Abstract
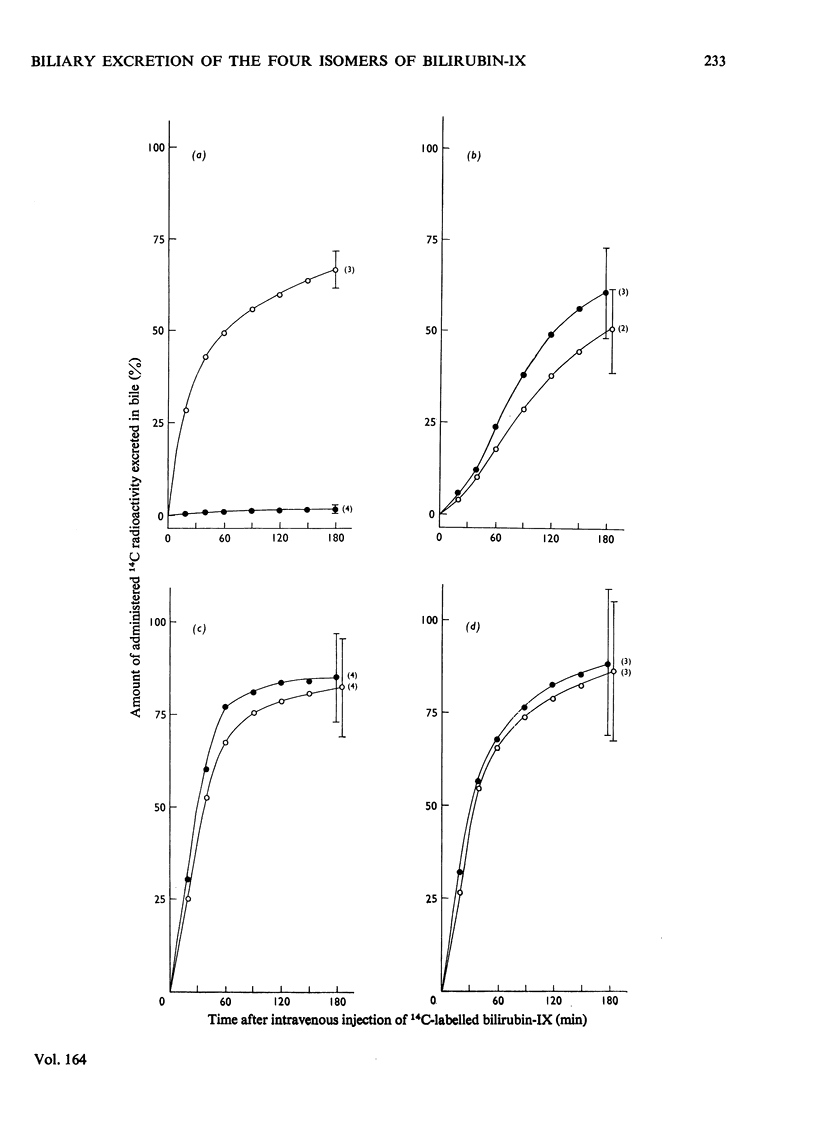
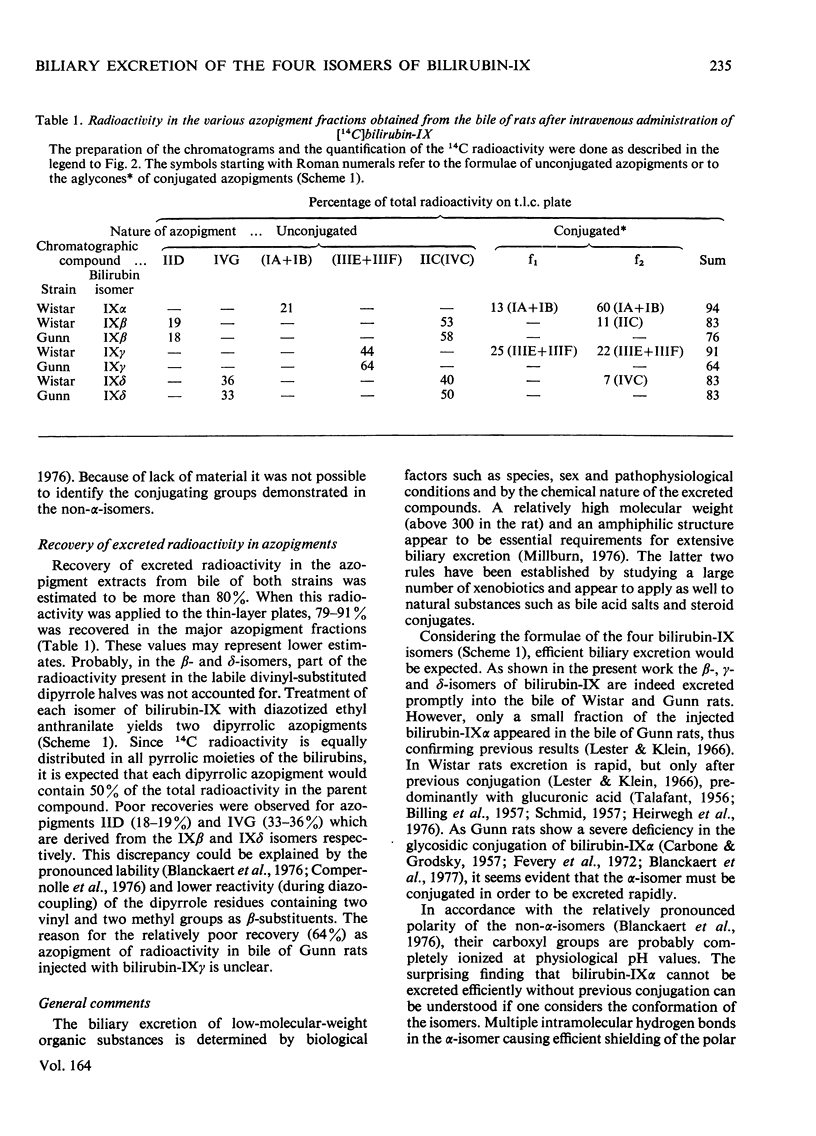
The biliary excretion of the four isomers of bilirubin-IX was studied in Wistar rats (JJ) and homozygous Gunn rats (jj). Synthetic preparations of 14C-labelled pigments were used. 1. After intravenous administration, the alpha-isomer was rapidly excreted in conjugated form in bile of Wistar rats. In Gunn rats excretion was insignificant. In contrast, both rat species promptly excreted the non-alpha-isomers at rates that were comparable with that found for bilirubin-IXalpha in Wistar rats. 2. In normal rats about 16% of the beta- and delta-isomers and at least 50% of the gamma-isomer were excreted as ester conjugates of the injected parent bile pigments. Conjugation of the beta- and delta-isomers had occurred exclusively at the carboxyl groups of pyrrole ring D and C respectively. For bilirubin-IXgamma no preference for any carboxyl group could be established. 3. In homozygous Gunn rats the non-alpha-isomers were apparently excreted chemically unaltered. This suggests that, as for bilirubin-IXalpha, conjugation of the non-alpha-isomers is also deficient in Gunn rats.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BILLING B. H., COLE P. G., LATHE G. H. The excretion of bilirubin as a diglucuronide giving the direct van den Bergh reaction. Biochem J. 1957 Apr;65(4):774–784. doi: 10.1042/bj0650774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanckaert N., Fevery J., Heirwegh K. P., Compernolle F. Characterization of the major diazo-positive pigments in bile of homozygous Gunn rats. Biochem J. 1977 Apr 15;164(1):237–249. doi: 10.1042/bj1640237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
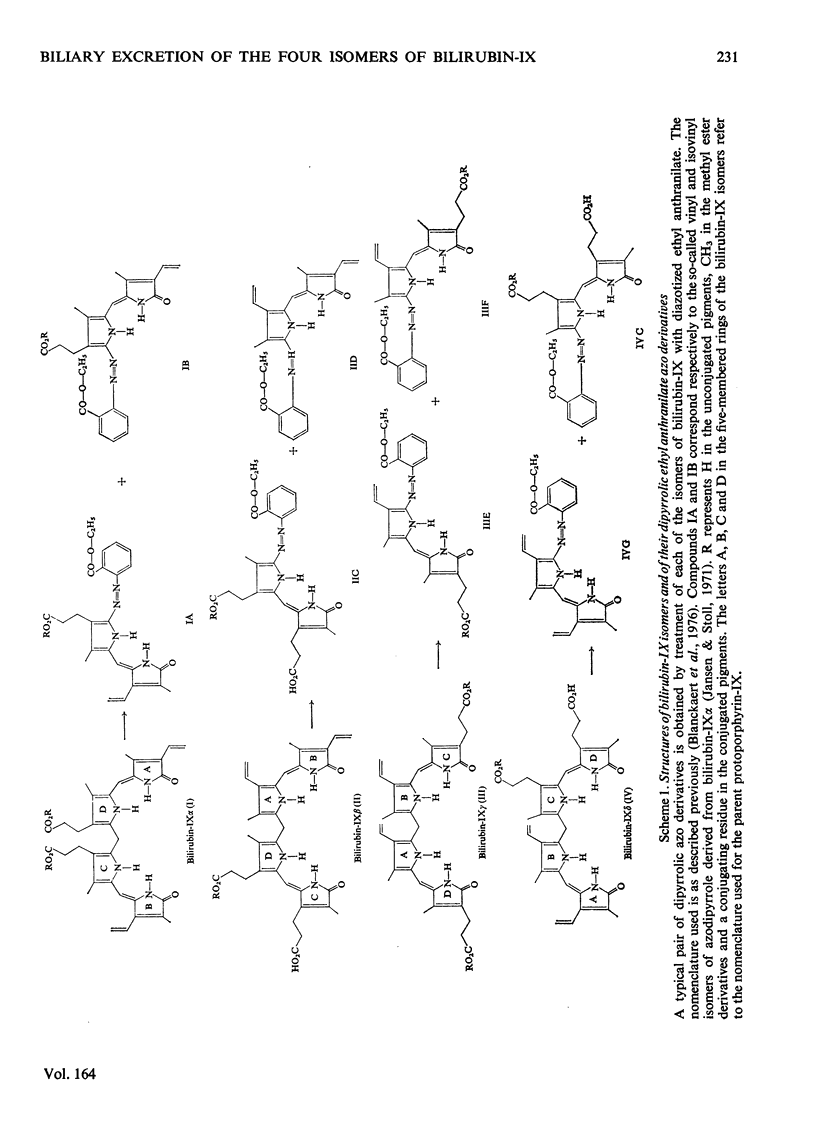
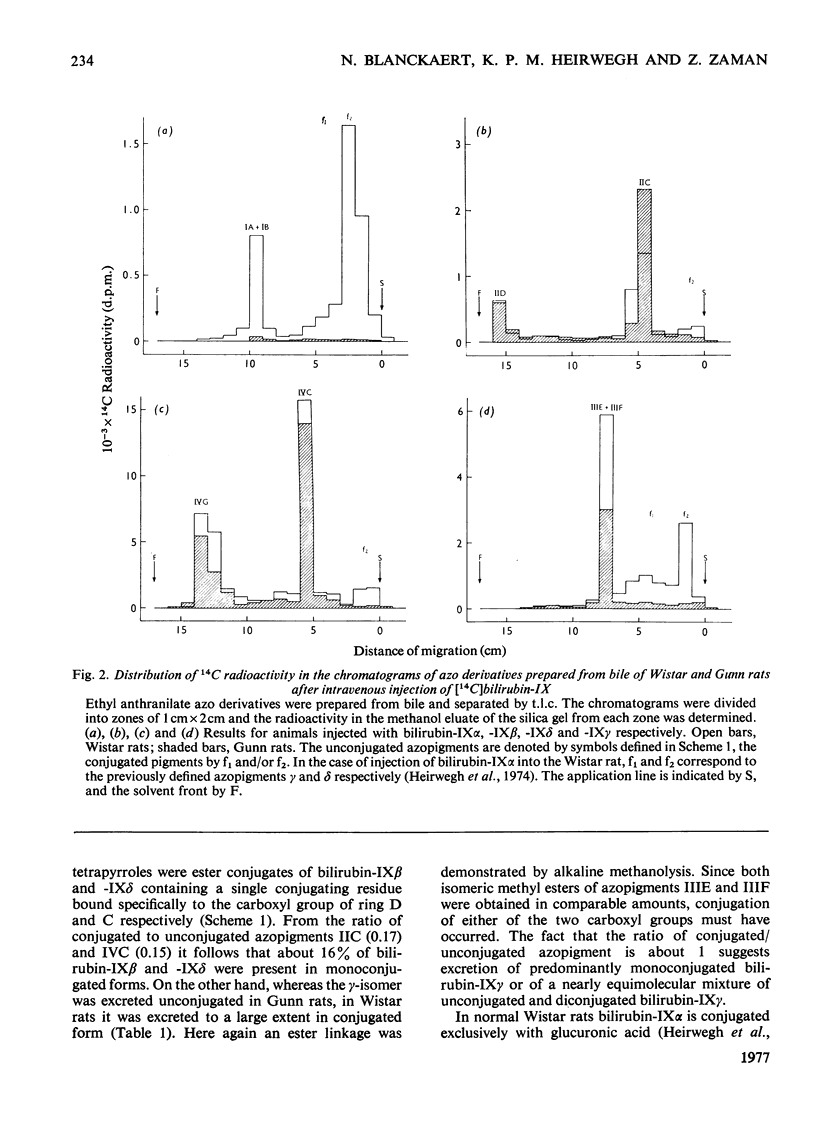
- Blanckaert N., Heirwegh K. P., Compernolle F. Synthesis and separation by thin-layer chromatography of bilirubin-IX isomers. Their identification as tetrapyrroles and dipyrrolic ethyl anthranilate azo derivatives. Biochem J. 1976 May 1;155(2):405–417. doi: 10.1042/bj1550405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blauer G., Harmatz D., Snir J. Optical properties of bilirubin-serum albumin complexes in aqueous solution. I. Dependence on pH. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 31;278(1):68–88. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnett R., Davies J. E., Hursthouse M. B. Structure of bilirubin. Nature. 1976 Jul 22;262(5566):327–328. doi: 10.1038/262326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARBONE J. V., GRODSKY G. M. Constitutional nonhemolytic hyperbilirubinemia in the rat: defect of bilirubin conjugation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Mar;94(3):461–463. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-22979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compernolle F., Blanckaert N., Heirwegh K. P. Mass spectral study of derivatives of the four bilirubin-IX isomers. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1976 Aug;3(4):155–160. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200030403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOG J. BILIRUBIN-PURIFICATION-PURITY. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1964;16:49–54. doi: 10.3109/00365516409060482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fevery J., Leroy P., Heirwegh K. P. Enzymic transfer of glucose and xylose from uridine diphosphate glucose and uridine diphosphate xylose to bilirubin by untreated and digitonin-activated preparations from rat liver. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(3):619–633. doi: 10.1042/bj1290619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray C. H., Nicholson D. C., Tipton G. Degradation of haem compounds to bile pigments. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 6;239(88):5–8. doi: 10.1038/newbio239005a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heirwegh K. P., Fevery J., Meuwissen J. A., De Groote J., Compernolle F., Desmet V., Van Roy F. P. Recent advances in the separation and analysis of diazo-positive bile pigments. Methods Biochem Anal. 1974;22:205–250. doi: 10.1002/9780470110423.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen F. H., Stoll M. S. Separation and structural analysis of vinyl- and isovinyl-azobilirubin derivatives. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(2):585–597. doi: 10.1042/bj1250585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzle C. C., Weibel M. H., Pelloni R. R., Hemmerich P. Structure and conformation of bilirubin. Opposing views that invoke tautomeric equilibria, hydrogen bonding and a betaine may be reconciled by a single resonance hybrid. Biochem J. 1973 Jun;133(2):364–368. doi: 10.1042/bj1330364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe G. H. The degradation of haem by mammals and its excretion as conjugated bilirubin. Essays Biochem. 1972;8:107–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R., Klein P. D. Bile pigment excretion: a comparison of the biliary excretion of bilirubin and bilirubin derivatives. J Clin Invest. 1966 Dec;45(12):1839–1846. doi: 10.1172/JCI105487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine W. G., Millburn P., Smith R. L., Williams R. T. The role of the hepatic endoplasmic reticulum in the biliary excretion of foreign compounds by the rat. The effect of phenobarbitone and SKF 525-A (diethylaminoethyl diphenylpropylacetate). Biochem Pharmacol. 1970 Jan;19(1):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(70)90344-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Carra P., Colleran E. Separation and identification of biliverdin isomers and isomer analysis of phycobilins and bilirubin. J Chromatogr. 1970 Aug 12;50(3):458–468. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)97973-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Máille E. R., Richards T. G., Short A. H. Acute taurine depletion and maximal rates of hepatic conjugation and secretion of cholic acid in the dog. J Physiol. 1965 Sep;180(1):67–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petryka Z. J. Identification of isomers differing from 9, alpha, in the early labelled bilirubin of the bile. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Nov;123(2):464–466. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. H., Yannoni C., Nagasawa S. Bilirubin excretion in rats with normal and impaired bilirubin conjugation: effect of phenobarbital. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2606–2613. doi: 10.1172/JCI106761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMID R., HAMMAKER L. METABOLISM AND DISPOSITION OF C14-BILIRUBIN IN CONGENITAL NONHEMOLYTIC JAUNDICE. J Clin Invest. 1963 Nov;42:1720–1734. doi: 10.1172/JCI104858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMID R. The identification of direct-reacting bilirubin as bilirubin glucuronide. J Biol Chem. 1957 Dec;229(2):881–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALAFANT E. Properties and composition of the bile pigment giving a direct diazo reaction. Nature. 1956 Aug 11;178(4528):312–312. doi: 10.1038/178312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaman Z., Akhtar M. Mechanism and stereochemistry of vinyl-group formation in haem biosynthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jan 2;61(1):215–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


