Abstract
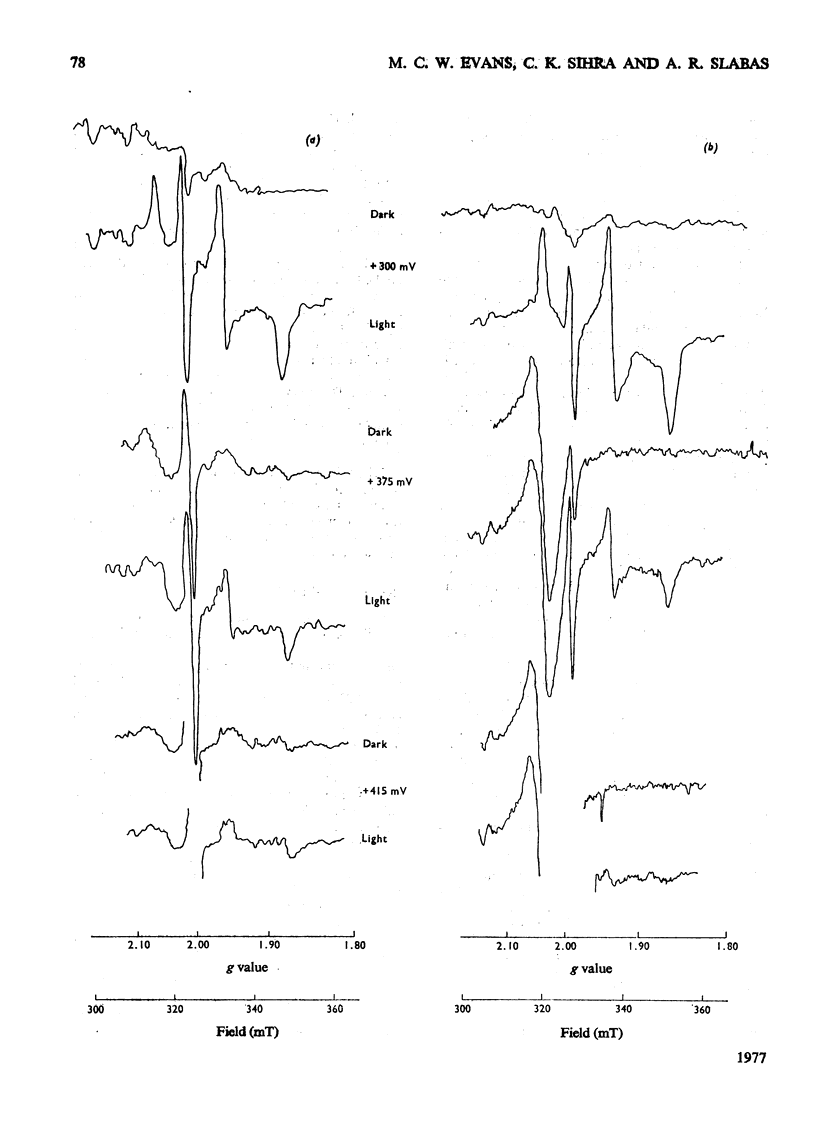
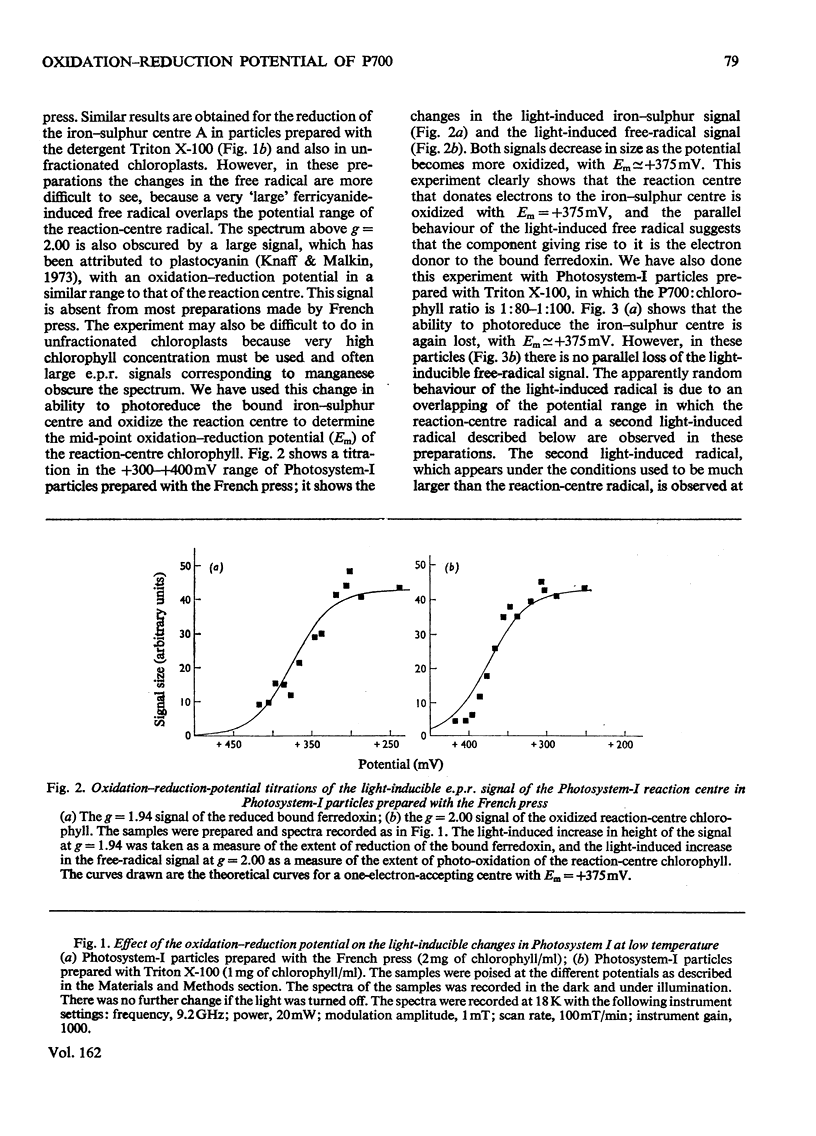
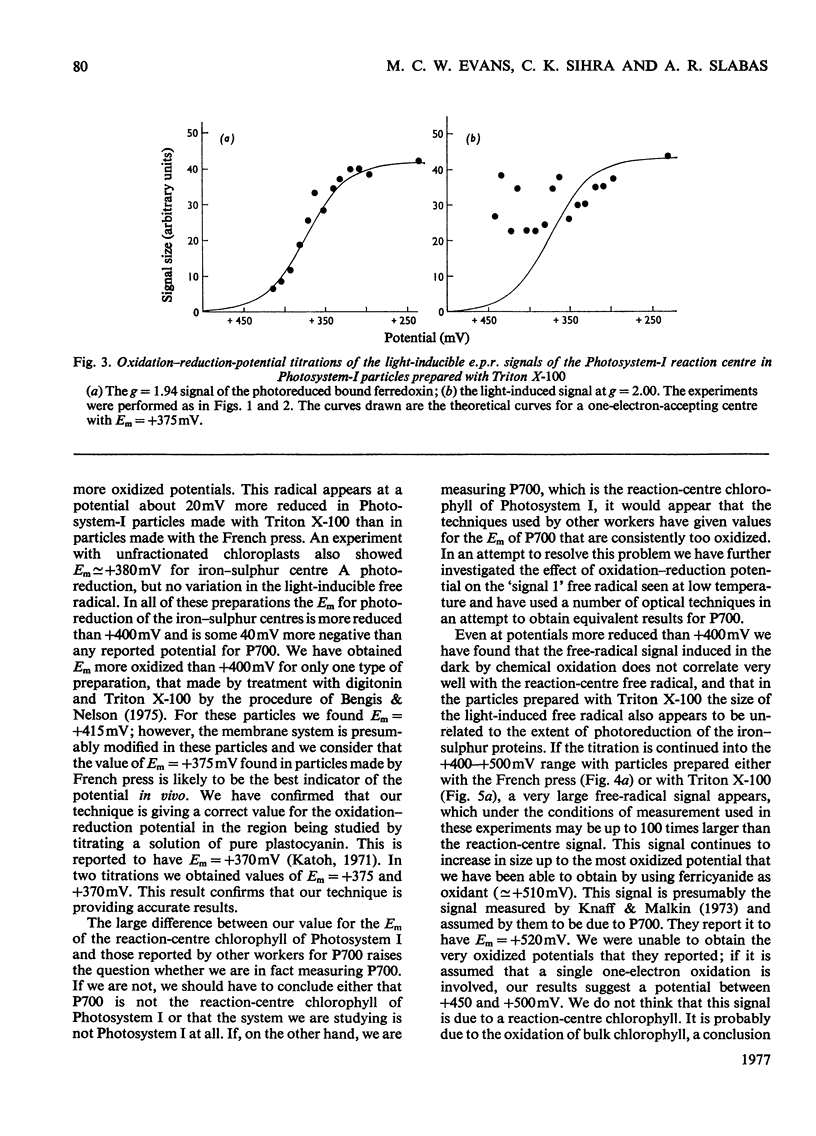
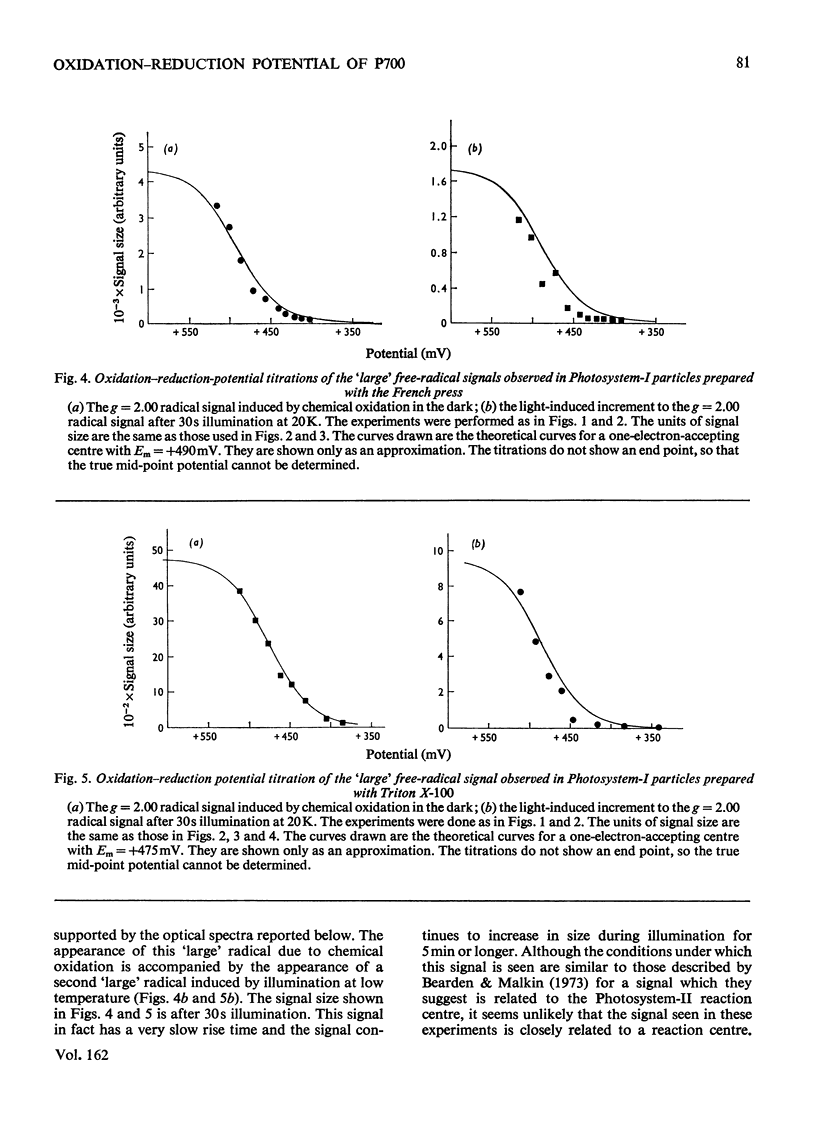
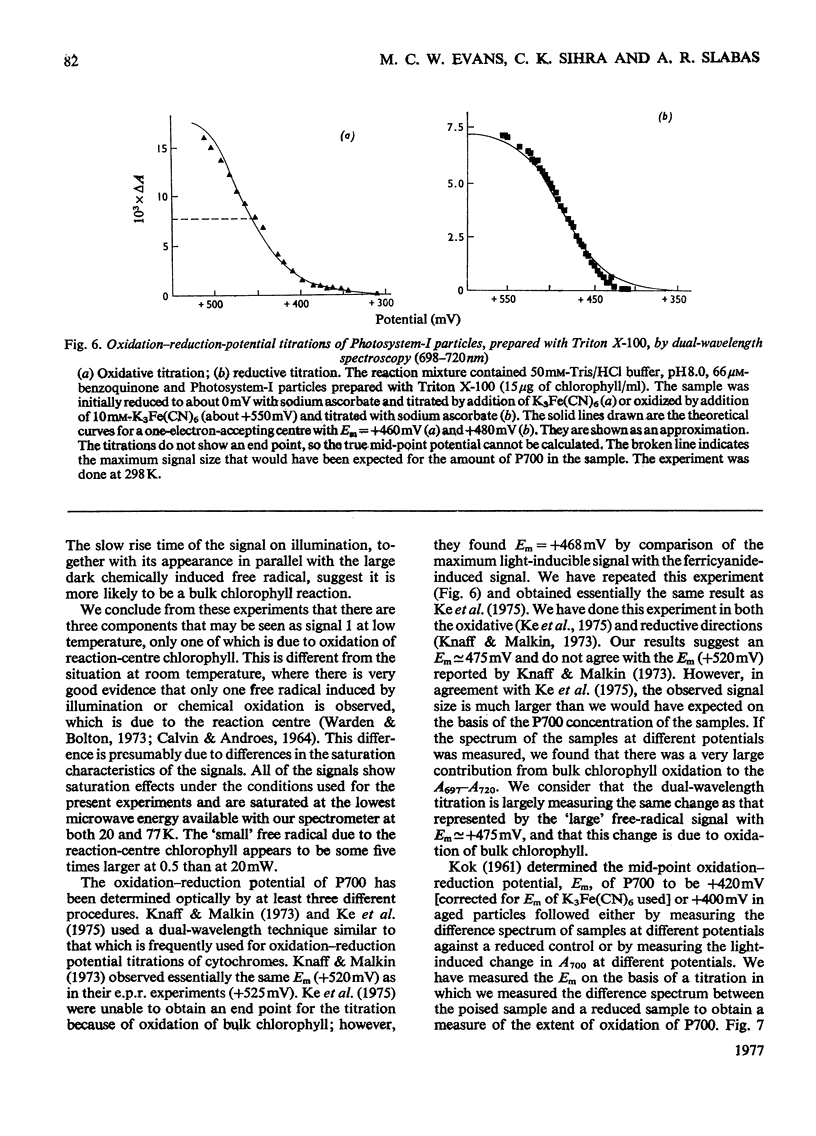
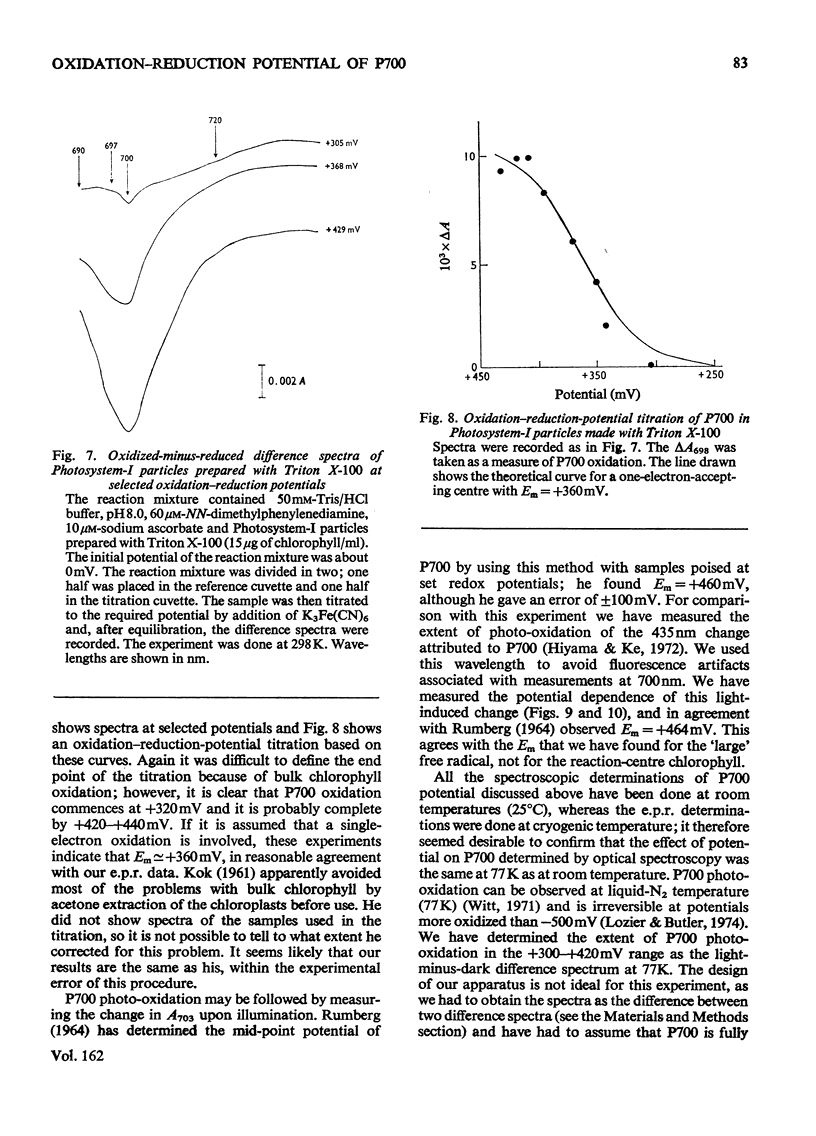
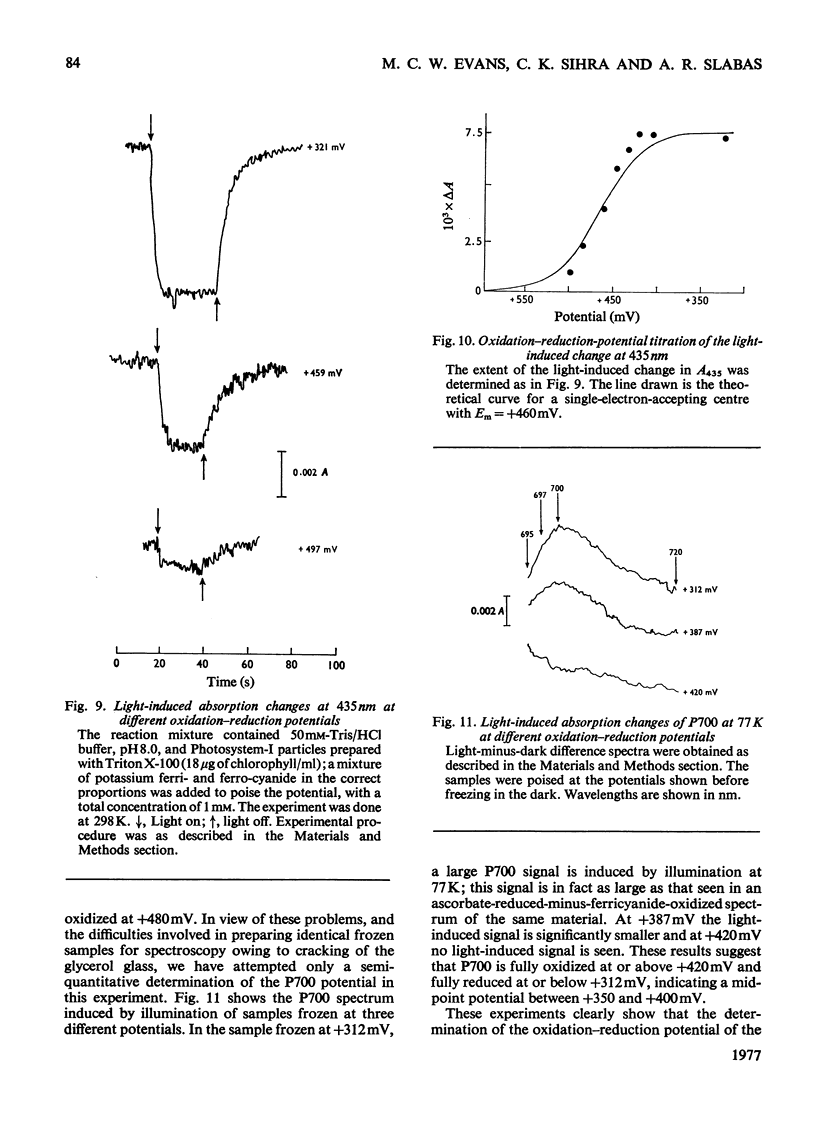
The oxidation-reduction potential of the reaction-centre chlorophyll of Photosystem I (P700) in spinach chloroplasts was determined by using the ability of the reaction centre to photoreduce the bound ferredoxin and to photo-oxidize P700 on illumination at 20K as an indicator of the oxidation state of P700. This procedure shows that P700 is oxidized with Em (pH8.0)(mid-point redox potential at pH8.0)congruent to +375mV. Further oxidation of the chloroplast preparations by high concentrations of K3Fe(CN)6(10mM) in the presence of mediating dyes leads to the appearance of a large radical signal with an apparent Em congruent to +470mVA second, light-inducible, radical also appears over the same potential range. We propose that these signals are due to bulk chlorophyll oxidation and not, as was previously thought [Knaff & Malkin (1973) Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 159, 555-562], to reaction-centre oxidation. A number of optical techniques were used to determine Em of P700. Dual-wavelength spectroscopy (697-720nm) indicates Em congruent to +460-+480mV. The spectrum of the sample during the titration showed a large contribution to the signal by bulk chlorophyll oxidation, in agreement with the electron-paramagnetic-resonance results and those of Ke, Sugahara & Shaw [(1975) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 408, 12-25]. The light-induced absorbance change at 435 nm, usually attributed to P700, showed a potential dependence similar to that of bulk chlorophyll oxidation. Determination of Em of P700 on the basis of the appearance of the P700 signal in oxidized-versus-reduced difference spectra showed Em (pH8.0) congruent to +360mV. Measurements of the effect of potential on the irreversible photo-oxidation of P700 at 77K showed that P700 became oxidized in this potential range. We conclude that the reaction-centre chlorophyll of Photosystem I has Em (pH8.0) congruent to +375mV.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEINERT H., KOK B. AN ATTEMPT AT QUANTITATION OF THE SHARP LIGHT-INDUCED ELECTRON PARAMAGNETIC RESONANCE SIGNAL IN PHOTOSYNTHETIC MATERIALS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Sep 25;88:278–288. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90183-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEINERT H., KOK B., HOCH G. The light induced electron paramagnetic resonance signal of photocatalyst P700. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Apr 20;7:209–212. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bearden A. J., Malkin R. Oxidation-reduction potential dependence of low-temperature photoreactions of chloroplast photosystem. II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 22;325(2):266–275. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bearden A. J., Malkin R. Quantitative EPR studies of the primary reaction of photosystem I in chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 14;283(3):456–468. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90262-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengis C., Nelson N. Purification and properties of the photosystem I reaction center from chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2783–2788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvin M., Androes G. M. Primary Quantum Conversion in Photosynthesis: Low-temperature photoparamagnetism bespeaks electron transfer and migration as the earliest event. Science. 1962 Nov 23;138(3543):867–873. doi: 10.1126/science.138.3543.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Commoner B., Heise J. J., Townsend J. LIGHT-INDUCED PARAMAGNETISM IN CHLOROPLASTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Oct;42(10):710–718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.10.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton P. L. Oxidation-reduction potential dependence of the interaction of cytochromes, bacteriochlorophyll and carotenoids at 77 degrees K in chromatophores of Chromatium D and Rhodopseudomonas gelatinosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 12;226(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Cammack R. The effect of the redox state of the bound iron-sulphur centres in spinach chloroplasts on the reversibility of P700 photooxidation at low temperatures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Mar 3;63(1):187–193. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Sihra C. K., Cammack R. The properties of the primary electron acceptor in the Photosystem I reaction centre of spinach chloroplasts and its interaction with P700 and the bound ferredoxin in various oxidation-reduction states. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 15;158(1):71–77. doi: 10.1042/bj1580071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Telfer A., Lord A. V. Evidence for the role of a bound ferredoxin as the primary electron acceptor of photosystem I in spinach chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 23;267(3):530–537. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJERTEN S., LEVIN O., TISELIUS A. Protein chromatography on calcium phosphate columns. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Nov;65(1):132–155. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiyama T., Ke B. Difference spectra and extinction coefficients of P 700 . Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 20;267(1):160–171. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90147-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOK B. On the reversible absorption change at 705 mu in photosynthetic organisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Nov;22(2):399–401. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90172-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOK B. Partial purification and determination of oxidation reduction potential of the photosynthetic chlorophyll complex absorbing at 700 millimicrons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 15;48:527–533. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ke B., Sugahara K., Shaw E. R. Further purification of "Triton subchloroplast fraction I" (TSF-I particles). Isolation of a cytochrome-free high-P-700 particle and a complex containing cytochromes f and b6, plastocyanin and iron-sulfur protein(s). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 10;408(1):12–25. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90154-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaff D. B., Malkin R. The oxidation-reduction potentials of electron carriers in chloroplast photosystem I fragments. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Nov;159(1):555–562. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90488-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin R., Bearden A. J. Primary reactions of photosynthesis: photoreduction of a bound chloroplast ferredoxin at low temperature as detected by EPR spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):16–19. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUMBERG B. ANALYSE DER PHOTOSYNTHESE MIT BLITZLIGHT. II. DIE EIGENSCHAFTEN DES REAKTIONSCYCLUS VON CHLOROPHYLL-A1-430-703. Z Naturforsch B. 1964 Aug;19:707–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sane P. V., Goodchild D. J., Park R. B. Characterization of chloroplast photosystems 1 and 2 separated by a non-detergent method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 4;216(1):162–178. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90168-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warden J. T., Jr, Bolton J. R. Simultaneous quantitative comparison of the optical changes at 700 nm (p700) and electron spin resonance signals in system I of green plant photosynthesis. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Sep 19;95(19):6435–6436. doi: 10.1021/ja00800a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witt H. T. Coupling of quanta, electrons, fields, ions and phosphrylation in the functional membrane of photosynthesis. Results by pulse spectroscopic methods. Q Rev Biophys. 1971 Nov;4(4):365–477. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500000834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



