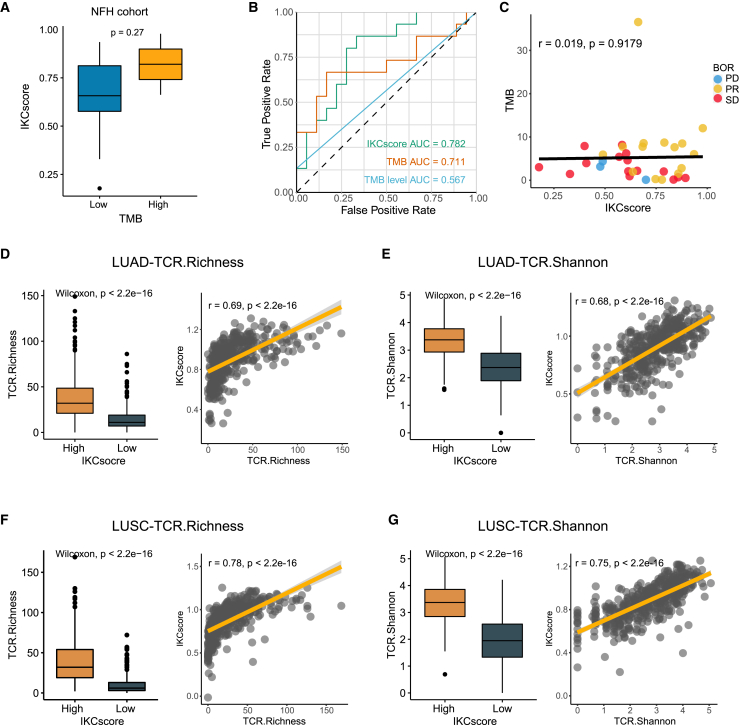
Figure 4.
Comparison and associations of TMB and TCR diversity with IKCscore
(A) Boxplot depicted IKCscore level in high TMB and low TMB groups (Wilcoxon test, p = 0.27).
(B) Comparison of ROC curves of IKCscore, continuous TMB, and TMB group (cutoff = 10 mut/Mb) in patients who owned TMB results (AUC = 0.782, 0.711, 0.567, respectively).
(C) Scatterplots showed that the IKCscore and TMB were irrelevant in the NFH cohort (Spearman test, r = 0.019, p = 0.9179). The dotted color indicates the different responses (PR: yellow; SD: red; PD: blue).
(D and E) TCR richness (D) and TCR Shannon (E) was positively associated with IKCscore in TCGA-LUAD (TCR.Richness: Wilcoxon test, p < 2.2e−16; Spearman test, r = 0.69, p < 2.2e-16; TCR.Shannon: Wilcoxon test, p < 2.2e−16; Spearman test, r = 0.68, p < 2.2e-16).
(F and G) TCR richness (F) and TCR Shannon (G) was positively associated with IKCscore in TCGA-LUSC (TCR.Richness: Wilcoxon test, p < 2.2e−16; Spearman test, r = 0.78, p < 2.2e-16; TCR.Shannon: Wilcoxon test, p < 2.2e−16; Spearman test, r = 0.75, p < 2.2e-16). TMB, Tumor mutation burden; TCR, T cell receptors.