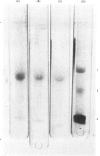
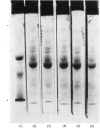
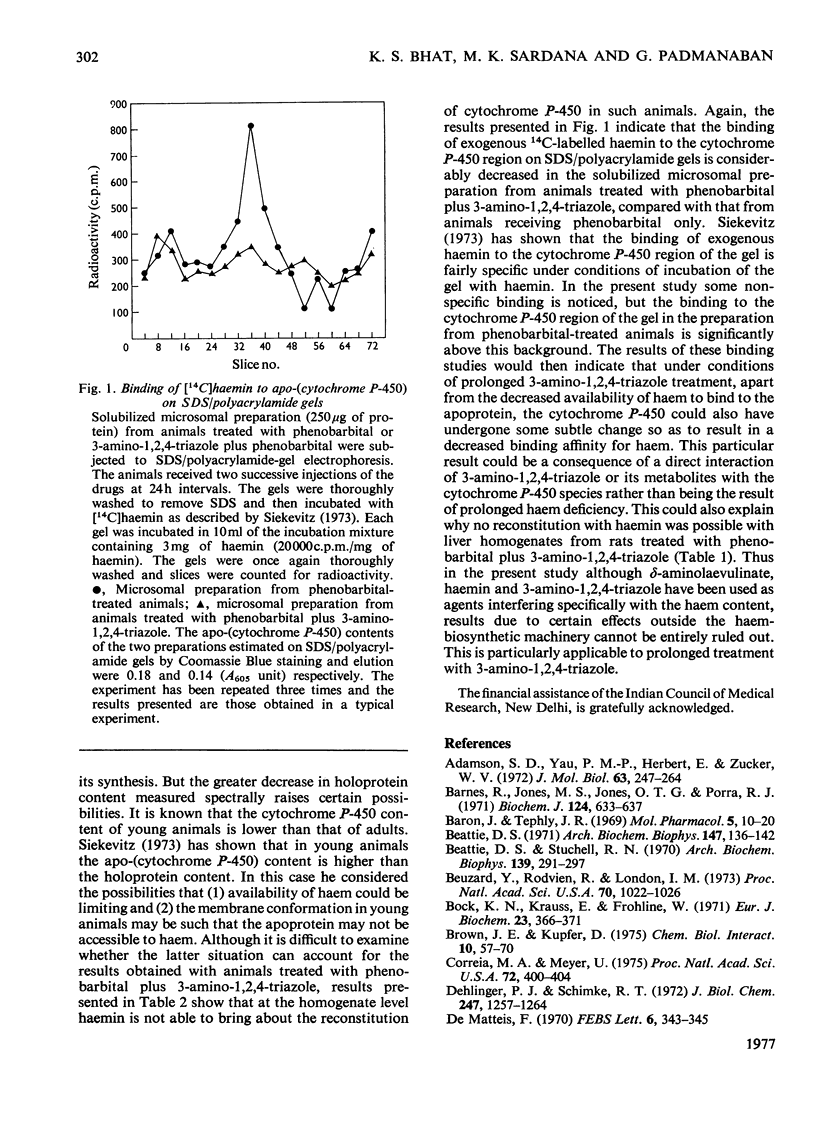
Abstract
By using 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole, an inhibitor of haem synthesis, and 2-allyl-2-isopropylacetamide, a drug that degrades the haem moiety of cytochrome P-450, the involvement of haem in cytochrome P-450 synthesis and assembly was investigated. Phenobarbital was used to stimulate apo-(cytochrome P-450) synthesis. Degradation of preformed cytochrome P-450 haem does not result in a concomitant release of the apoprotein from the endoplasmic reticulum. The availability of haem for cytochrome P-450 synthesis in the normal animal is not rate-limiting. Prolonged inhibition of haem synthesis in vivo decreases the rate of apo-(cytochrome P-450) synthesis, although this effect is not discernible under conditions of short-term inhibition of haem synthesis. Under the former conditions exogenous haemin is able to counteract the decrease in the rate of apoprotein synthesis. In animals receiving successive injections of phenobarbital plus 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole, compared with those receiving phenobarbital only, the holo-(cytochrome P-450) content measured spectrally shows a greater decrease than could be accounted for by the decrease in the content of the total apoprotein. In addition to less haem being available under these conditions, the free apoprotein appears to have undergone some modification, such that its haem-binding capacity is considerably decreased. This particular effect could be due to a direct interaction of 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole or its metabolites with cytochrome P-450 rather than a consequence of haem deficiency. Apo-(cytochrome P-450) is capable of binding to the endoplasmic reticulum in a form and at a site, which can be reconstituted with haemin to yield the functional protein.
Full text
PDF





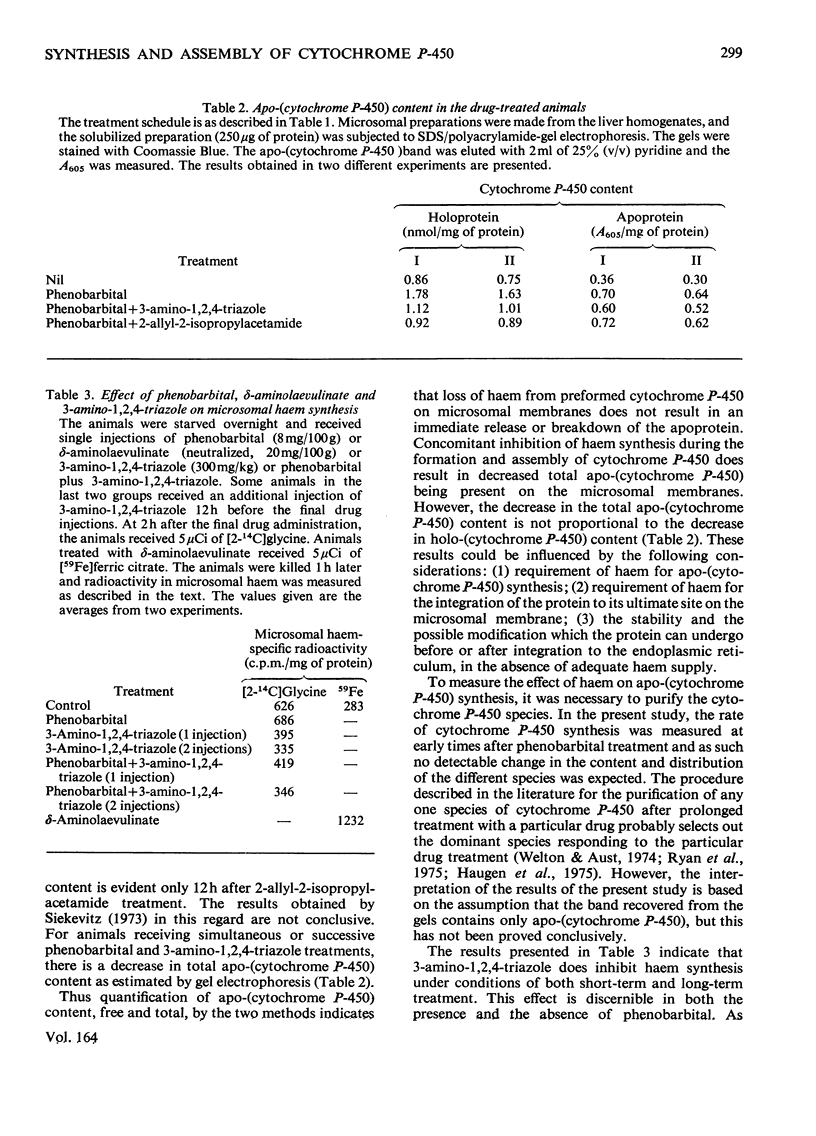

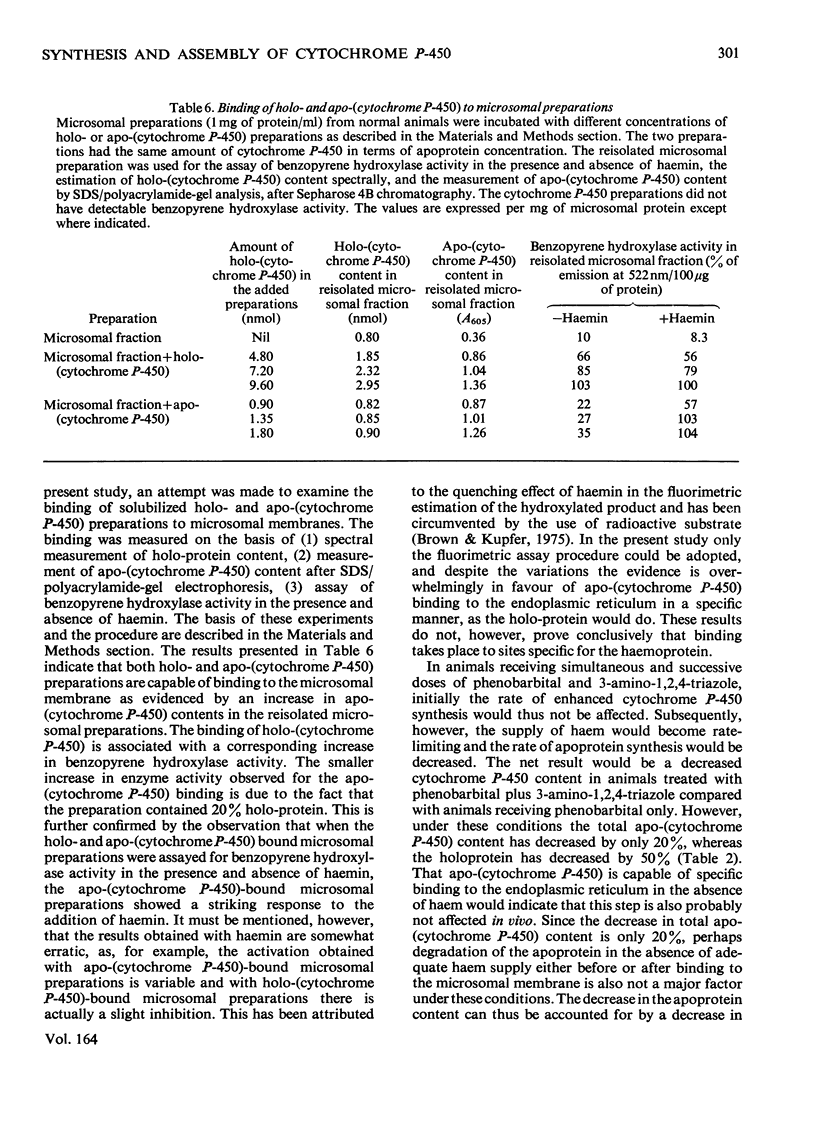

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson S. D., Yau P. M., Herbert E., Zucker W. V. Involvement of hemin, a stimulatory fraction from ribosomes and a protein synthesis inhibitor in the regulation of hemoglobin synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jan 28;63(2):247–264. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90373-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes R., Jones M. S., Jones O. T., Porra R. J. Ferrochelatase and -aminolaevulate synthetase in brain, heart, kidney and liver of normal and porphyric rats. The induction of -aminolaevulate synthetase in kidney cytosol and mitochondria by allylisopropylacetamide. Biochem J. 1971 Sep;124(3):633–637. doi: 10.1042/bj1240633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron J., Tephly T. R. Effect of 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole on the stimulation of hepatic microsomal heme synthesis and induction of hepatic microsomal oxidases produced by phenobarbital. Mol Pharmacol. 1969 Jan;5(1):10–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beattie D. S., Stuchell R. N. Studies on the induction of hepatic delta-aminolevulinic acid synthetase in rat liver mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Aug;139(2):291–297. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90480-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beattie D. S. The possible relationship between heme synthesis and mitochondrial biogenesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Nov;147(1):136–142. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90319-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuzard Y., Rodvien R., London I. M. Effect of hemin on the synthesis of hemoglobin and other proteins in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1022–1026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock K. W., Krauss E., Fröhling W. Regulation of -aminolevulinic acid synthetase by drugs and steroids in vivo and in isolated perfused rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Nov 11;23(2):366–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Kupfer D. Interactions of heme with hepatic microsomal mono-oxygenase. Effect on benzpyrene hydroxylation. Chem Biol Interact. 1975 Jan;10(1):57–70. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(75)90046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correia M. A., Meyer U. A. Apocytochrome P-450: reconstitution of functional cytochrome with hemin in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):400–404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Matteis F. Rapid loss of cytochrome P-450 and haem caused in the liver microsomes by the porphyrogenic agent 2-allyl-2-isopropylacetamide. FEBS Lett. 1970 Feb 25;6(4):343–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehlinger P. J., Schimke R. T. Effects of phenobarbital, 3-methylcholanthrene, and hematin on the synthesis of protein components of rat liver microsomal membranes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1257–1264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druyan R., Kelly A. The effect of exogenous -aminolaevulinate on rat liver haem and cytochromes. Biochem J. 1972 Oct;129(5):1095–1099. doi: 10.1042/bj1291095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Cadavid N. P. The biosynthesis of mitochondrial cytochromes. Subcell Biochem. 1974 Dec;3(4):275–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granick S. The induction in vitro of the synthesis of delta-aminolevulinic acid synthetase in chemical porphyria: a response to certain drugs, sex hormones, and foreign chemicals. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 25;241(6):1359–1375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugen D. A., Coon M. J. Induction of multiple forms of mouse liver cytochrome P-450. Evidence for genetically controlled de novo protein synthesis in response to treatment with beta-naphthoflavone or phenobarbital. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1817–1827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugen D. A., van der Hoeven T. A., Coon M. J. Purified liver microsomal cytochrome P-450. Separation and characterization of multiple forms. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3567–3570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa Y., Mason H. S. Cytochrome P450 associated with free hepatic polyribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 5;86(3):559–575. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LABBE R. F., NISHIDA G. A new method of hemin isolation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Nov;26(2):437–437. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legon S., Jackson R. J., Hunt T. Control of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates by haemin. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 31;241(109):150–152. doi: 10.1038/newbio241150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin W., Jacobson M., Kuntzman R. Incorporation of radioactive- -aminolevulinic acid into microsomal cytochrome P 450 : selective breakdown of the hemoprotein by allylisopropylacetamide and carbon tetrachloride. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jan;148(1):262–269. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90140-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. Y., Levin W. Partial purification of cytochromes P-450 and P-448 from rat liver microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Feb 16;46(3):1334–1339. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell C. R., Rabinovitz M. Evidence for an inhibitor in the control of globin synthesis by hemin in a reticulocyte lysate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Apr 10;35(1):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90485-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. I. EVIDENCE FOR ITS HEMOPROTEIN NATURE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2370–2378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajamanickam C., Amrutavalli J., Rao M. R., Padmanaban G. Effect of hexachlorobenzene on haem synthesis. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(2):381–387. doi: 10.1042/bj1290381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajamanickam C., Rao M. R., Padmanaban G. On the sequence of reactions leading to cytochrome P-450 synthesis-effect of drugs. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 25;250(6):2305–2310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. R., Padmanaban G. Biochemical effects of the porphyrinogenic drug allylisopropylacetamide. A comparative study with phenobarbital. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;134(4):859–868. doi: 10.1042/bj1340859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan D., Lu Y. H., Kawalek J., West S. B., Levin L. Highly purified cytochrome P-448 and P=450 from rat liver microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jun 16;64(4):1134–1141. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90812-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekevitz P. The differentiation of rat liver endoplasmic reticulum membranes: apo--cytochrome P450 as a membrane protein. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(6):471–489. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song C. S., Moses H. L., Rosenthal A. S., Gelb N. A., Kappas A. The influence of postnatal development on drug-induced hepatic porphyria and the synthesis of cytochrome P-450. A biochemical and morphological study. J Exp Med. 1971 Nov 1;134(5):1349–1371. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.5.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEALE F. W. Cleavage of the haem-protein link by acid methylethylketone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Oct;35:543–543. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90407-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. E., Ryan D., Levin W. An improved staining procedure for the detection of the peroxidase activity of cytochrome P-450 on sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1976 Sep;75(1):168–176. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welton A. F., Aust S. D. Multiplicity of cytochrome P450 hemoproteins in rat liver microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Feb 27;56(4):898–906. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80273-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. S. Alterations of the aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase system during riboflavin depletion and repletion. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Feb;160(2):623–630. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90439-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. S., Strickhart F. S. Interactions between solubilized cytochrome P-450 and hepatic microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 25;250(20):7968–7972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]