Abstract
Primary cardiac lymphoma is a rare disease with the potential to be fatal. This case reports a patient who developed primary cardiac lymphoma resulting in cardiac tamponade. Despite a compromised general condition, the lymphoma was diagnosed through a transvenous tumor biopsy. Chemotherapy led to significant improvement in the patient’s condition. Malignant lymphoma can be treated with chemotherapy. Therefore, the performance of tumor biopsies even in patients with poor general condition enabled the initiation of treatment.
Key Words: cancer, echocardiography, imaging, shortness of breath
Graphical Abstract
History of Presentation
A 53-year-old man presented with a 2-week history of palpitation and dyspnea. Physical examination was unremarkable. The electrocardiogram showed an incomplete right bundle branch block. Chest radiograph revealed cardiac enlargement and bilateral pleural effusions. Blood tests showed hemoglobin 13.1 g/dL, lactate dehydrogenase 358 U/L, and soluble interleukin-2 receptor 1,380 U/mL; human immunodeficiency virus antibody was negative. Thyroid function was normal. Transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) revealed a mobile and solid mass measuring 79 × 55 mm, occupying most of the right atrium (RA) (Figures 1A and 1B, Videos 1 and 2). Left ventricular systolic function was preserved with an ejection fraction of 75%. The cardiac-gated magnetic resonance imaging showed a multilobulated mass measuring approximately 80 mm, almost entirely occupying the RA with attachment to the lateral wall of the RA (Figure 2).
Take-Home Message
-
•
This report highlights the importance of tumor biopsy, even in cases of poor condition.
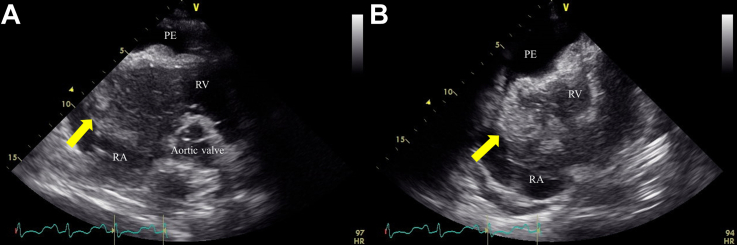
Figure 1.
Transthoracic Echocardiogram
The images revealed a mobile mass occupying most of the right atrium (RA) and protruding into the right ventricle (RV) (arrows), with pericardial effusion (PE): (A) parasternal view and (B) apical view.
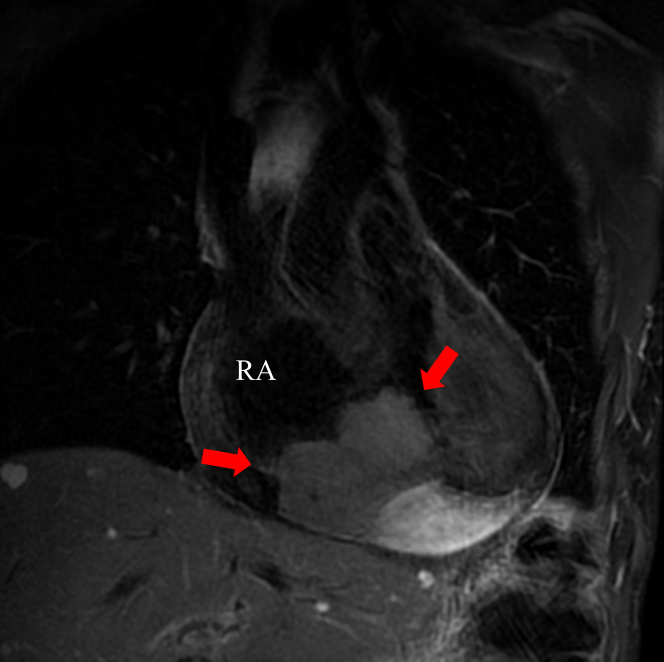
Figure 2.
Fat-Suppressed T2-Weighted Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging
The images revealed a mass with irregular margins that was attached to the lateral wall of the right atrium (RA), infiltrating the myocardium and occupying almost the entire RA (arrows). It showed mild hyperintensity on fat-suppressed T2-weighted images.
Past Medical History
The patient underwent an annual medical examination without any previous medical history or cardiovascular risk factors.
Differential Diagnosis
Based on the clinical course, we considered the differential diagnosis of cardiac malignant tumors (eg, lymphoma, sarcoma).
Investigations
Fluorine-18 (18F)–fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) showed increased FDG avidity in the cardiac mass lesion (SUVmax [the maximum standardized uptake value] 23.62) and no lymph nodes and other organs (Figure 3). Coronary angiography showed no significant stenosis in the coronary arteries and no blood vessels feeding the tumor. Cardiac tamponade developed, and pericardiocentesis was performed. Pericardial effusion was exudative, and cytologic examination revealed the presence of atypical cells; however, no malignant cells were identified (class Ⅱ). After that, the patient experienced worsening dyspnea. A transvenous biopsy of the RA mass was subsequently performed under TTE guidance (Figure 4, Video 3).
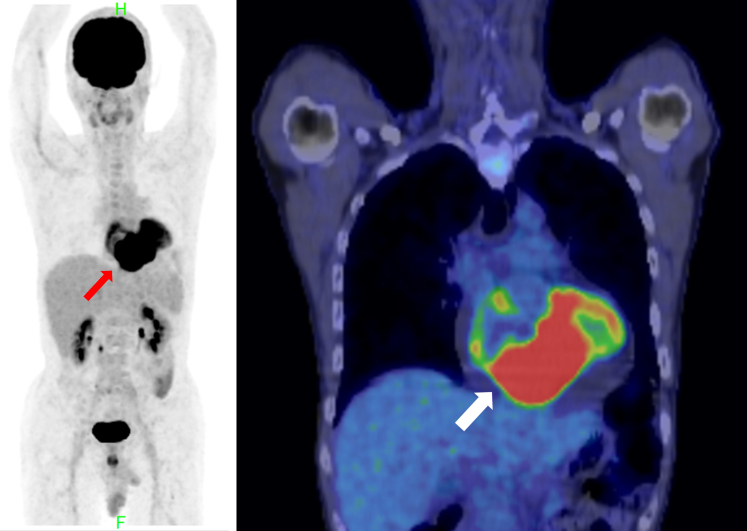
Figure 3.
Fluorine-18 Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography
Increased fluorodeoxyglucose avidity in the cardiac mass lesion (arrow) and no lymph nodes and other organs are shown.
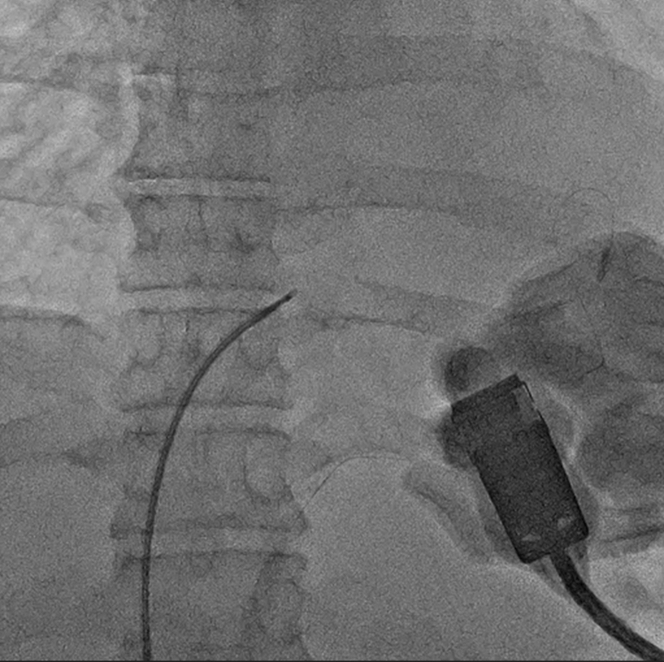
Figure 4.
Radiograph Image at the Time of Biopsy
Biopsy was performed with the guidance of transthoracic echocardiography while confirming the location of the tumor with biopsy forceps.
Management
B-cell lymphoma was diagnosed by flow cytometry of the mass biopsy, and the patient received chemotherapy with intravenous rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone (R-CHOP) immediately prior to pathologic diagnosis, given the patient’s compromised general condition. Thereafter, the tumor tended to shrink, pericardial effusion disappeared, and symptoms improved. Pathologic examination showed diffuse proliferation of large lymphoid cells (Figure 5), and immunostaining revealed positivity for CD20 and negativity for CD3. Furthermore, these atypical cells were highly expressed for BCL2, BCL6, and MYC. Ki-67 labeling index was more than 95% for tumor cells. Finally, the diagnosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) was made. Fluorescence in situ hybridization could not be performed due to insufficient sample materials. Considering DLBCL with high expression of MYC and BCL2, the patient received chemotherapy with dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisolone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (DA-EPOCH-R) for 6 cycles.
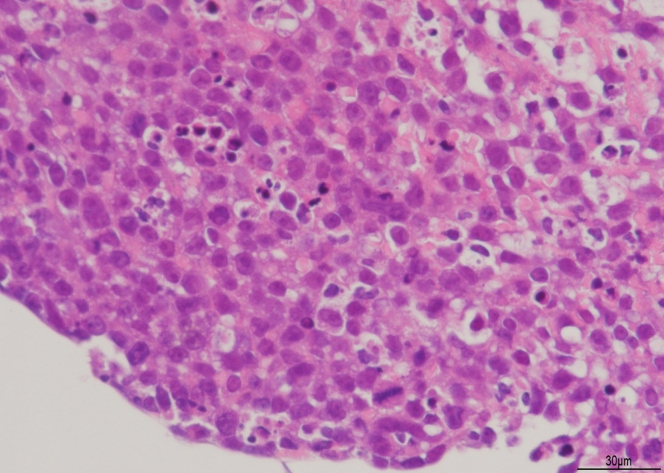
Figure 5.
Pathologic Findings
This pathologic image was captured at 400× magnification. Hematoxylin and eosin stain shows diffuse and cohesive infiltrates of large atypical cells.
Outcome and Follow-Up
The patient underwent cardiac TTE and 18F-FDG PET after chemotherapy. TTE showed resolution of the pericardial effusion, preserved left ventricular systolic function (Figure 6A and 6B, Video 4), and the RA mass had shrunk in size (15 × 11 mm) (Figures 6C and 6D, Videos 5 and 6). The patient achieved complete response (CR) as confirmed by 18F-FDG PET (Figure 6E).
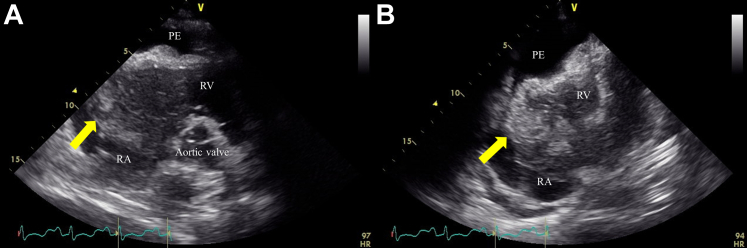
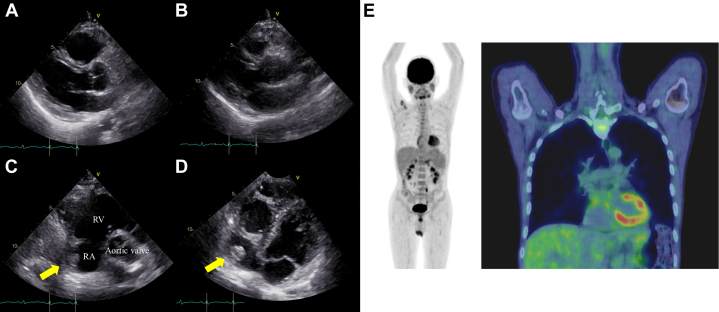
Figure 6.
Follow-Up Imaging
Transthoracic echocardiogram showed resolution of the pericardial effusion and preserved left ventricular systolic function (A: diastolic image, B: systolic image). The right atrial mass has shrunk in size (15 × 11 mm) (arrows). (C and D) Fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography showed only physiological uptake around the heart and within the myocardium (E). RA = right atrium; RV = right ventricle.
Discussion
Primary cardiac lymphoma accounts for 1% of primary cardiac tumors and 0.5% of extranodal lymphomas.1 Most commonly, the tumor is partially located within the RA of the heart and the most common subtype is DLBCL.2 Dyspnea, arrhythmia, heart failure, and chest pain may be caused by tumor. In cases where the disease affects the pericardium, effusion or hemorrhage may occur.2 Primary cardiac lymphoma can be fatal if diagnosed late and generally has a poor prognosis. In this case, cardiac tamponade occurred and the course was acute, but transthoracic echocardiography–guided tumor biopsy was performed, leading to the diagnosis of DLBCL, and enabling treatment. Due to the patient’s poor respiratory condition, we decided to perform biopsy under transthoracic echocardiography guidance instead of the generally considered biopsy under transesophageal echocardiography guidance. The biopsy was clearly visualized and successfully performed without any complications, despite the potential risks of cardiac tamponade and pulmonary embolism due to thrombus or tumor associated with transvenous biopsy. Surgical resection does not improve prognosis with primary cardiac lymphoma.3 The standard treatment of DLBCL is chemotherapy with R-CHOP.4 Double-hit lymphomas with translocations involving MYC and either BCL2 or BCL6, and triple-hit lymphomas involving the translocation of MYC, BCL2, and BCL6, have a poor prognosis in DLBCL. R-CHOP therapy alone may prove inadequate in the treatment of these aggressive lymphomas.5 Although DA-EPOCH-R therapy has demonstrated efficacy in treating primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma, a DLBCL subtype, it has not proven useful in treating DLBCL and is not a typical form of treatment.6,7 Retrospective studies indicate that DA-EPOCH-R therapy is a valuable treatment option for double-hit lymphoma.8 Although fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis was not conducted due to the limited sample size, high expression of MYC and BCL2 proteins led us to initiate DA-EPOCH-R therapy due to the aggressiveness of the lymphoma. Finally, the patient achieved CR. The median survival period for primary cardiac malignant lymphoma is 12 months, and factors associated with poor prognosis include immune status, left ventricular involvement, presence of extracardiac disease, and arrhythmia.9 It has been suggested that cases lacking these poor prognostic factors or those treated with chemotherapy may have a better long-term prognosis. This case did not exhibit such poor prognostic factors, and because chemotherapy led to CR, it was thought that long-term survival could be expected.
Conclusions
We experienced a case in which DLBCL caused by cardiac tamponade was diagnosed, treated, and improved. Early detection and intervention are critical for primary cardiac lymphoma, which carries a poor prognosis.
Funding Support and Author Disclosures
The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Footnotes
The authors attest they are in compliance with human studies committees and animal welfare regulations of the authors’ institutions and Food and Drug Administration guidelines, including patient consent where appropriate. For more information, visit the Author Center.
Appendix
For supplemental videos, please see the online version of this paper.
Appendix
Video of Figure 1A
This transthoracic echocardiographic parasternal video revealed a mobile mass occupying most the right atrium and protruding into the right ventricle, with pericardial effusion.
Video of Figure 1B
This transthoracic echocardiographic apical video revealed a mobile mass occupying most of the right atrium and protruding into the right ventricle, with pericardial effusion.
Video of Figures 6A and 6B
This transthoracic echocardiographic parasternal video showed resolution of the pericardial effusion and preserved left ventricular systolic function.
Video of Figure 6C
This transthoracic echocardiographic parasternal video demonstrated a reduction in the size of the right atrial mass.
Video of Figure 6C
This transthoracic echocardiographic apical video demonstrated a reduction in the size of the right atrial mass.
References
- 1.Patel J., Melly L., SheppardAnn M.N. Primary cardiac lymphoma: B- and T-cell cases at a specialist UK centre. Ann Oncol. 2010;21:1041–1045. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdp424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Petrich A., Cho A.I., Billett H. Primary cardiac lymphoma: an analysis of presentation, treatment, and outcome patterns. Cancer. 2011;117:581–589. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yin K., Brydges H., Lawrence K.W., et al. Primary cardiac lymphoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022;164:573–580.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2020.09.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Coiffier B., Lepage E., Briere J., et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:235–242. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa011795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dunleavy K. Double-hit lymphomas: current paradigms and novel treatment approaches. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2014;2014:107–112. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2014.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dunleavy K., Pittaluga S., Maeda L.S., et al. Dose-adjusted EPOCH-rituximab therapy in primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:1408–1416. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1214561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bartlett N.L., Wilson W.H., Jung S., et al. Dose-adjusted EPOCH-R compared with R-CHOP as frontline therapy for diffuse large b-cell lymphoma: clinical outcomes of the phase III intergroup trial alliance/CALGB 50303. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37:1790–1799. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.01994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Petrich A.M., Gandhi M., Jovanovic B., et al. Impact of induction regimen and stem cell transplantation on outcomes in double-hit lymphoma: a multicenter retrospective analysis. Blood. 2014;124:2354–2361. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-05-578963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Petrich A., Cho S.I., Billett H. Primary cardiac lymphoma: an analysis of presentation, treatment, and outcome patterns. Cancer. 2011;117:581–589. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Video of Figure 1A
This transthoracic echocardiographic parasternal video revealed a mobile mass occupying most the right atrium and protruding into the right ventricle, with pericardial effusion.
Video of Figure 1B
This transthoracic echocardiographic apical video revealed a mobile mass occupying most of the right atrium and protruding into the right ventricle, with pericardial effusion.
Video of Figures 6A and 6B
This transthoracic echocardiographic parasternal video showed resolution of the pericardial effusion and preserved left ventricular systolic function.
Video of Figure 6C
This transthoracic echocardiographic parasternal video demonstrated a reduction in the size of the right atrial mass.
Video of Figure 6C
This transthoracic echocardiographic apical video demonstrated a reduction in the size of the right atrial mass.