Abstract
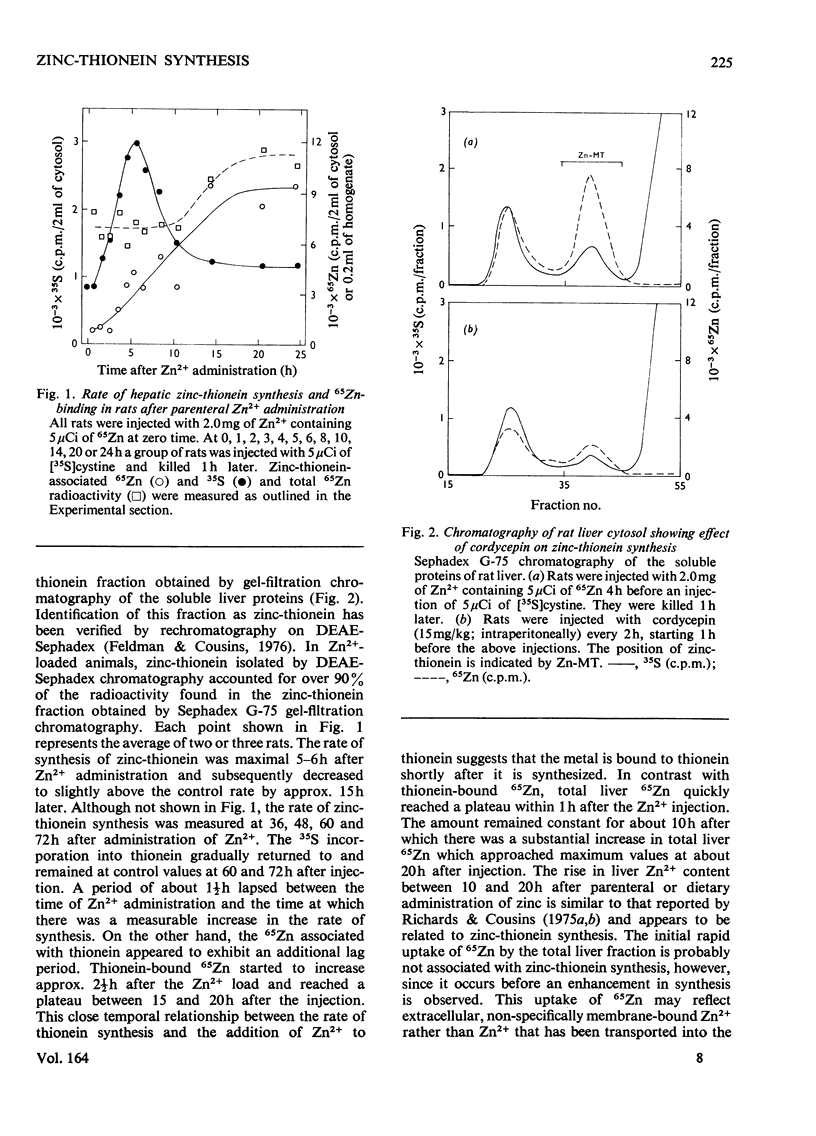
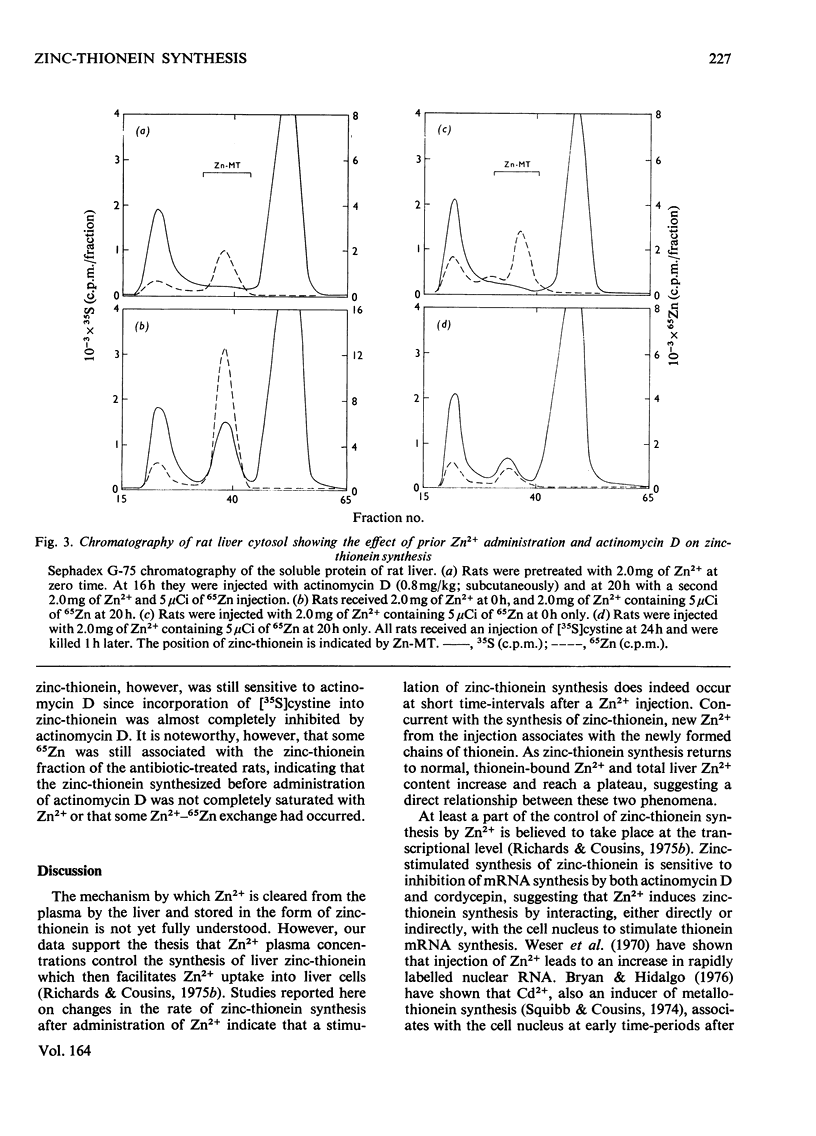
The rate of [35S]cystine incorporation into hepatic zinc-thionein (a metallothionein) was stimulated, with a maximum of 5-6h, after parenteral administration of 2mg of Zn2+ containing 65Zn. The binding of 65Zn to zinc-thionein was measurable by 2-1/2h and reached a plateau by 18h after the injection. A net increase in the hepatic 65Zn content was observed subsequent to the decrease in the rate of zinc-thionein synthesis. The incorporation of both 65Zn and [35S]cystine into zinc-thionein was inhibited by prior administration of either actinomycin D or cordycepin. A second injection of Zn2+, 20h after the initial injection, yielded a 4.9-fold greater increase in zinc-thionein synthesis compared with that after only one injection; however, this synthesis was also inhibitable by actinomycin D. These data support the concept that hepatic zinc-thionein synthesis responds quickly to changes in Zn2+ status and that Zn2+ is bound subsequent to synthesis of nascent thionein chains. The mechanism of control of zinc-thionein synthesis by Zn2+ appears to involve changes in the amounts of a short-lived, poly(A)-containing RNA whose translation can be derepressed by additional exposure to Zn2+.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bremner I., Young B. W. Isolation of (copper, zinc)-thioneins from the livers of copper-injected rats. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):517–520. doi: 10.1042/bj1570517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan S. E., Hidalgo H. A. Nuclear 115cadmium: uptake and disappearance correlated with cadmium-binding protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 9;68(3):858–866. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91224-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. W., Whanger P. D., Weswig P. H. Biological function of metallothionein. I. Synthesis and degradation of rat liver metallothionein. Biochem Med. 1975 Feb;12(2):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(75)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousins R. J., Wynveen R. A., Squibb K. S., Richards M. P. Double label counting of metal nuclides with 3H or 14C by liquid scintillation counting. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 12;65(1-2):412–417. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90526-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Philipson L., Wall R., Adesnik M. Polyadenylic acid sequences: role in conversion of nuclear RNA into messenger RNA. Science. 1971 Oct 29;174(4008):507–510. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4008.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman S. L., Cousins R. J. Degradation of hepatic zinc-thionein after parenteral zinc administration. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 15;160(3):583–588. doi: 10.1042/bj1600583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosky L., Roberts B., Jr, O'Dell R. G., Imblum R. L. Differential effects of actinomycin D on nucleic acid and protein synthesis in rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Aug;126(2):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90423-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards M. P., Cousins R. J. Influence of parenteral zinc and actinomycin D on tissue zinc uptake and the synthesis of a zinc - binding protein. Bioinorg Chem. 1975 Apr;4(3):215–224. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3061(00)80104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards M. P., Cousins R. J. Mammalian zinc homeostasis: requirement for RNA and metallothionein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jun 16;64(4):1215–1223. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90822-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards M. P., Cousins R. J. Metallothionein and its relationship to the metabolism of dietary zinc in rats. J Nutr. 1976 Nov;106(11):1591–1599. doi: 10.1093/jn/106.11.1591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards M. P., Cousins R. J. Zinc-binding protein: relationship to short term changes in zinc metabolism. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Oct;153(1):52–56. doi: 10.3181/00379727-153-39479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squibb K. S., Cousins R. J. Control of cadmium binding protein synthesis in rat liver. Environ Physiol Biochem. 1974;4(1):24–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squibb K. S., Cousins R. J., Silbon B. L., Levin S. Liver and intestinal metallothionein: function in acute cadmium toxicity. Exp Mol Pathol. 1976 Oct;25(2):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(76)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb M. Binding of cadmium ions by rat liver and kidney. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Oct 15;21(20):2751–2765. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb M., Verschoyle R. D. An investigation of the role of metallothioneins in protection against the acute toxicity of the cadmium ion. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Mar 15;25(6):673–679. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weser U., Hübner L., Jung H. Zn(2+)-Induced stimulation of nuclear RNA synthesis in rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1970 May 1;7(4):356–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80205-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winge D. R., Premakumar R., Rajagopalan K. V. Metal-induced formation of metallothionein in rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Sep;170(1):242–252. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zähringer J., Baliga B. S., Munro H. N. Novel mechanism for translational control in regulation of ferritin synthesis by iron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):857–861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


