Abstract
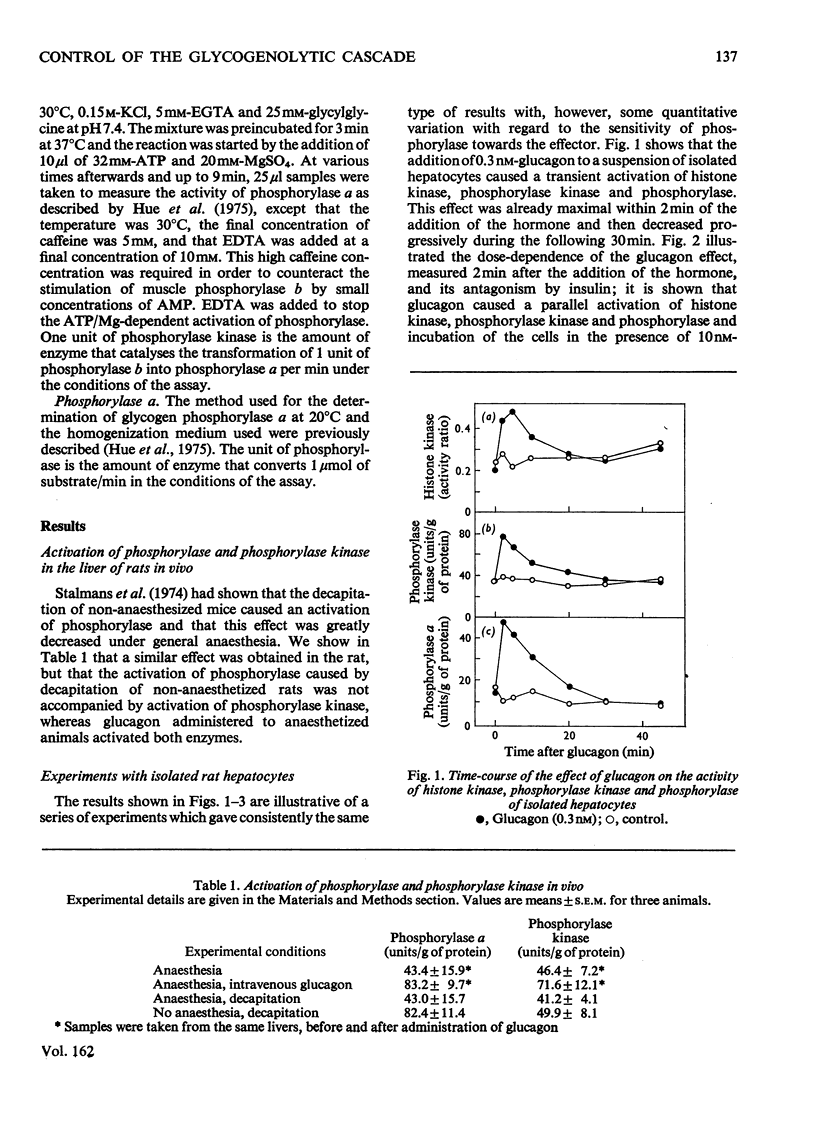
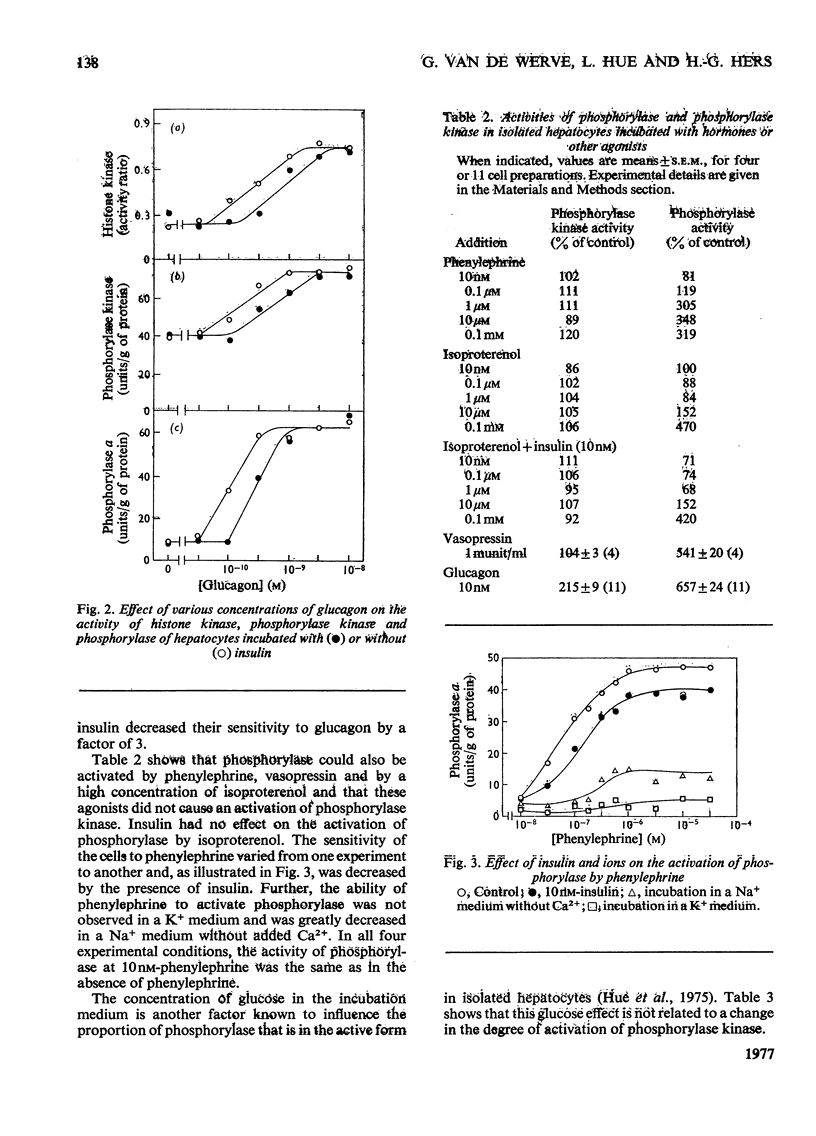
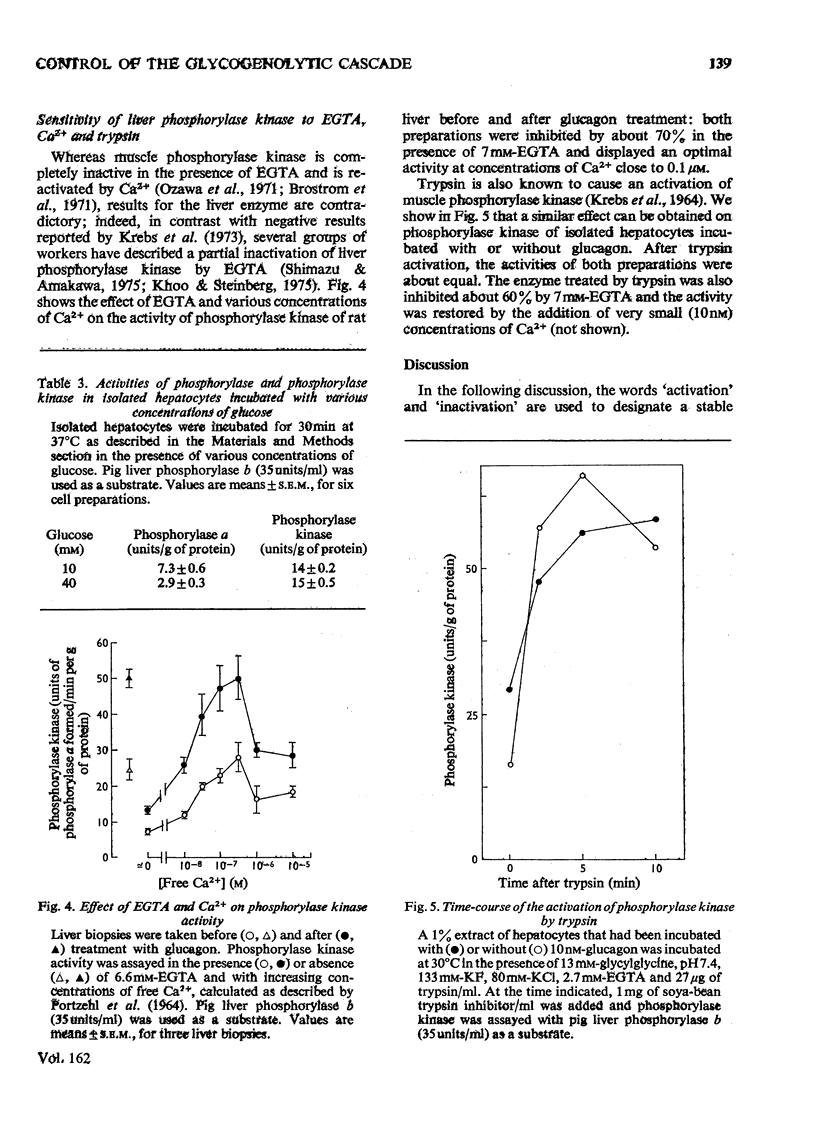
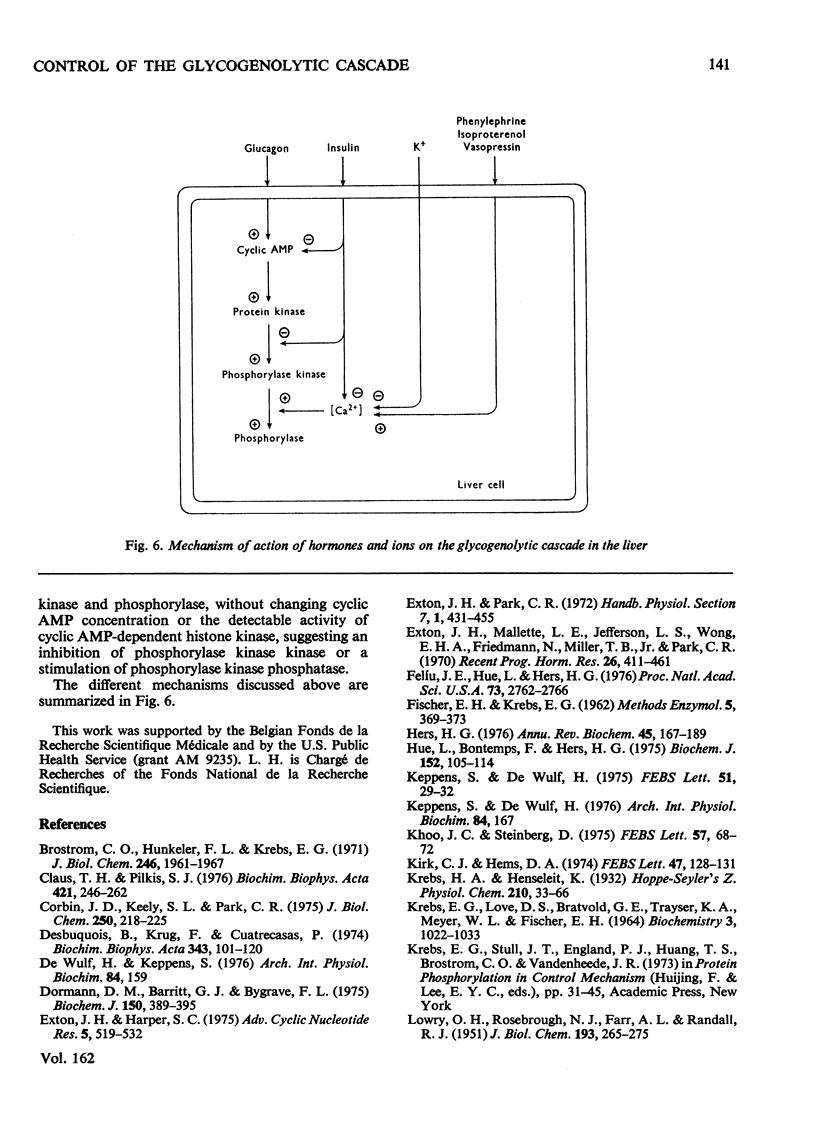
1. A parallel dose-dependent activation of histone kinase, phosphorylase kinase and phosphorylase was observed in isolated hepatocytes incubated in the presence of glucagon; the effect of suboptimal concentrations of glucagon was antagonized by insulin. 2. An activation of phosphorylase which was not accompanied by a stable change in the activity of phosphorylase kinase was observed in hepatocytes incubated with phenylephrine, isoproterenol or vasopressin as well as on decapitation of unanesthetized animals. A dissociation of the two enzymic activities was also observed in hepatocytes incubated in the presence of a high concentration of glucose, in which phosphorylase was strongly inactivated with no change in the activity of phosphorylase kinase. 3. The activation of phosphorylase by phenylephrine in isolated hepatocytes was counteracted by insulin, greatly decreased by the absence of Ca2+ from the incubation medium, and completely suppressed by the replacement of Na+ by K+. 4. In a liver extract, phosphorylase kinase could also be activated by trypsin. Control, glucagon-activated or trypsin-activated phosphorylase kinase was inhibited by about 70% by EGTA and the activity was restored by the addition of Ca2+. 5. The mechanisms that control the activity of phosphorylase kinase and of phosphorylase are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brostrom C. O., Hunkeler F. L., Krebs E. G. The regulation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase by Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1961–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claus T. H., Pilkis S. J. Regulation by insulin of gluconeogenesis in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 24;421(2):246–262. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90291-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Keely S. L., Park C. R. The distribution and dissociation of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases in adipose, cardiac, and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):218–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Wulf H., Keppens S. Proceedings: Is calcium the second messenger in liver for cyclic AMP-independent glycogenolytic hormones? Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1976 Feb;84(1):159–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbuquois B., Krug F., Cuatrecasas P. Inhibitors of glucagon inactivation. Effect on glucagon--receptor interactions and glucagon-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in liver cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 20;343(1):101–120. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90242-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman D. M., Barritt G. J., Bygrave F. L. Stimulation of hepatic mitochondrial calcium transport by elevated plasma insulin concentrations. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;150(3):389–395. doi: 10.1042/bj1500389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Harper S. C. Role of cyclic AMP in the actions of catecholamines on hepatic carbohydrate metabolism. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:519–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Mallette L. E., Jefferson L. S., Wong E. H., Friedmann N., Miller T. B., Jr, Park C. R. The hormonal control of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1970;26:411–461. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571126-5.50014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feliú J. E., Hue L., Hers H. G. Hormonal control of pyruvate kinase activity and of gluconeogenesis in isolated hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2762–2766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hers H. G. The control of glycogen metabolism in the liver. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:167–189. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.001123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hue L., Bontemps F., Hers H. The effects of glucose and of potassium ions on the interconversion of the two forms of glycogen phosphorylase and of glycogen synthetase in isolated rat liver preparations. Biochem J. 1975 Oct;152(1):105–114. doi: 10.1042/bj1520105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS E. G., LOVE D. S., BRATVOLD G. E., TRAYSER K. A., MEYER W. L., FISCHER E. H. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF RABBIT SKELETAL MUSCLE PHOSPHORYLASE B KINASE. Biochemistry. 1964 Aug;3:1022–1033. doi: 10.1021/bi00896a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., De Wulf H. Proceedings: Angiotensin exerts a direct glycogenolytic action on the liver. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1976 Feb;84(1):167–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., de Wulf H. The activation of liver glycogen phosphorylase by vasopressin. FEBS Lett. 1975 Mar 1;51(1):29–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80848-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoo J. C., Steinberg D. Stimulation of rat liver phosphorylase kinase by micromolar concentrations of Ca2+. FEBS Lett. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):68–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80154-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Hems D. A. Hepatic action of vasopressin: lack of a role for adenosine-3',5'-cyclic monophosphate. FEBS Lett. 1974 Oct 1;47(1):128–131. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80441-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa E., Hosoi K., Ebashi S. Reversible stimulation of muscle phosphorylase b kinase by low concentrations of calcium ions. J Biochem. 1967 Apr;61(4):531–533. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTZEHL H., CALDWELL P. C., RUEEGG J. C. THE DEPENDENCE OF CONTRACTION AND RELAXATION OF MUSCLE FIBRES FROM THE CRAB MAIA SQUINADO ON THE INTERNAL CONCENTRATION OF FREE CALCIUM IONS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 25;79:581–591. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., Claus T. H., Johnson R. A., Park C. R. Hormonal control of cyclic 3':5'-AMP levels and gluconeogenesis in isolated hepatocytes from fed rats. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6328–6336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Jensen P., Lake W., Friedmann N., Goodman D. B. Cyclic nucleotides and cellular calcium metabolism. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:375–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherline P., Lynch A., Glinsmann W. H. Cyclic AMP and adrenergic receptor control of rat liver glycogen metabolism. Endocrinology. 1972 Sep;91(3):680–690. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-3-680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimazu T., Amakawa A. Regulation of glycogen metabolism in liver by the autonomic nervous system. VI. Possible mechanism of phosphorylase activation by the splanchnic nerve. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 7;385(2):242–256. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90352-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalmans W., De Wulf H., Hue L., Hers H. G. The sequential inactivation of glycogen phosphorylase and activation of glycogen synthetase in liver after the administration of glucose to mice and rats. The mechanism of the hepatic threshold to glucose. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jan 3;41(1):127–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalmans W., Hers H. G. The stimulation of liver phosphorylase b by AMP, fluoride and sulfate. A technical note on the specific determination of the a and b forms of liver glycogen phosphorylase. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):341–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalmans W. The role of the liver in the homeostasis of blood glucose. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1976;11:51–97. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152811-9.50009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudilovsky O. In vivo regulation of hepatic protein kinase by adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate mediated glucagon stimulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 May 7;58(1):85–91. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90894-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolbert M. E., Butcher F. R., Fain J. N. Lack of correlation between catecholamine effects on cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and gluconeogenesis in isolated rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 25;248(16):5686–5692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolbert M. E., Fain J. N. Studies on the regulation of gluconeogenesis in isolated rat liver cells by epinephrine and glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1162–1166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Werve G., Van den Berghe G., Hers H. G. A simplified procedure for the assay of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate by the activation of liver phosphorylase. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jan 3;41(1):97–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03248.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenheede J. R., Keppens S., De Wulf H. The activation of liver phosphorylase b kinase by glucagon. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jan 15;61(2):213–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)81040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Ashby C. D., Gonzalez C., Calkins D., Fischer E. H. Krebs EG: Purification and characterization of a protein inhibitor of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1977–1985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witt J. J., Roskoski R., Jr Rapid protein kinase assay using phosphocellulose-paper absorption. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 26;66(1):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90743-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Werve G., Stalmans W., Hers H. G. The effect of insulin on the glycogenolytic cascade and on the activity of glycogen synthase in the liver of anaesthetized rabbits. Biochem J. 1977 Jan 15;162(1):143–146. doi: 10.1042/bj1620143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



