Abstract
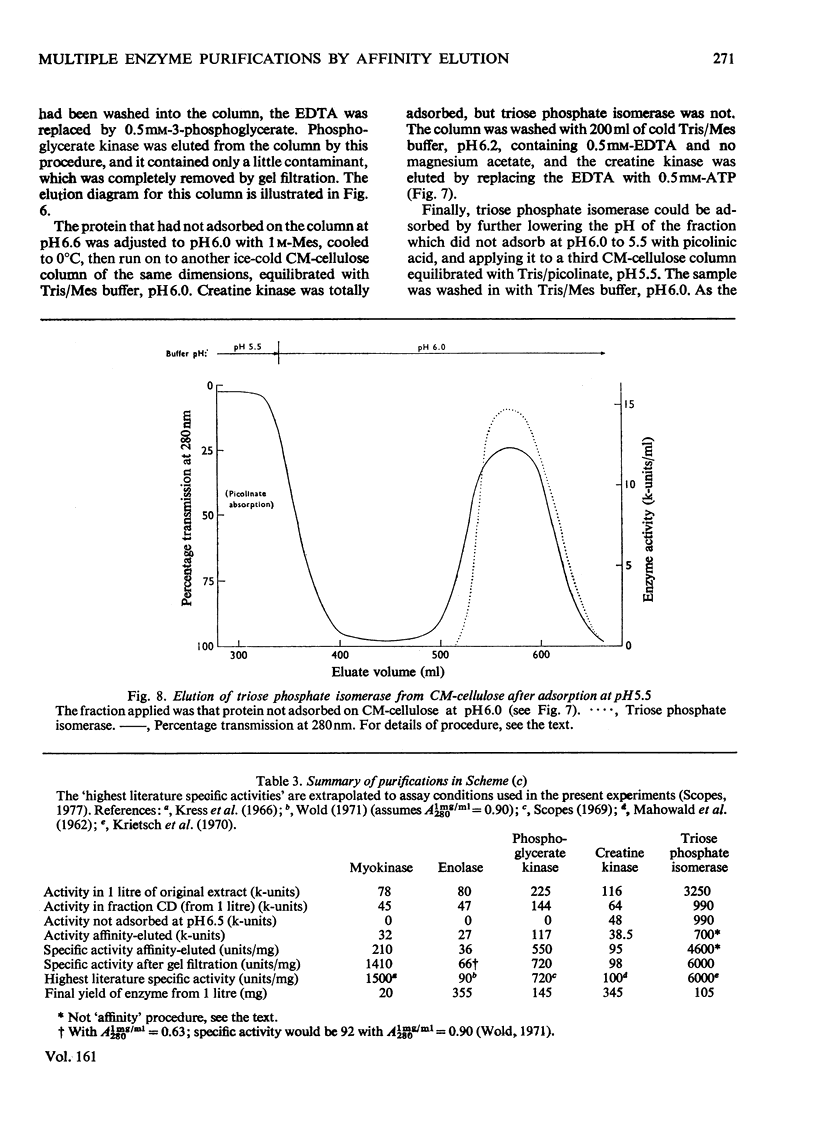
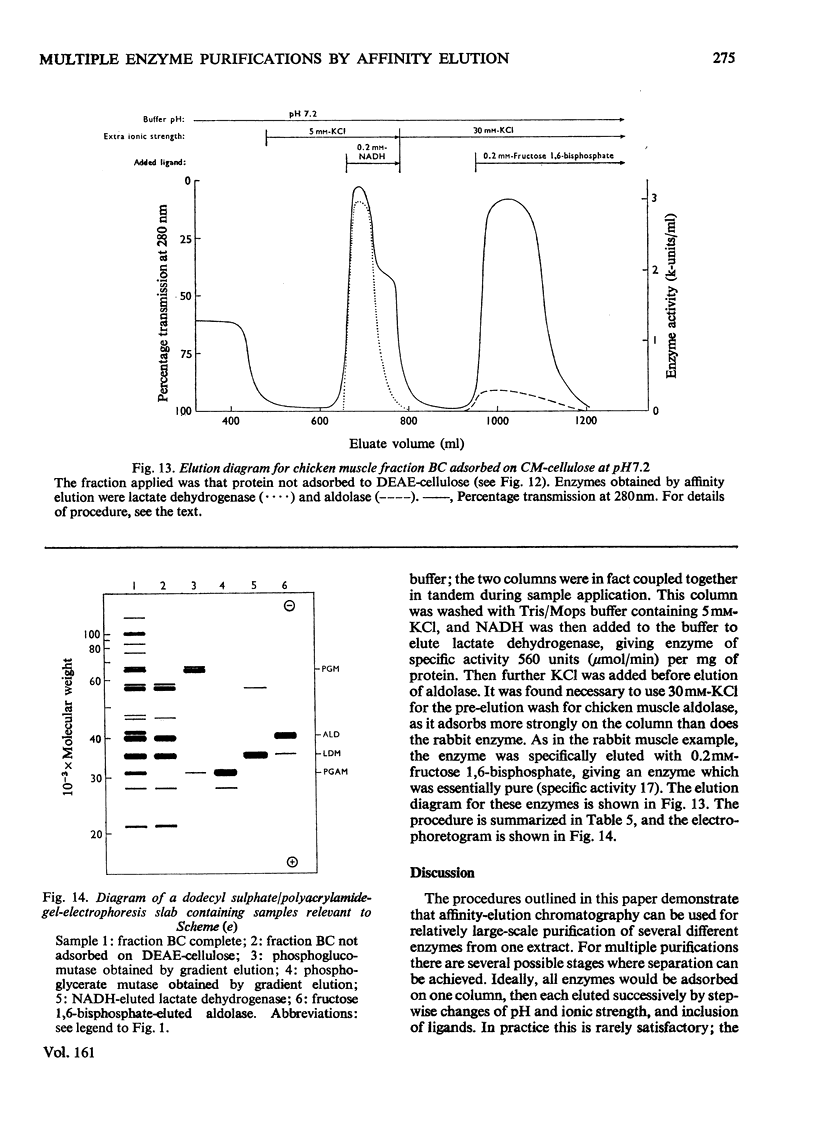
1. Starting with (NH4)2SO4 fractions of muscle extracts, procedures for purifying four to six separate enzymes from each fraction by using affinity-elution-chromatographic techniques are described. 2. Schemes for purifying 12 separate enzymes from rabbit muscle, and eight from chicken muscle extracts, are included. In nearly all cases the overall procedure involves three steps: the initial (NH4)2SO4 fractionation, the ion-exchange chromatography with affinity elution of the enzyme, and gel filtration. The specific activities of the enzymes so purified are comparable with the highest values in the literature. 3. The five schemes described include illustrations of affinity elution of the separate enzymes at different pH values, at different ionic strengths and in combination with conventional gradient elution. They also include stepwise adsorption on columns at different pH values. 4. Separation of two electrophoretically differing forms of phosphoglycerate kinase was achieved by gradient affinity elution from CM-cellulose. The lower-pI form was eluted by a lower concentration of substrate than the higher-pI form.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bondar R. J., Pon N. G. Purification of rabbit muscle pyruvate kinase by CM-sephadex and evidence for an endogenous inhibitor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;191(3):743–747. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodelius P., Mosbach K. Separation of the isoenzymes of lactate dehydrogenase by affinity chromatography using an immobilized AMP-analogue. FEBS Lett. 1973 Sep 15;35(2):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80290-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chappel A., Scopes R. K., Holmes R. S. A high specific activity form of mammalian liver aldolase. FEBS Lett. 1976 Apr 15;64(1):59–61. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80248-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson J. E., Noltmann E. A. The effect of pH and temperature on the kinetic parameters of phosphoglucose isomerase. Participation of histidine and lysine in a proposed dual function mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1401–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisolia S., Cleland W. W. Influence of salt, substrate, and cofactor concentrations on the kinetic and mechanistic behavior of phosphoglycerate mutase. Biochemistry. 1968 Mar;7(3):1115–1121. doi: 10.1021/bi00843a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto T., Handler P. Phosphoglucomutase. 3. Purification and properties of phosphoglucomutases from flounder and shark muscle. J Biol Chem. 1966 Sep 10;241(17):3940–3948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress L. F., Bono V. H., Jr, Noda L. The sulfhydryl groups of rabbit muscle adenosine triphosphate-adenosine monophosphate phosphotransferase. Activity of enzyme treated with mercurials. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2293–2300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krietsch W. K., Pentchev P. G., Klingenbürg H., Hofstätter T., Bücher T. The isolation and crystallization of yeast and rabbit liver triose phosphate isomerase and a comparative characterization with the rabbit muscle enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jun;14(2):289–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHOWALD T. A., NOLTMANN E. A., KUBY S. A. Studies on adenosine triphosphate transphosphorylases. III. Inhibition reactions. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1535–1548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penhoet E. E., Rutter W. J. Detection and isolation of mammalian fructose-diphosphate aldolases. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:240–249. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesce A., Fondy T. P., Stolzenbach F., Castillo F., Kaplan N. O. The comparative enzymology of lactic dehydrogenases. 3. Properties of the H4 and M4 enzymes from a number of vertebrates. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 10;242(9):2151–2167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putman S. J., Coulson A. F., Farley I. R., Riddleston B., Knowles J. R. Specificity and kinetics of triose phosphate isomerase from chicken muscle. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(2):301–310. doi: 10.1042/bj1290301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes R. K. Crystalline 3-phosphoglycerate kinase from skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1969 Jul;113(3):551–554. doi: 10.1042/bj1130551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes R. K. Measurement of protein by spectrophotometry at 205 nm. Anal Biochem. 1974 May;59(1):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes R. K. Methods for starch-gel electrophoresis of sarcoplasmic proteins. An investigation of the relative mobilities of the glycolytic enzymes from the muscles of a variety of species. Biochem J. 1968 Mar;107(2):139–150. doi: 10.1042/bj1070139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes R. K., Penny I. F. Subunit sizes of muscle proteins, as determined by sodium dodecyl sulphate gel electrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 25;236(2):409–415. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90221-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes R. K. Purification of glycolytic enzymes by using affinity-elution chromatography. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 1;161(2):253–263. doi: 10.1042/bj1610253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes R. K. Studies with a reconstituted muscle glycolytic system. The rate and extent of creatine phosphorylation by anaerobic glycolysis. Biochem J. 1973 May;134(1):197–208. doi: 10.1042/bj1340197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torralba A., Grisolia S. The purification and properties of phosphoglycerate mutase from chicken breast muscle. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 25;241(8):1713–1718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VandeBerg J. L., Cooper D. W., Close P. J. Mammalian testis phosphoglycerate kinase. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 9;243(123):48–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


