Abstract
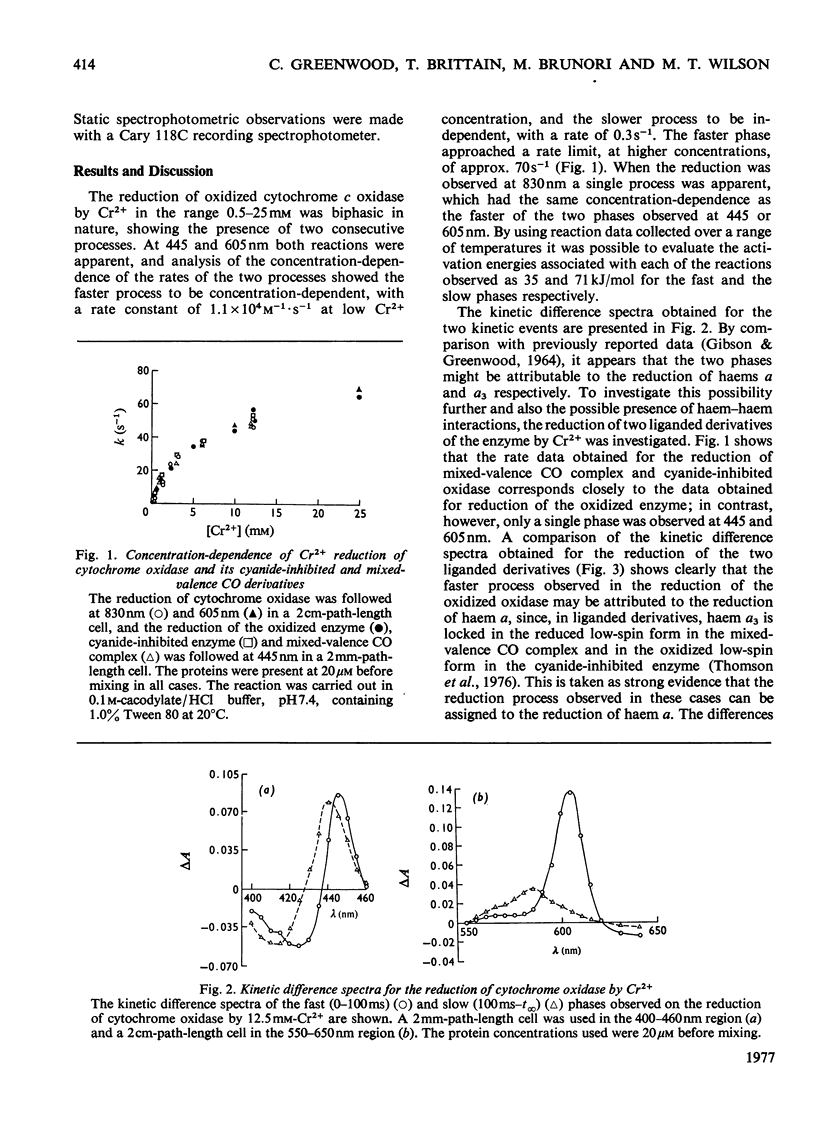
The reduction of cytochrome c oxidase by Cr2+, followed by means of stopped-flow spectrophotometry, exhibits two phases: the faster Cr2+-concentration-dependent reaction has an initial rate constant of 1.1 X 10(4)M-1-S-1, but reaches a rate limit at high concentration of reductant; the slower phase is concentration-independent with a rate of 0.3S-1. The activation energies of the fast and the slow processes are 35 and 71 kJ/mol respectively. The reduction kinetics of the mixed-valence CO complex and the cyanide-inhibited enzyme were compared with those of the fully oxidized forms: both the liganded species have a fast phase identical with that found in the oxidized oxidase. A comparison of the kinetic difference spectra obtained for the fast phase of reduction of oxidized oxidase with those obtained on reduction of the liganded species suggests that the rapid phase arises from the reduction ofhaem a, and the slow phase from the reduction of haem a3.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEINERT H., GRIFFITHS D. E., WHARTON D. C., SANDS R. H. Properties of the copper associated with cytochrome oxidase as studied by paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jul;237:2337–2346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEINERT H., PALMER G. OXIDATION-REDUCTION OF THE COPPER COMPONENT OF CYTOCHROME OXIDASE. KINETIC STUDIES WITH A RAPID FREEZING TECHNIQUE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Apr;239:1221–1227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brittain T., Wilson M. T., Greenwood C. The reduction of carboxymethyl-cytochrome c by chromous ions. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;141(2):455–461. doi: 10.1042/bj1410455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON Q. H., GREENWOOD C. THE REACTION OF CYTOCHROME OXIDASE WITH CYTOCHROME C. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:888–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON Q. H., GREENWOOD C. THE SPECTRA AND SOME PROPERTIES OF CYTOCHROME OXIDASE COMPONENTS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:586–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson Q. H., Milnes L. Apparatus for rapid and sensitive spectrophotometry. Biochem J. 1964 Apr;91(1):161–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0910161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood C., Brittain T. Studies on partially reduced mammalian cytochrome oxidase reactions with ferrocytochrome c. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):591–598. doi: 10.1042/bj1570591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood C., Wilson M. T., Brunori M. Studies on partially reduced mammalian cytochrome oxidase. Reactions with carbon monoxide and oxygen. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;137(2):205–215. doi: 10.1042/bj1370205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muijsers A. O., Tiesjema R. H., Henderson R. W., Van Gelder B. F. Biochemical and biophysical studies on cytochrome aa 3 . VII. The effect of cytochrome c on the oxidation-reduction potential of isolated cytochrome aa 3 . Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 20;267(1):216–221. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90154-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls P., Petersen L. C., Miller M., Hansen F. B. Ligand-induced spectral changes in cytochrome c oxidase and their possible significance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 9;449(2):188–196. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutin N., Yandell J. K. Mechanisms of the reactions of cytochrome c. Rate and equilibrium constants for ligand binding to horse heart ferricytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6932–6936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. J., Brittain T., Greenwood C., Springall J. Determination of the heme spin states in cytochrome c oxidase using magnetic circular dichroism. FEBS Lett. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):94–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80877-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. F., Lindsay J. G., Brocklehurst E. S. Heme-heme interaction in cytochrome oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;256(2):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. T., Greenwood C., Brunori M., Antonini E. Kinetic studies on the reaction between cytochrome c oxidase and ferrocytochrome c. Biochem J. 1975 Apr;147(1):145–153. doi: 10.1042/bj1470145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YONETANI T. Studies on cytochrome oxidase. I. Absolute and difference absorption spectra. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:845–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YONETANI T. Studies on cytochrome oxidase. III. Improved preparation and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jun;236:1680–1688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yong F. C., King T. E. Studies on cytochrome oxidase. IX. Heme-copper interaction. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6384–6388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Buuren K. J., Nicholis P., van Gelder B. F. Biochemical and biophysical studies on cytochrome aa 3 . VI. Reaction of cyanide with oxidized and reduced enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;256(2):258–276. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


