Abstract
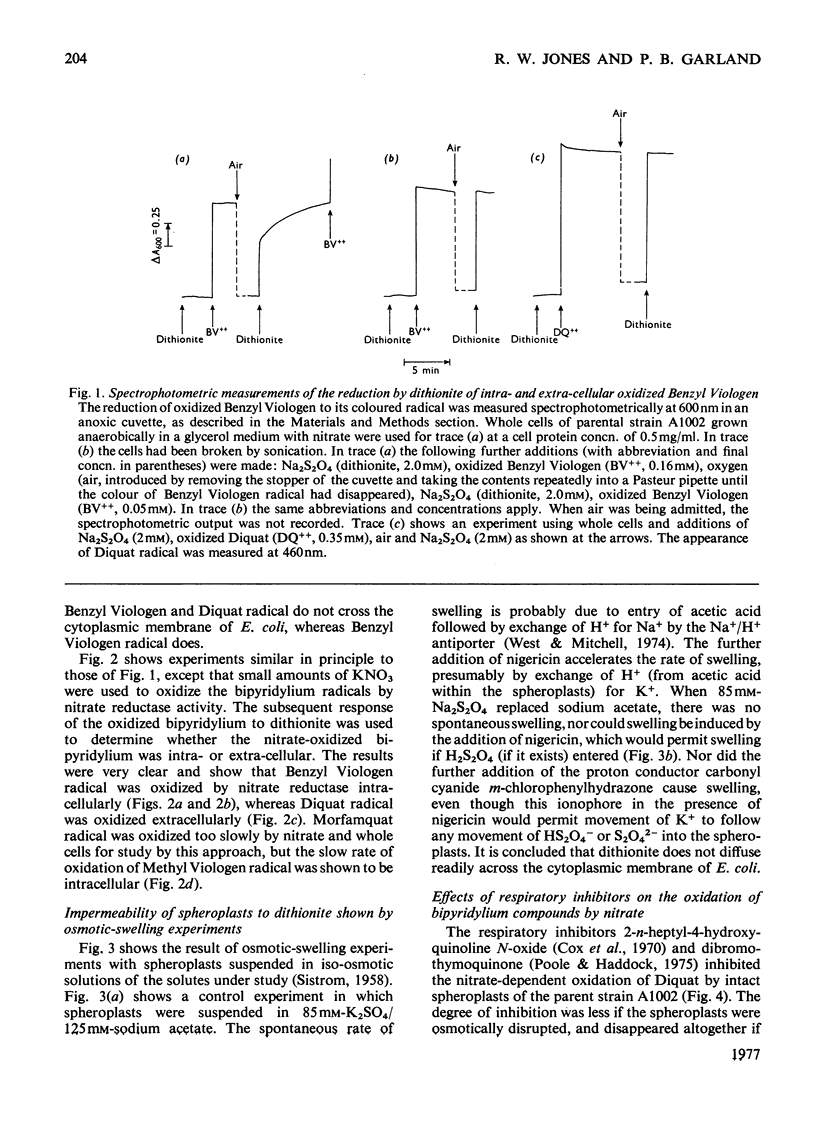
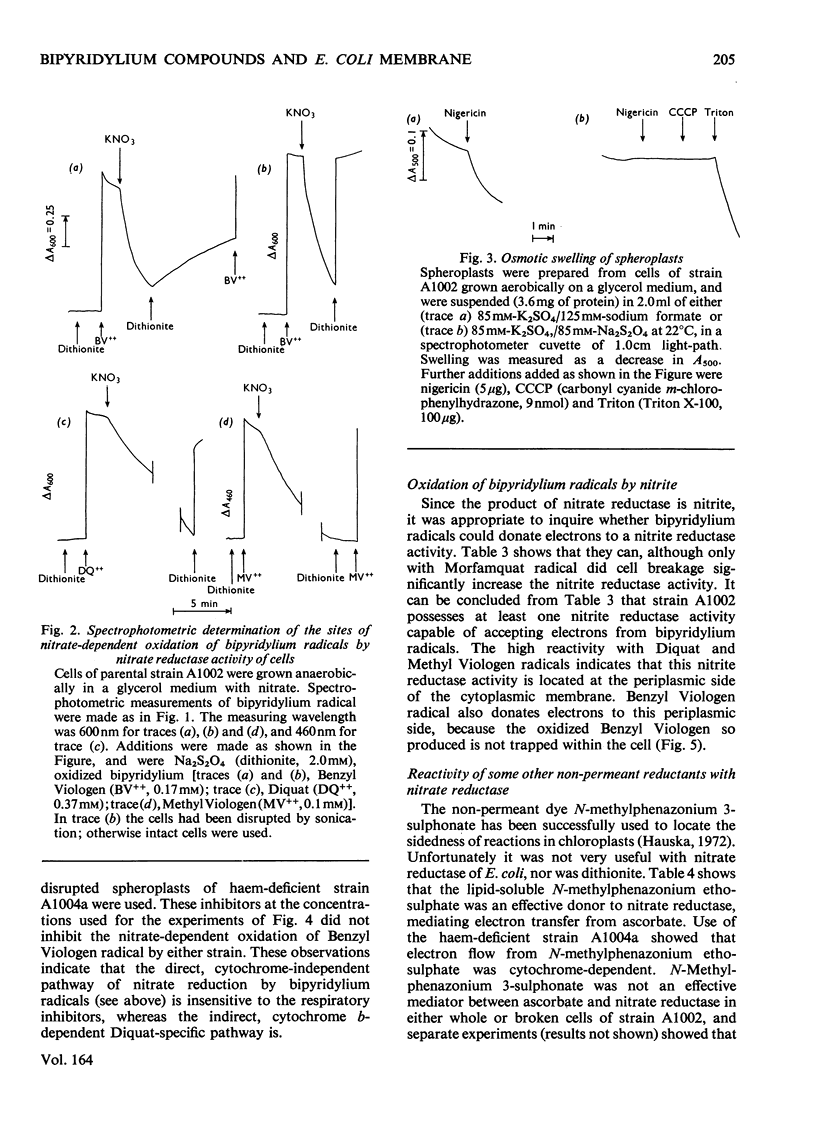
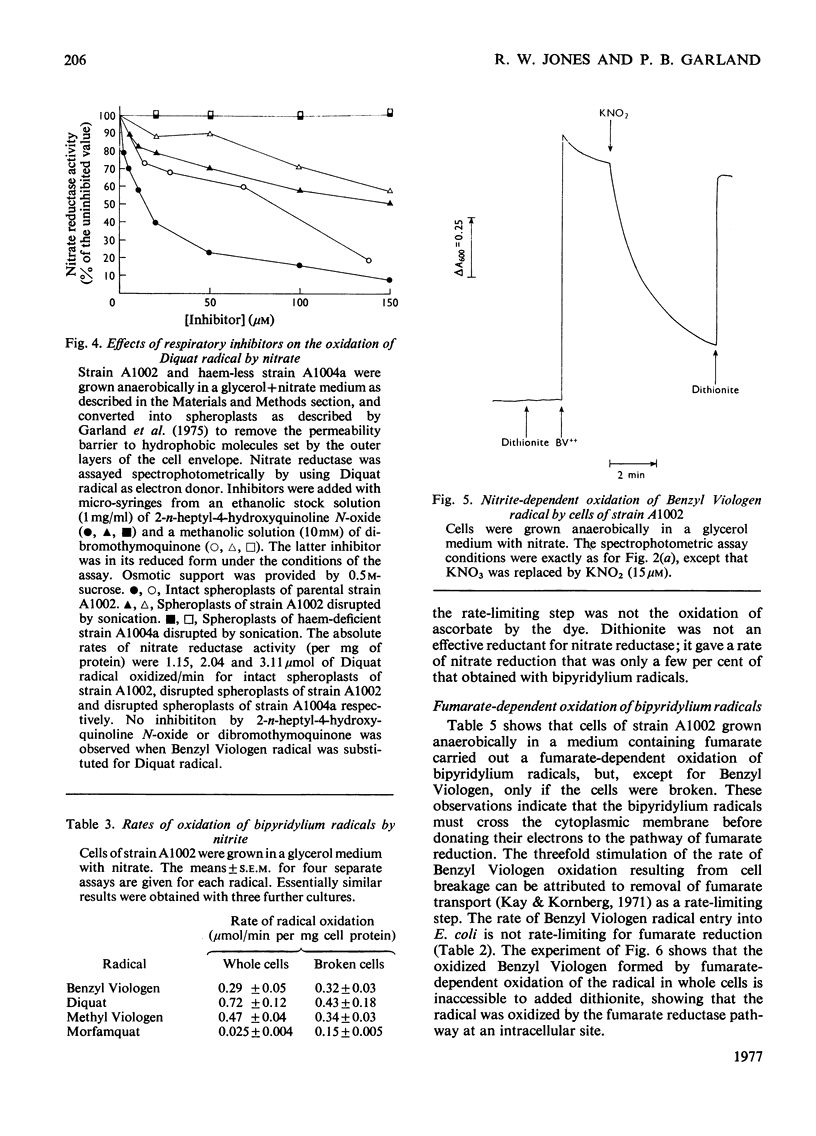
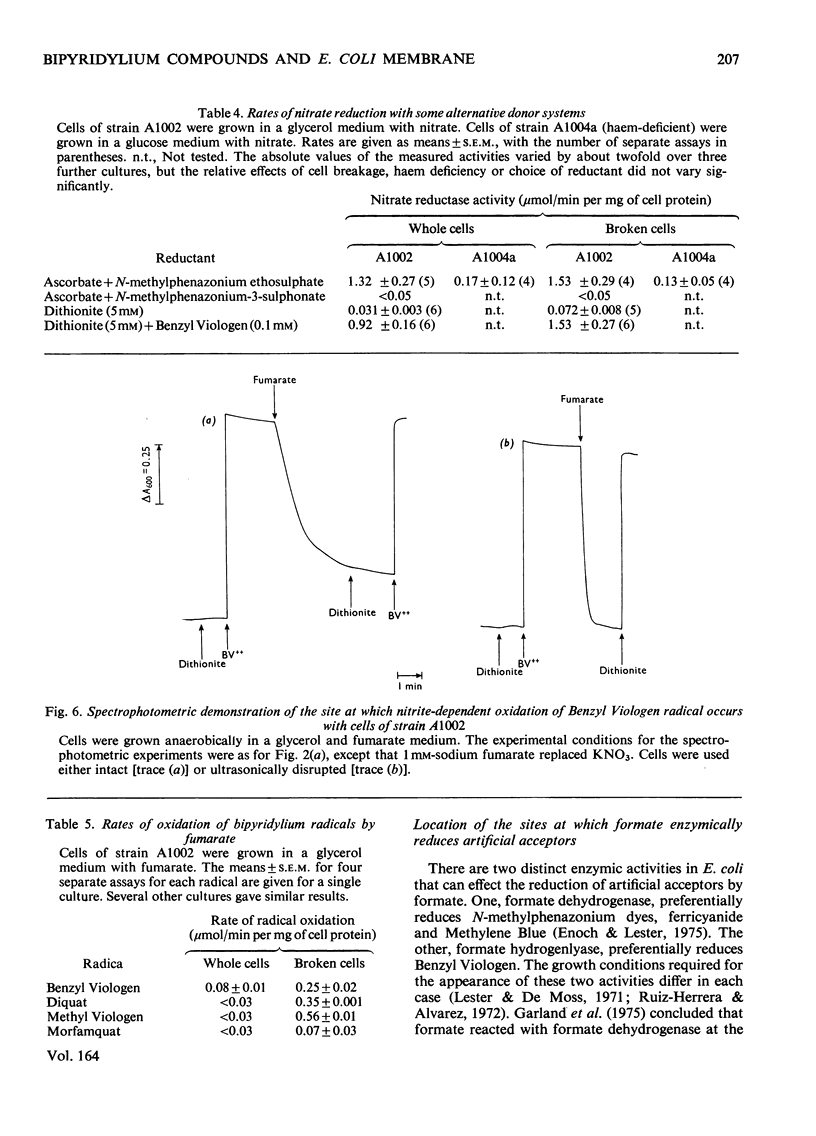
The ability of the oxidized and singly reduced species of several bipyridylium cations to cross the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli was studied to locate the sites of reaction of the dyes with anaerobic respiratory enzymes. Benzyl Viologen radical crossed the membrane rapidly, whereas the oxidized species did not. The oxidized or radical species of Methyl Viologen, Morfamquat or Diquat did not rapidly cross the membrane. It was also shown that the dithionite anion does not cross the cytoplasmic membrane of E. coli. Diquat radical donates electrons to the nitrate reductase pathway at the periplasmic aspect of the membrane, whereas Benzyl Viologen radical reacted directly with nitrate reductase itself (EC 1.7.99.4) at the cytoplasmic aspect of the membrane. Thus the pathway of electron transfer in the nitrate reductase pathway is transmembranous. Formate hydrogenlyase (EC 1.2.1.2) and an uncharacterized nitrite reductase activity react with bipyridylium dyes at the periplasmic aspect of the membrane. Fumarate reductase (succinate dehydrogenase; EC 1.3.99.1) reacts with bipyridylium radicals, and formate dehydrogenase (cytochrome) (EC 1.2.2.1) with ferricyanide, at the cytoplasmic aspect of the membrane. The differing charge and membrane permeation of oxidized and radical species of bipyridylium dyes greatly complicate their use as potentiometric mediators in suspensions of cells or membrane vesicles.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. S., Lyle I. G., Paterson R. Electron transfer across membranes using vitamin K1 and coenzyme Q10 as carrier molecules. Nature. 1976 Jan 15;259(5539):147–148. doi: 10.1038/259147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer D. H., Clegg R. A. A transmembrane location for the proton-translocating reduced ubiquinone leads to nitrate reductase segment of the respiration chain of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):54–57. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80417-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., RICKENBERG H. V. Concentration spécifique réversible des amino acides chez Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Nov;91(5):693–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. B., Newton N. A., Gibson F., Snoswell A. M., Hamilton J. A. The function of ubiquinone in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(3):551–562. doi: 10.1042/bj1170551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton M., Palmieri F., Capano M., Quagliariello E. The transport of sulphate and sulphite in rat liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1974 Jul;142(1):127–137. doi: 10.1042/bj1420127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton M., Palmieri F., Capano M., Quagliariello E. The transport of thiosulphate in rat liver mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 15;46(1):247–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80379-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge A. D. The mode of action of the bipyridylium herbicides, paraquat and diquat. Endeavour. 1971 Sep;30(111):130–135. doi: 10.1016/0160-9327(71)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton P. L., Wilson D. F. Redox potentiometry in mitochondrial and photosynthetic bioenergetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 31;346(2):165–212. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(74)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch H. G., Lester R. L. The purification and properties of formate dehydrogenase and nitrate reductase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6693–6705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futai M. Orientation of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli prepared by different procedures. J Membr Biol. 1974;15(1):15–28. doi: 10.1007/BF01870079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage J. C. The action of paraquat and diquat on the respiration of liver cell fractions. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):757–761. doi: 10.1042/bj1090757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland P. B., Downie J. A., Haddock B. A. Proton translocation and the respiratory nitrate reductase of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;152(3):547–559. doi: 10.1042/bj1520547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddock B. A. The reconstitution of oxidase activity in membranes derived from a 5-aminolaevulinic acid-requiring mutant of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;136(4):877–884. doi: 10.1042/bj1360877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauska G. Lipophilicity and catalysis of photophosphorylation I Sulfonated phenazonium compounds are ineffective in mediating cyclic photophosphorylation in photosystem-I-subchloroplast vesicles. FEBS Lett. 1972 Dec 1;28(2):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80716-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauska G., Reimer S., Trebst A. Native and artificial energy-conserving sites in cyclic photophosphorylation systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 25;357(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. W., Gray T. A., Garland P. B. A study of the permeability of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli to reduced and oxidized benzyl viologen and methyl viologen cations: complications in the use of viologens as redox mediators for membrane-bound enzymes. Biochem Soc Trans. 1976;4(4):671–673. doi: 10.1042/bst0040671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R. L., DeMoss J. A. Effects of molybdate and selenite on formate and nitrate metabolism in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1006–1014. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1006-1014.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor C. H. Anaerobic cytochrome b1 in Escherichia coli: association with and regulation of nitrate reductase. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1111–1116. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1111-1116.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton N. A., Cox G. B., Gibson F. The function of menaquinone (vitamin K 2 ) in Escherichia coli K-12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 20;244(1):155–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90132-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole R. K., Haddock B. A. Dibromothymoquinone : an inhibitor of aerobic electron transport at the level of ubiquinone in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1975 Mar 15;52(1):13–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80626-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SISTROM W. R. On the physical state of the intracellularly accumulates substrates of beta-galactoside-permease in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Sep;29(3):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha S., Ouitrakul R., Izawa S., Good N. E. Electron transport and photophosphorylation in chloroplasts as a function of the electron acceptor. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3204–3209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Synthesis and sideedness of membrane-bound respiratory nitrate reductase (EC1.7.99.4) in Escherichia coli lacking cytochromes. Biochem J. 1975 May;148(2):329–333. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorneley R. N. A convenient electrochemical preparation of reduced methyl viologen and a kinetic study of the reaction with oxygen using an anaerobic stopped-flow apparatus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 26;333(3):487–496. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90133-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner J. H. The localization of glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli. J Membr Biol. 1974;15(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01870078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I. C., Mitchell P. Proton/sodium ion antiport in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;144(1):87–90. doi: 10.1042/bj1440087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


