Abstract
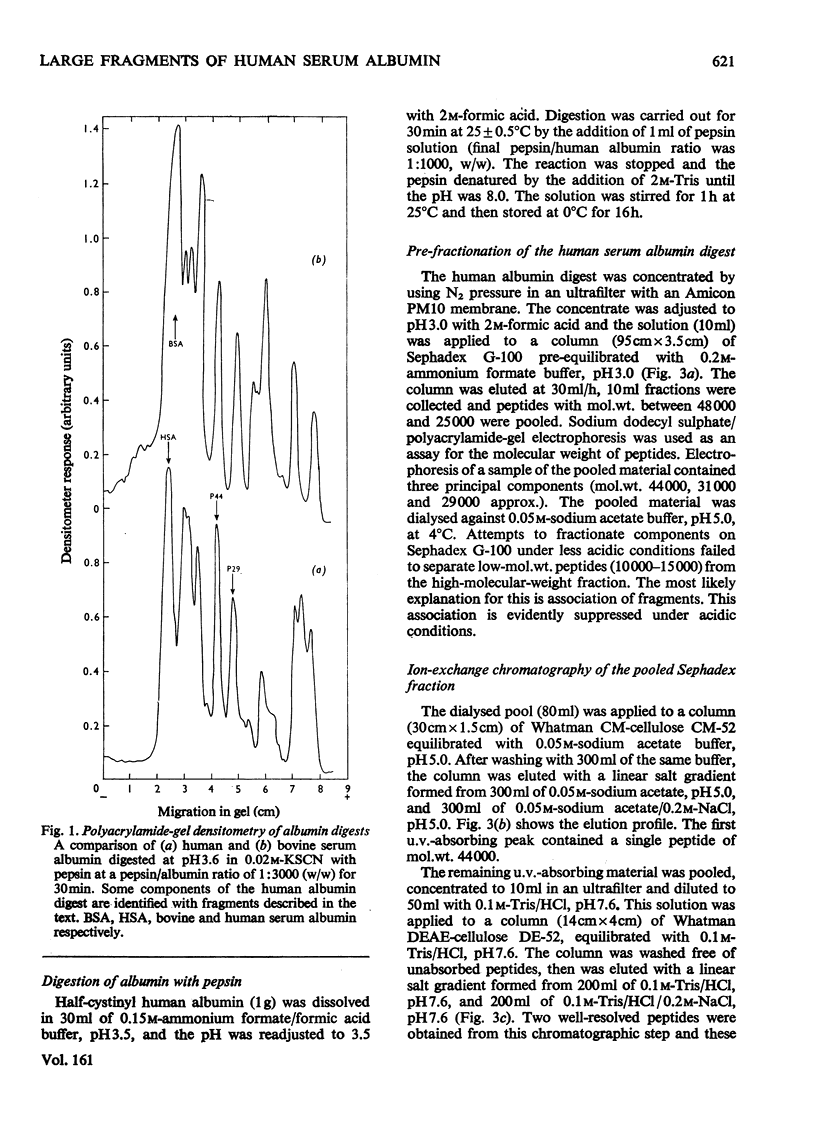
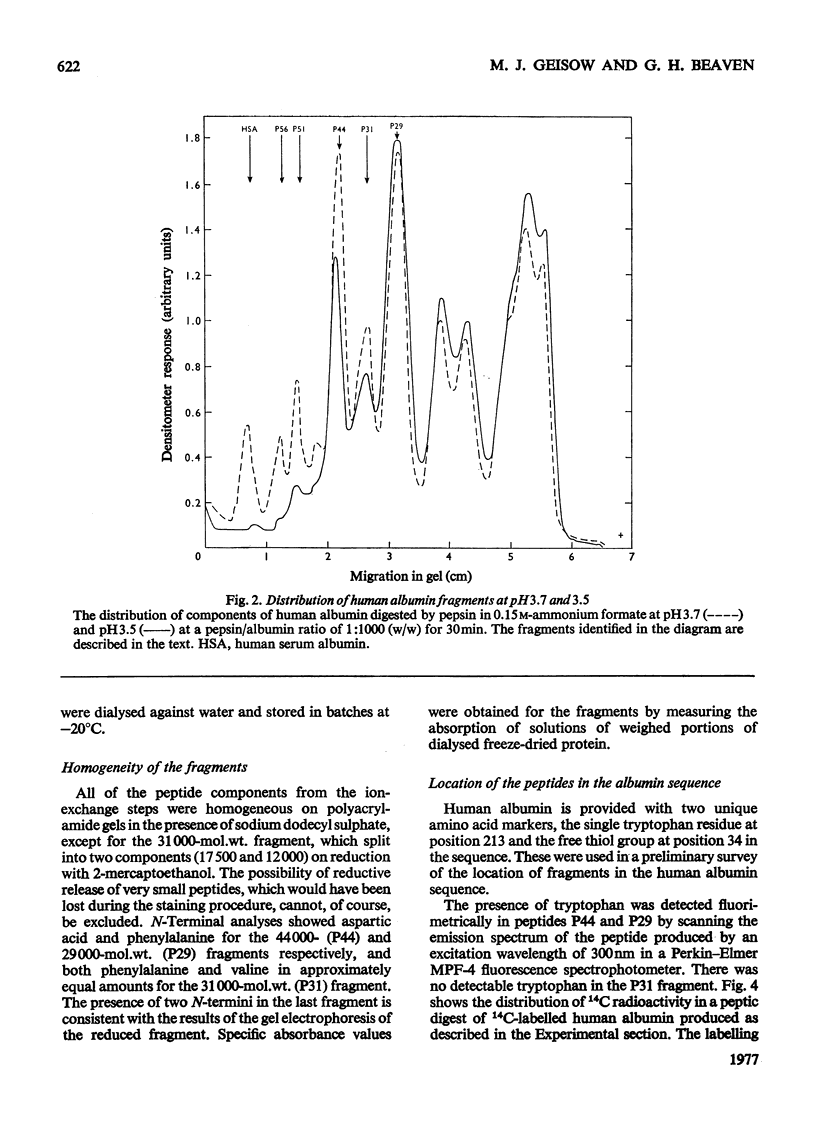
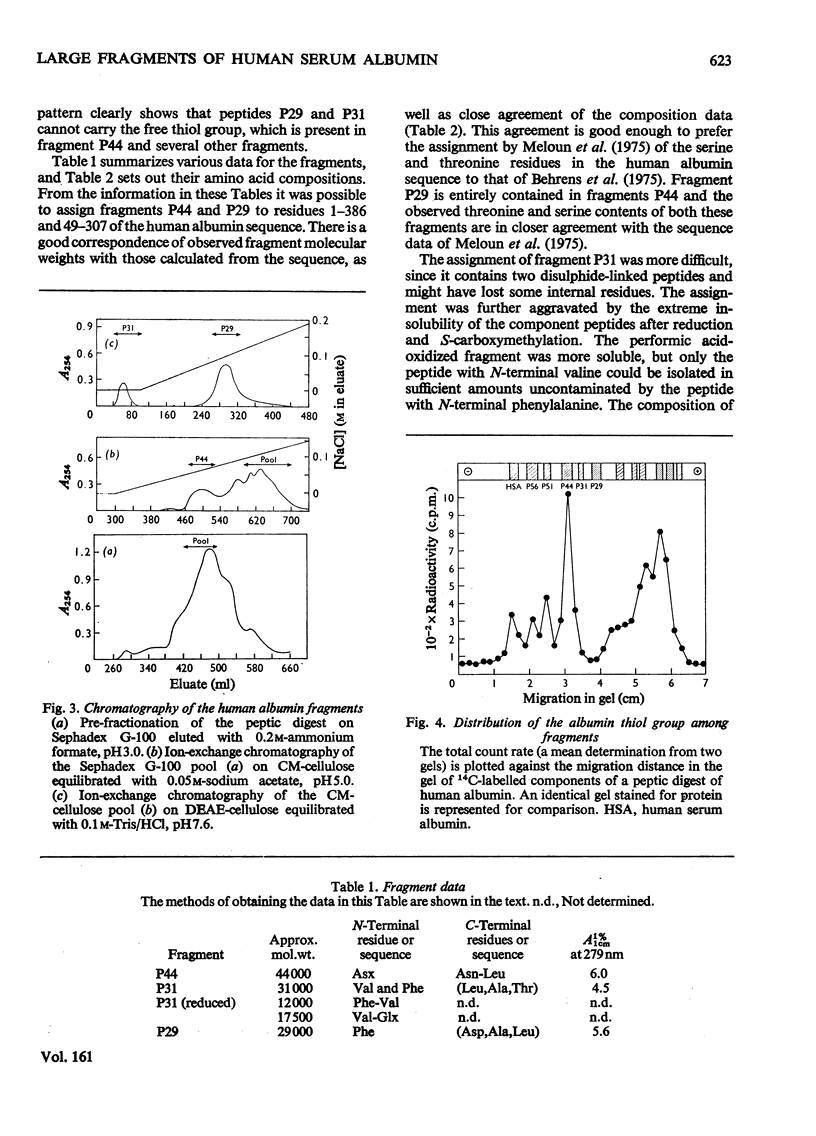
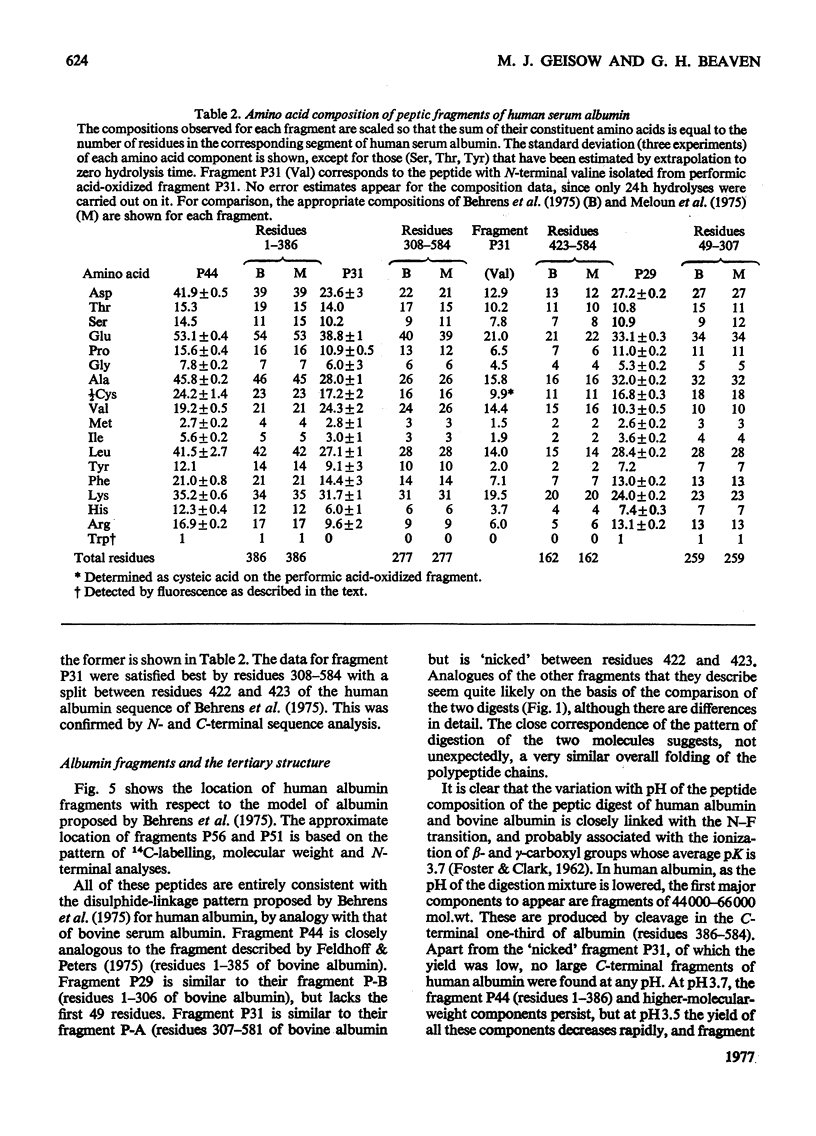
Large fragments of human serum albumin were produced by treatment of the native protein with pepsin at pH3.5. Published sequences of human albumin [Behrens, Spiekerman & Brown (1975) Fed. Proc. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 34, 591; Meloun, Moravek & Kostka (1975) FEBSLett.58, 134-137]were used to locate the fragments in the primary structure. The fragments support both the sequence and proposed disulphide-linkage pattern (Behrens et al., 1975). As the pH of a solution of albumin is lowered from pH4 to pH3.5, the protein undergoes a reversible conformational change known as the N-F transition. The distribution of large fragments of human albumin digested with pepsin in the above pH region was critically dependent on pH. It appeared that this distribution was dependent on the conformation of the protein at low pH, rather than the activity of pepsin. The yields of the large fragments produced by peptic digestion at different values of pH suggested that the C-terminal region of albumin unfolds or separates from the rest of the molecule during the N-F transition. The similarity of peptic fragments of human and bovine albumin produced under identical conditions supports the proposed similar tertiary structure of these molecules.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson L. O. The heterogeneity of bovine serum albumin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 28;117(1):115–133. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90159-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braam W. G., Harmsen B. J., Van Os G. A. Relationship between the conformation of bovine serum albumin and its digestion by pepsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 27;236(1):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90155-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braam W. G., Hilak M. C., Harmsen B. J., van Os G. A. Short digestion of bovine serum albumin with pepsin. Isolation and characterization of fragments and their location in the albumin molecule. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1974;6(1):21–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1974.tb02354.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOSTER J. F., CLARK P. A re-examination of the acid titration behavior of human mercaptalbumin. Changes in amphoteric properties associated with the N-F transformation. J Biol Chem. 1962 Oct;237:3163–3170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldhoff R. C., Peters T., Jr Fragments of bovine serum albumin produced by limited proteolysis. Isolation and characterization of peptic fragments. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 7;14(20):4508–4514. doi: 10.1021/bi00691a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilak M. C., Harmsen B. J., Braam W. G., Joordens J. J., Van Os G. A. Conformational studies on large fragments of bovine serum albumin in relation to the structure of the molecule. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1974;6(2):95–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1974.tb02366.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilak M. C., Harmsen B. J., Joordens J. J., Van Os G. A. Binding of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate to bovine serum albumin and albumin fragments obtained after proteolytic hydrolysis. Localization and nature of the primary PLP binding site. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1975;7(5):411–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1975.tb02461.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P. Limited pepsin digestion of bovine plasma albumin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jun;156(2):509–520. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloun B., Morávek L., Kostka V. Complete amino acid sequence of human serum albumin. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):134–137. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTERSON M. S., GREENE R. C. MEASUREMENT OF LOW ENERGY BETA-EMITTERS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION BY LIQUID SCINTILLATION COUNTING OF EMULSIONS. Anal Chem. 1965 Jun;37:854–857. doi: 10.1021/ac60226a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T., Jr, Feldhoff R. C. Fragments of bovine serum albumin produced by limited proteolysis. Isolation and characterization of tryptic fragments. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 29;14(15):3384–3391. doi: 10.1021/bi00686a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. G., Feldhoff R. C., Clute O. L., Peters T., Jr Fragments of bovine serum albumin produced by limited proteolysis. Conformation and ligand binding. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4578–4583. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


