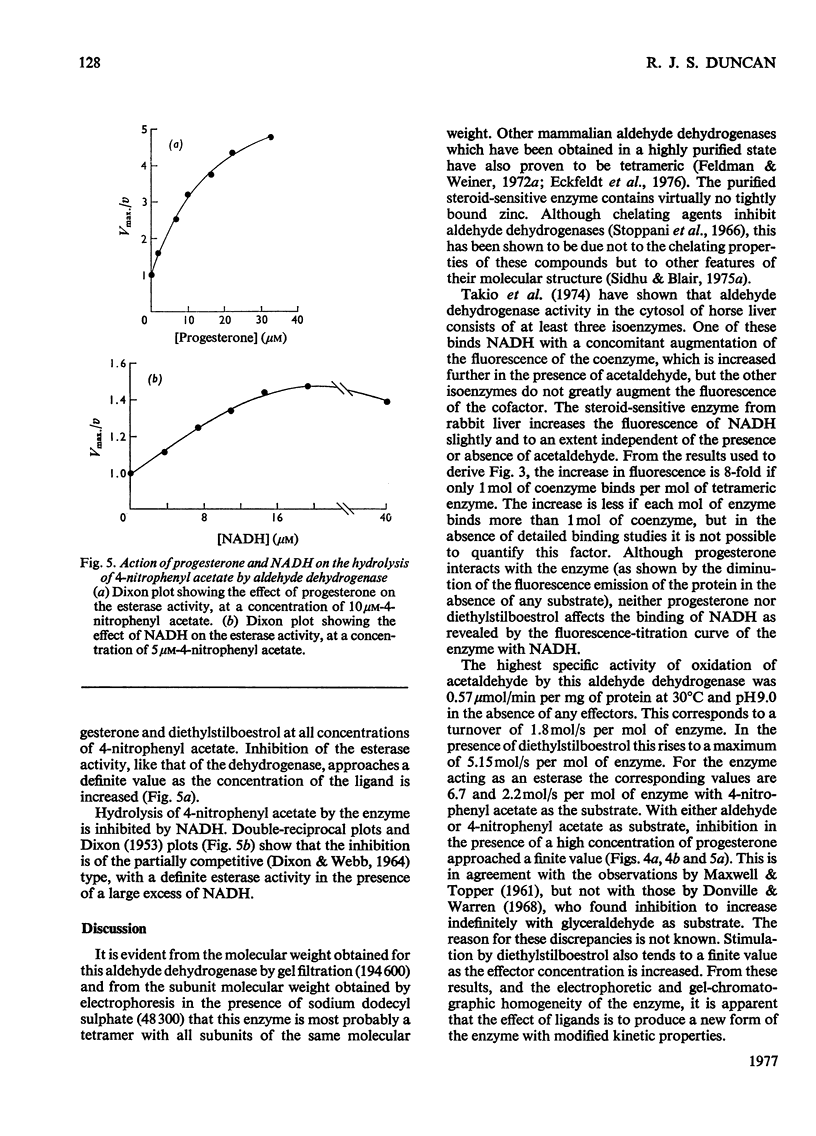
A steroid-sensitive aldehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.3) was purified from rabbit liver and is homogeneous by the criterion of electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gels with or without sodium dodecyl sulphate. The enzyme is tetrameric, of subunit mo.wt. 48 300, and contains no tightly bound zinc. The fluorescence of the protein is decreased in the presence of progesterone, which is inhibitory to the reactions catalysed by the enzyme. When NADH is bound to the enzyme, the fluorescence of the coenzyme is augmented to an extent independent of the presence of steroids or acetaldehyde. The purified enzyme catalyses the oxidation of acetaldehyde and glucuronolactone, and the hydrolysis of 4-nitrophenyl acetate. Each of these reactions is inhibited by progesterone in such a manner as to suggest the formation of a catalytically active enzyme-hormone complex. Diethylstilboestrol inhibits the hydrolysis of esters by this enzyme, but stimulates the oxidation of aldehydes, except at low aldehyde concentrations; the ligand is then inhibitory. NADH inhibits the hydrolysis of 4-nitrophenyl acetate by the enzyme in a partially competitive fashion.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douville A. W., Warren J. C. Steroid-protein interaction at sites which influence catalytic activity. Biochemistry. 1968 Nov;7(11):4052–4059. doi: 10.1021/bi00851a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. S. The preparation of some biochemically important aldehydes. Can J Biochem. 1975 Aug;53(8):920–922. doi: 10.1139/o75-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R. J., Kline J. E., Sokoloff L. Identiy of brain alcohol dehydrogenase with liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 1;153(3):561–566. doi: 10.1042/bj1530561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R. J., Sourkes T. L. Some enzymic aspects of the production of oxidized or reduced metabolites of catecholamines and 5-hydroxytryptamine by brain tissues. J Neurochem. 1974 May;22(5):663–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker A. K., Rueckert R. R. Observations on molecular weight determinations on polyacrylamide gel. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):5074–5080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckfeldt J. H., Yonetani T. Kinetics and mechanism of the F1 isozyme of horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Mar;173(1):273–281. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90260-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckfeldt J., Mope L., Takio K., Yonetani T. Horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Purification and characterization of two isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 10;251(1):236–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. I., Weiner H. Horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. I. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 10;247(1):260–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. I., Weiner H. Horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. II. Kinetics and mechanistic implications of the dehydrogenase and esterase activity. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 10;247(1):267–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield N. J. Enzyme ligand complexes: spectroscopic studies. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1975 May;3(1):71–110. doi: 10.3109/10409237509102553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEZDY F. J., BENDER M. L. The kinetics of the alpha-chymotrypsin-catalyzed hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl acetate. Biochemistry. 1962 Nov;1:1097–1106. doi: 10.1021/bi00912a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz I. M., Darnall D. W. Protein subunits: a table (second edition). Science. 1969 Oct 3;166(3901):126–128. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3901.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koivula T., Koivusalo M. Partial purification and properties of a phenobarbital-induced aldehyde dehydrogenase of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 20;410(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer R. J., Deitrich R. A. Isolation and characterization of human liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 25;243(24):6402–6408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham A. N., Millbank L., Richens A., Rowe D. J. Liver enzyme induction by anticonvulsant drugs, and its relationship to disturbed calcium and folic acid metabolism. J Clin Pharmacol. 1973 Aug-Sep;13(8):337–342. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1973.tb00221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAXWELL E. S. A study of the mechanism by which steroid hormones influence rabbit liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1699–1703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAXWELL E. S., TOPPER Y. J. Steroid-sensitive aldehyde dehydrogenase from rabbit liver. J Biol Chem. 1961 Apr;236:1032–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marselos M., Hänninen O. Enhancement of D-glucuronolactone and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase activities in the rat liver by inducers of drug metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 May 15;23(10):1457–1466. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90383-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu R. S., Blair A. H. Human liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Esterase activity. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7894–7898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu R. S., Blair A. H. The action of chelating agents on human liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1975 Nov;151(2):443–445. doi: 10.1042/bj1510443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppani A. O., Schwarcz M. N., Freda C. E. Action of zinc-complexing agents on nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-linked aldehyde dehydrogenases from yeast and liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Feb;113(2):464–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90216-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


