Abstract
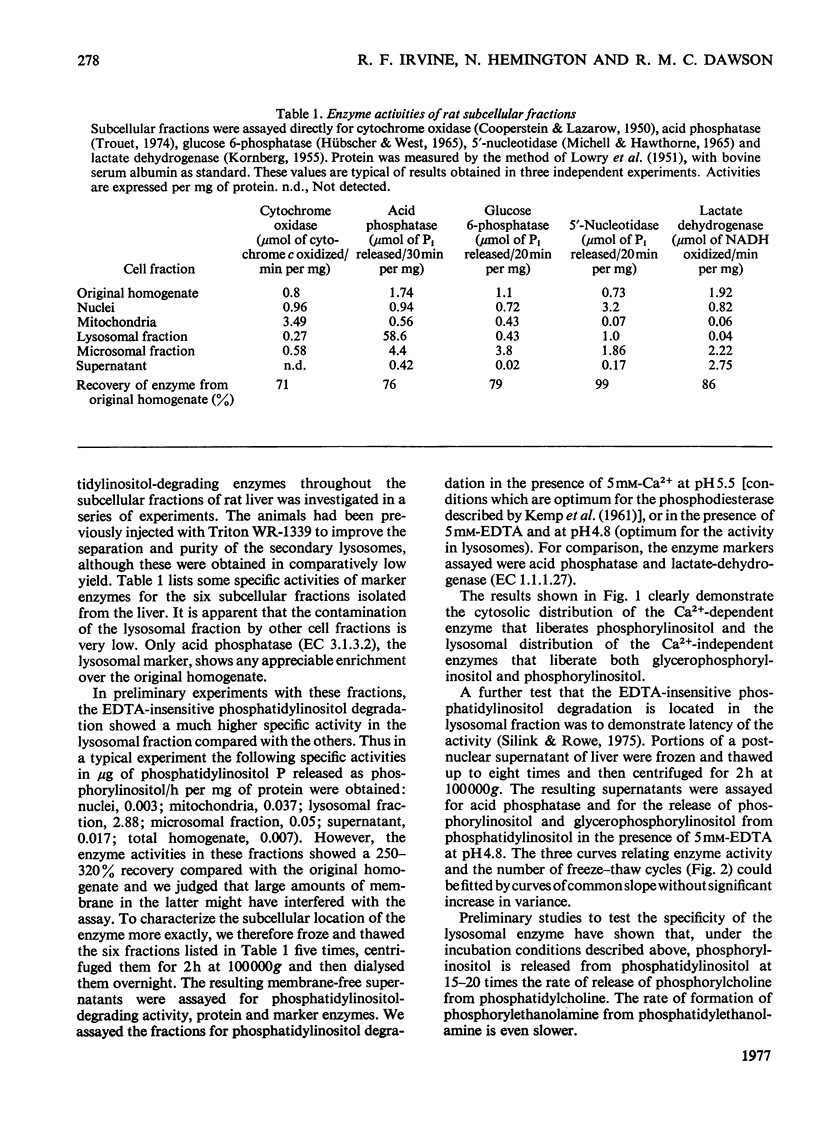
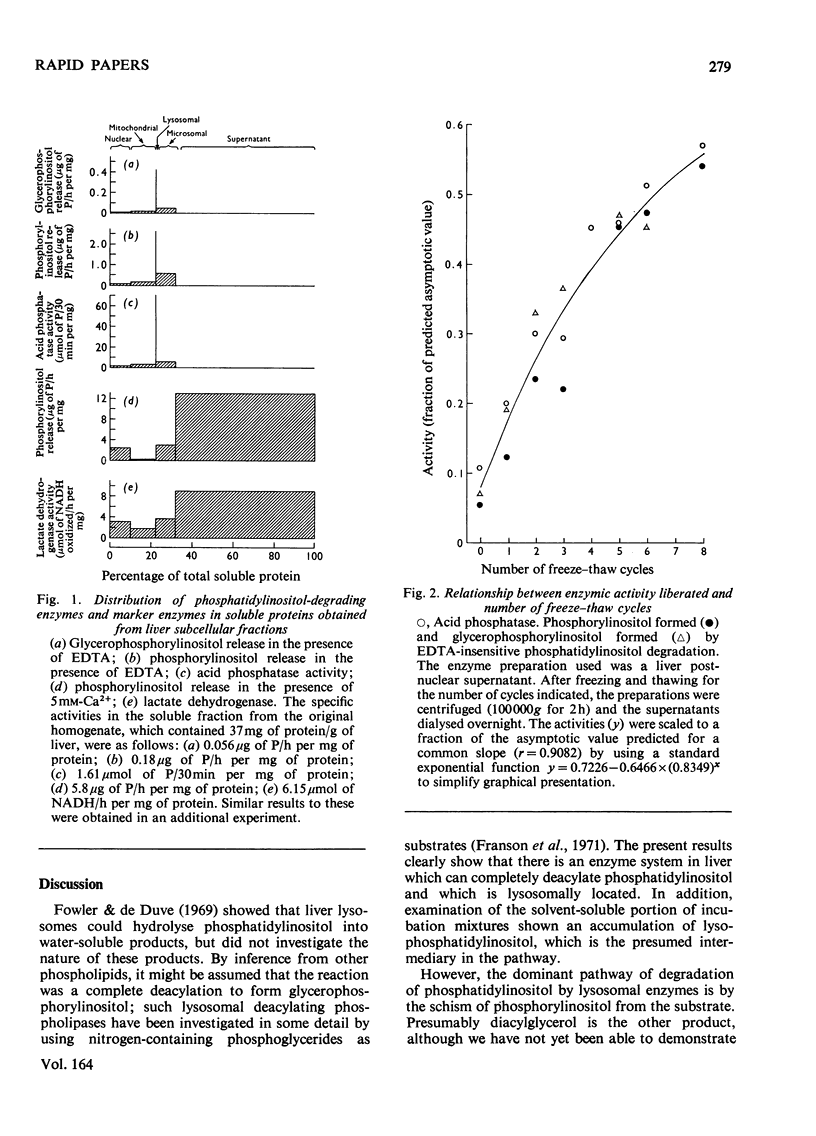
The major pathway by which liver lysosomal enzymes degrade phosphatidylinositol is through an EDTA-insensitive formation of phosphorylinositol. This is in distinct contrast with the Ca2+-dependent production of phosphorylinositol from phosphatidylinositol, which is located in the cytosol. Lysosomal enzymes can also totally deacylate phosphatidylinositol, producing glycerophosphorylinositol.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COOPERSTEIN S. J., LAZAROW A. A microspectrophotometric method for the determination of cytochrome oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1951 Apr;189(2):665–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. Studies on the enzymic hydrolysis of monophosphoinositide by phospholipase preparations from P. notatum and ox pancreas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 May;33(1):68–77. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90499-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Clarke N. D-myoinositol 1:2-cyclic phosphate 2-phosphohydrolase. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):113–118. doi: 10.1042/bj1270113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Freinkel N., Jungalwala F. B., Clarke N. The enzymic formation of myoinositol 1:2-cyclic phosphate from phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):605–607. doi: 10.1042/bj1220605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Hemington N. A phosphodiesterase in rat kidney cortex that hydrolyses glycerylphosphorylinositol. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 15;162(2):241–245. doi: 10.1042/bj1620241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler S., De Duve C. Digestive activity of lysosomes. 3. The digestion of lipids by extracts of rat liver lysosomes. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 25;244(2):471–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franson R., Waite M., LaVia M. Identification of phospholipase A 1 and A 2 in the soluble fraction of rat liver lysosomes. Biochemistry. 1971 May 11;10(10):1942–1946. doi: 10.1021/bi00786a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUEBSCHER G., WEST G. R. SPECIFIC ASSAYS OF SOME PHOSPHATASES IN SUBCELLULAR FRACTIONS OF SMALL INTESTINAL MUCOSA. Nature. 1965 Feb 20;205:799–800. doi: 10.1038/205799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayase K., Tappel A. L. Specificity and other properties of lysosomal lipase of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 10;245(1):169–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin-Neaverson M. Acetylcholine causes a net decrease in phosphatidylinositol and a net increase in phosphatidic acid in mouse pancreas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jun 4;58(3):763–768. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80483-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin L. E. Dynamic aspects of phospholipids during protein secretion. Int Rev Cytol. 1968;23:187–208. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jafferji S. S., Michell R. H. Effects of calcium-antagonistic drugs on the stimulation by carbamoylcholine and histamine of phosphatidylinositol turnover in longitudinal smooth muscle of guinea-pig ileum. Biochem J. 1976 Nov 15;160(2):163–169. doi: 10.1042/bj1600163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Michell R. H. Breakdown of phosphatidylinositol provoked by muscarinic cholinergic stimulation of rat parotid-gland fragments. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):583–590. doi: 10.1042/bj1420583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Michell R. H. The relationship of calcium to receptor-controlled stimulation of phosphatidylinositol turnover. Effects of acetylcholine, adrenaline, calcium ions, cinchocaine and a bivalent cation ionophore on rat parotid-gland fragments. Biochem J. 1975 Jun;148(3):479–485. doi: 10.1042/bj1480479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEMP P., HUBSCHER G., HAWTHORNE J. N. Phosphoinositides. 3. Enzymic hydrolysis of inositol-containing phospholipids. Biochem J. 1961 Apr;79:193–200. doi: 10.1042/bj0790193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kariya M., Kaplan A. Effects of acidic phospholipids, nucleotides, and heparin on the activity of lipase from rat liver lysosomes. J Lipid Res. 1973 Mar;14(2):243–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Michell R. H. A membrane-bound activity catalysing phosphatidylinositol breakdown to 1,2-diacylglycerol, D-myoinositol 1:2-cyclic phosphate an D-myoinositol 1-phosphate. Properties and subcellular distribution in rat cerebral cortex. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;131(3):433–442. doi: 10.1042/bj1310433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Hawthorne J. N. The site of diphosphoinositide synthesis in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Nov 22;21(4):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oron Y., Löwe M., Selinger Z. Incorporation of inorganic [32P] phosphate into rat parotid phosphatidylinositol. Induction through activation of alpha adrenergic and cholinergic receptors and relation to K+ release. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 Jan;11(1):79–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silink M., Rowe P. B. The localization of glutamate carboxypeptidase in rat liver lysosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 13;381(1):28–36. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90186-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trouet A. Isolation of modified liver lysosomes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:323–329. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


