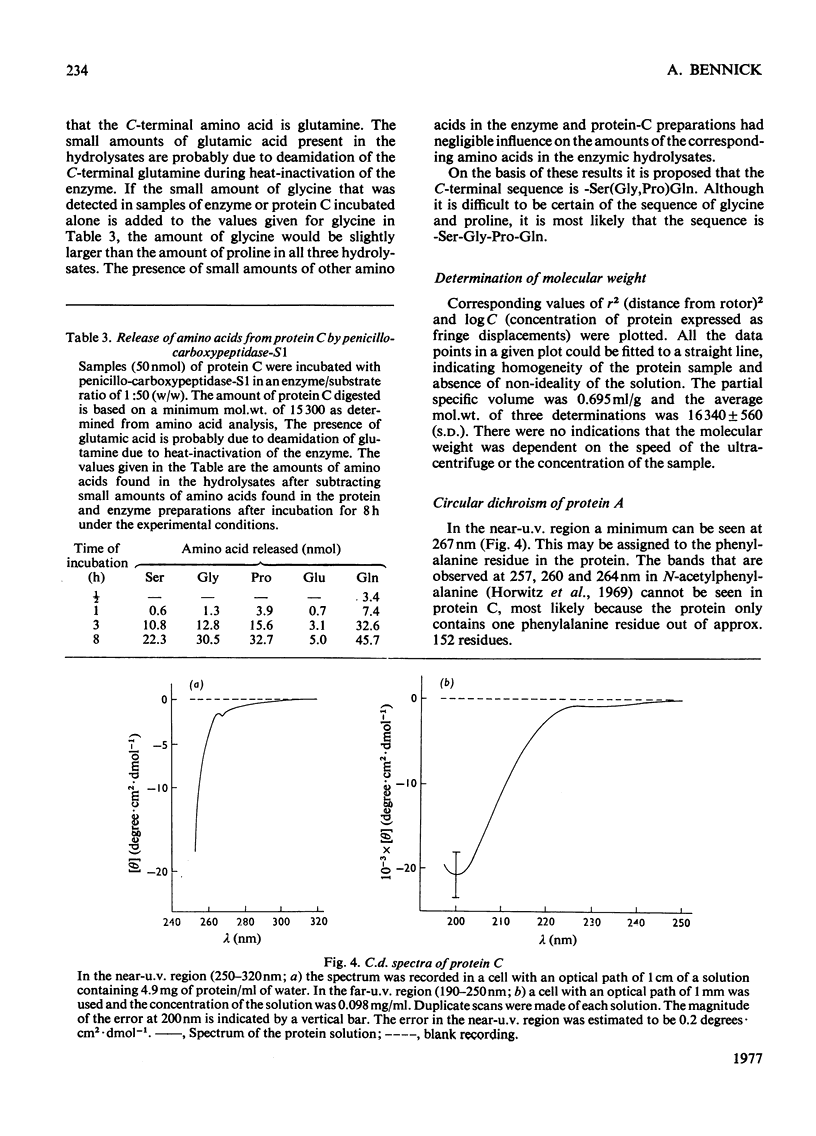
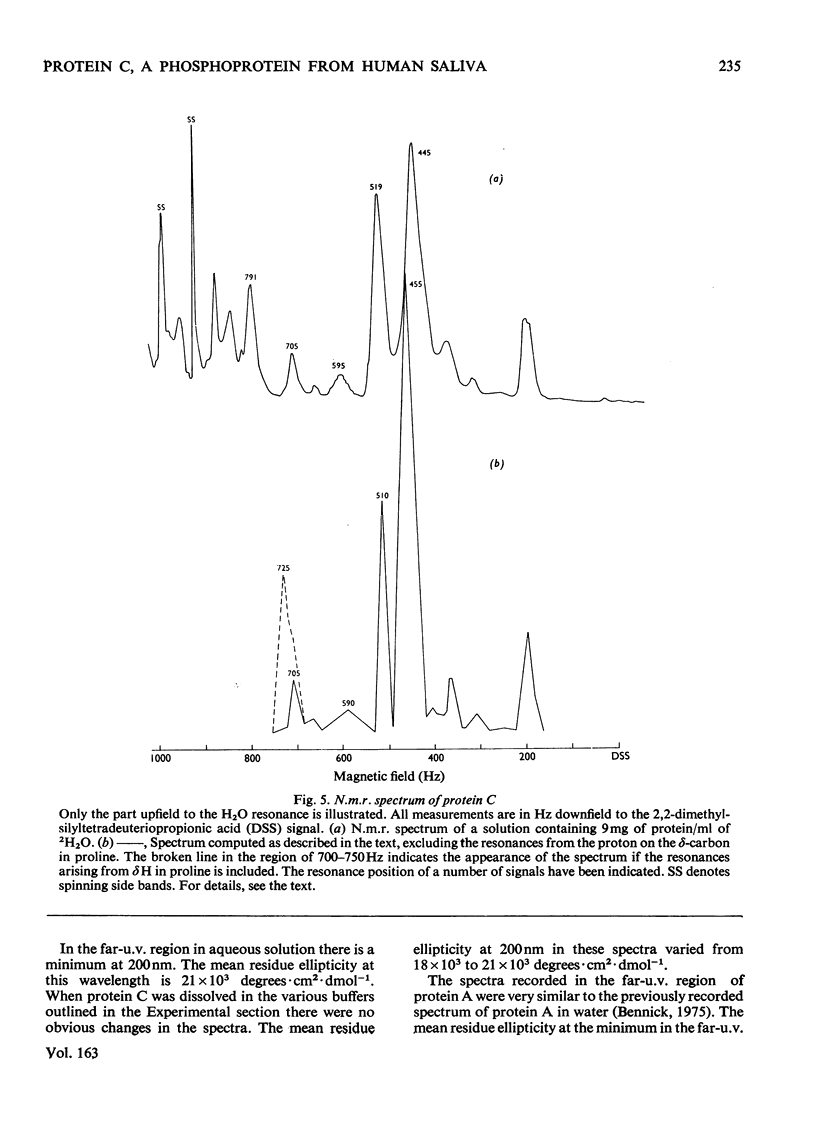
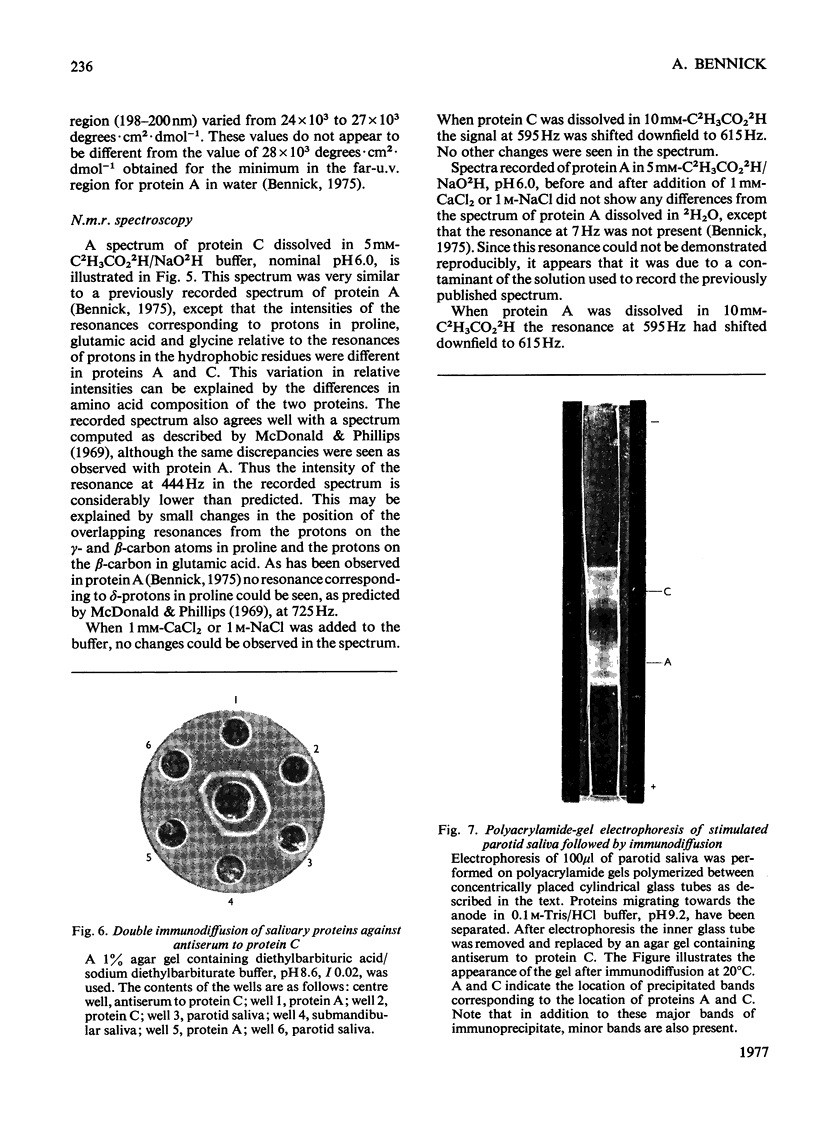
Abstract
The isolation of a highly purified phosphoprotein, previously named protein C, from human parotid saliva is described. A chemical and physical characterization of protein C was undertaken and the properties of protein C were compared with those of a related protein A. The content of glycine, proline and dicarboxylicamino acids accounts for 83% of the total resideus of protein C and it contains 2.0 mol of P/mol of protein, most likely as phosphoserine. The protein also contains 1.2% glucose, but no hexosamine. The N-terminus is blocked and the proposed C-terminal sequence is -Ser(Gly, Pro)Gln. The molecular weight determined from ultracentrifugation is 16300. Circular dichroism and nuclear magnetic resonance fail to demonstrate the presence of polyproline structure, and there are no conformational changes under a variety of conditions. With specific antisera to protein C the protein can be detected in submandibular as well as in parotid saliva, but there is only reaction of partial identity of proteins A and C. It is proposed that at least part of the difference between proteins A and C is due to the presence of an additional length of peptide at the C-terminus of protein C.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azen E. A., Denniston C. L. Genetic polymorphism of human salivary proline-rich proteins: further genetic analysis. Biochem Genet. 1974 Aug;12(2):109–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00487820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A. Chemical and physical characteristics of a phosphoprotein from human parotid saliva. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;145(3):557–567. doi: 10.1042/bj1450557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A., Connell G. E. Purification and partial characterization of four proteins from human parotid saliva. Biochem J. 1971 Jul;123(3):455–464. doi: 10.1042/bj1230455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A. The binding of calcium to a salivary phosphoprotein, protein A, common to human parotid and submandibular secretions. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 1;155(1):163–169. doi: 10.1042/bj1550163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A. The binding of calcium to a salivary phosphoprotein, protein C, and comparison with calcium binding to protein A, a related salivary phosphoprotein. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):241–245. doi: 10.1042/bj1630241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrambach A., Reisfeld R. A., Wyckoff M., Zaccari J. A procedure for rapid and sensitive staining of protein fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., LEVINTHAL C. A fine-structure genetic and chemical study of the enzyme alkaline phosphatase of E. coli. I. Purification and characterization of alkaline phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:470–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. I., Oppenheim F. G. The isolation from human parotid saliva of a further group of proline-rich proteins. Arch Oral Biol. 1974 Aug;19(8):627–632. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90130-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz J., Strickland E. H., Billups C. Analysis of vibrational structure in the near-ultraviolet circular dichroism and absorption spectra of phenylalanine and its derivatives. J Am Chem Soc. 1969 Jan 1;91(1):184–190. doi: 10.1021/ja01029a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. R., Hofmann T. Penicillocarboxypeptidase-S, a nonspecific SH-dependent exopeptidase. Can J Biochem. 1972 Dec;50(12):1297–1310. doi: 10.1139/o72-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller P. J., Robinovitch M., Iversen J., Kauffman D. L. The protein composition of rat parotid saliva and secretory granules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 27;379(2):562–570. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90162-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. J., Ellison S. A., Bahl O. P. The isolation from human parotid saliva and partial characterization of the protein core of a major parotid glycoprotein. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Jul;18(7):827–837. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison V., Schellman J. Location of proline derivatives in conformational space. II. Theoretical optical activity. Biopolymers. 1970;9(5):569–588. doi: 10.1002/bip.1970.360090503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson S., Sottrup-Jensen L., Petersen T. E., Morris H. R., Dell A. Primary structure of the vitamin K-dependent part of prothrombin. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 25;44(2):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80723-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara H., Sasaki R. M. High recovery of tryptophan from acid hydrolysates of proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Apr 29;35(2):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald C. C., Phillips W. D. Proton magnetic resonance spectra of proteins in random-coil configurations. J Am Chem Soc. 1969 Mar 12;91(6):1513–1521. doi: 10.1021/ja01034a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Zytkovicz T. H., Howard J. B. The mode of action of vitamin K. Identification of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid as a component of prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6347–6350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim F. G., Hay D. I., Franzblau C. Proline-rich proteins from human parotid saliva. I. Isolation and partial characterization. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov;10(23):4233–4238. doi: 10.1021/bi00799a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percy M. E., Buchwald B. M. A manual method of sequential Edman degradation followed by dansylation for the determination of protein sequences. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jan;45(1):60–67. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A., Otsuka A. A., Poser J. W., Kristaponis J., Raman N. Characterization of a gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein from bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1447–1451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinovitch M. R., Keller P. J., Iversen J., Kauffman D. L. Demonstration of a class of proteins loosely associated with secretory granule membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 13;382(2):260–24b. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEIFTER S., DAYTON S. The estimation of glycogen with the anthrone reagent. Arch Biochem. 1950 Jan;25(1):191–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Fernlund P., Egan W., Roepstorff P. Vitamin K dependent modifications of glutamic acid residues in prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2730–2733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D., Kirshner N., Schramm M. Non-parallel transport of membrane proteins and content proteins during assembly of the secretory granule in rat parotid gland. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 14;375(1):87–105. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]