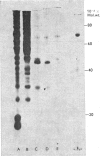
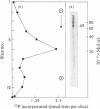
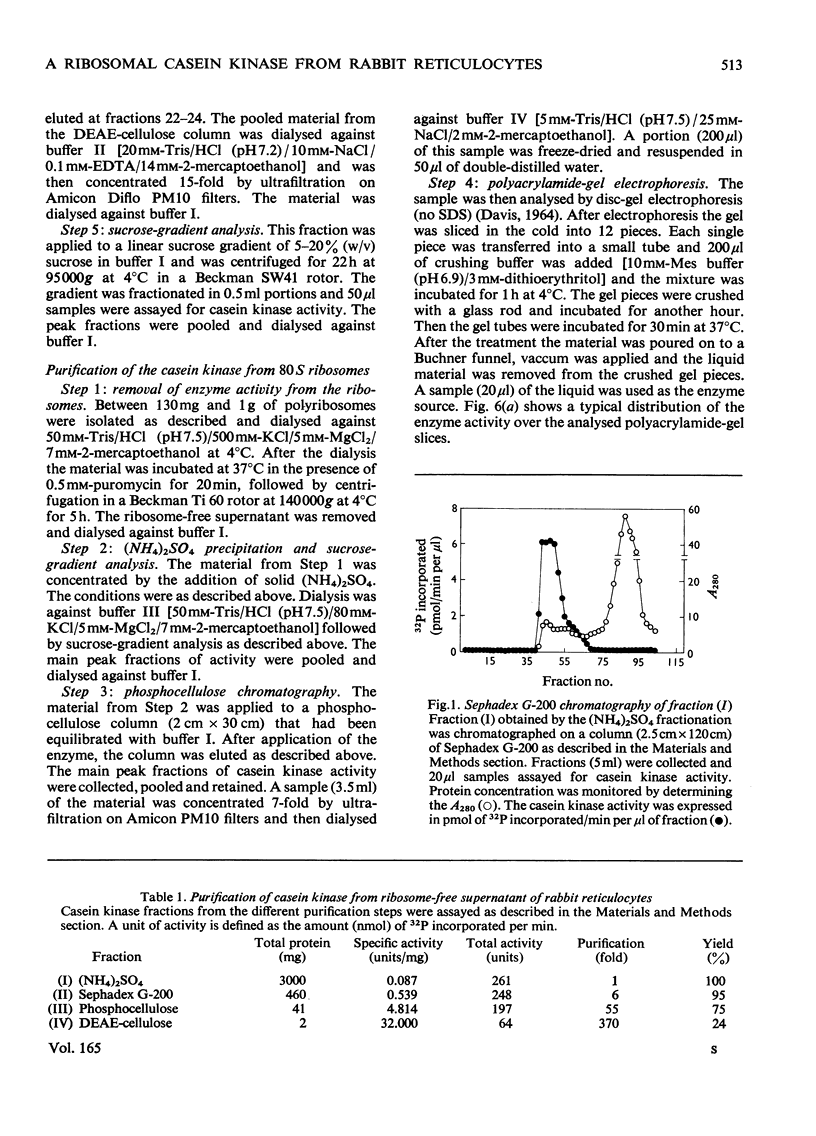
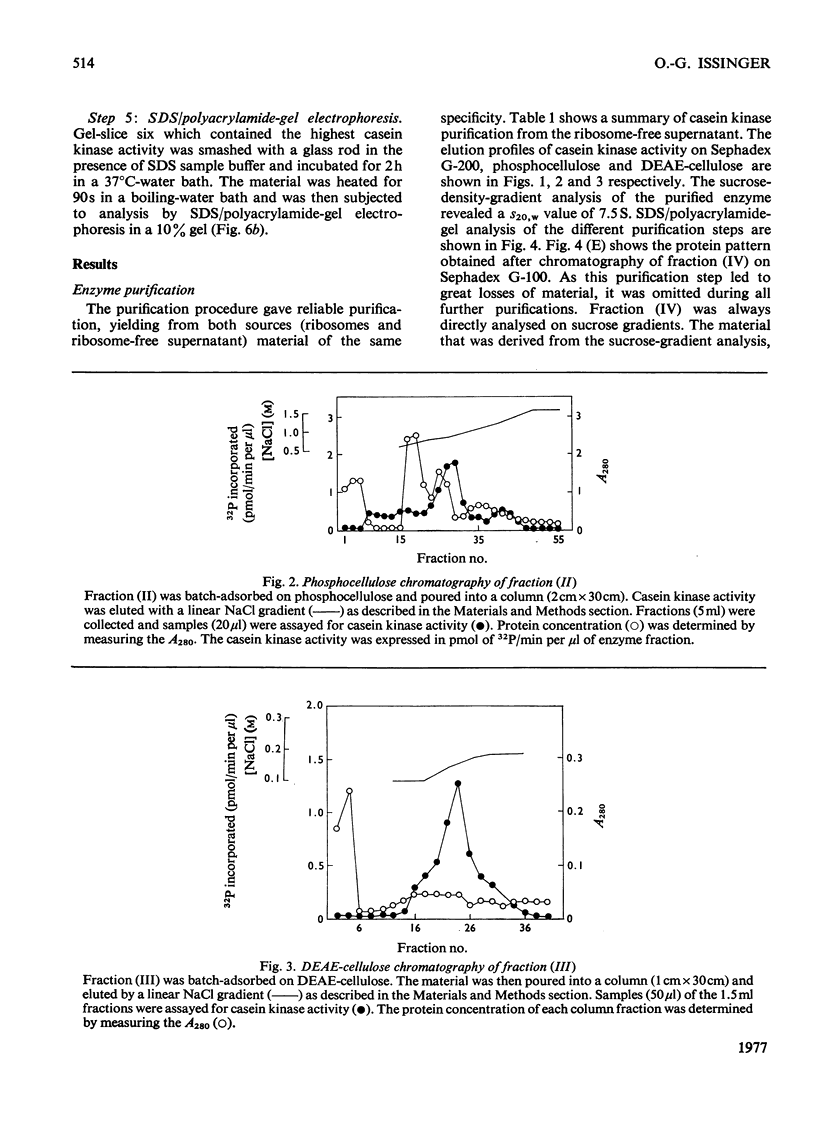
Abstract
A casein kinase was isolated and purifed from rabbit reticulocytes. About 90% of the enzyme activity co-sedimented with the ribosomal fraction, whereas about 10% of the enzyme activity was found in the ribosome-free supernatant. Both casein kinases (the ribosome-bound enzyme as well as the free enzyme) showed identical activity and the same molecular weight. On sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis a single band of about 70 000 mol.wt. was observed. Sucrose-gradient analysis, however, showed that the enzyme activity sedimented with a s20,w of approx. 7.5S. This observation suggested that the casein kinase is a dimer composed of subunits of identical molecular weight. The enzyme utilizes GTP as well as ATP as a phosphoryl donor. It preferentially phosphorylates acidic proteins, in particular the model substrates casein and phosvitin. Casein kinase is cyclic AMP-indepenoent. The Km values for ATP and GTP with phosvitin as a substrate were determined as 1.2 and 8.8 micrometer respectively.
Full text
PDF

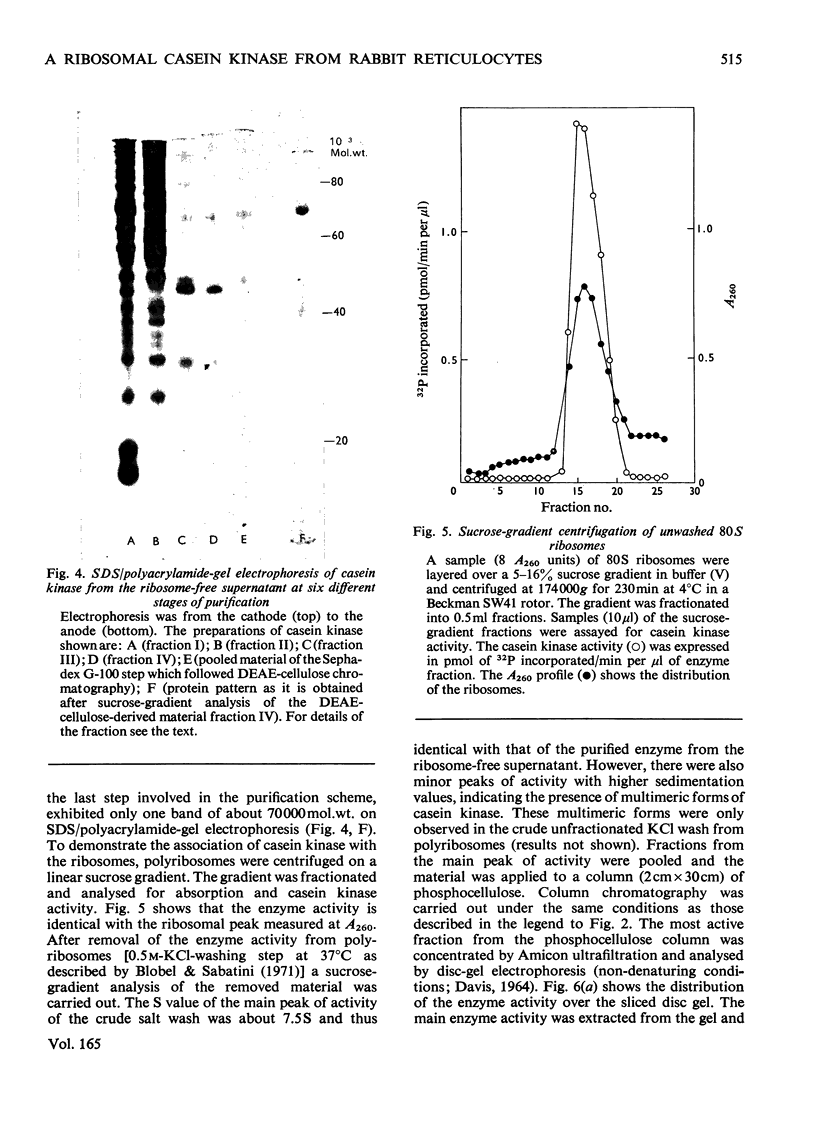
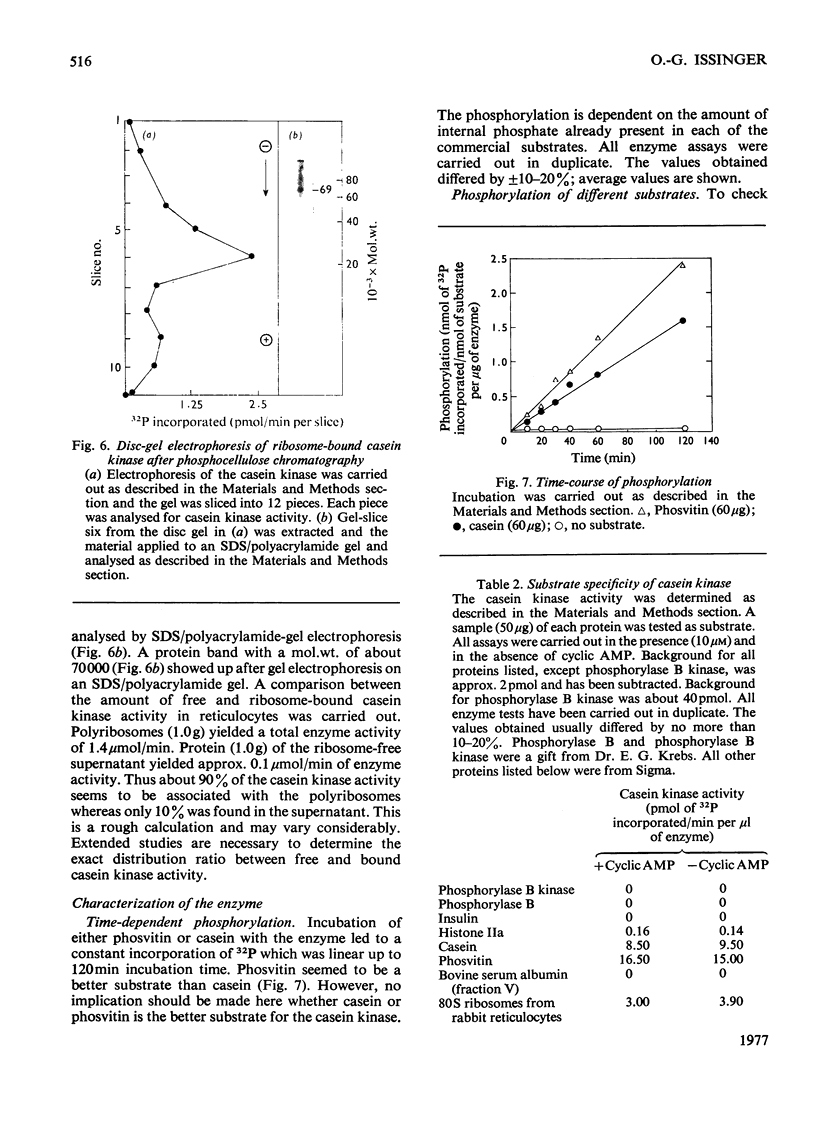


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN E. H., SCHWEET R. S. Synthesis of hemoglobin in a cell-free system. I. Properties of the complete system. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:760–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggio B., Moret V. Multiple forms of phosvitin kinase from rat liver cytosol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Nov 13;250(2):346–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham E. W., Farrell H. M., Jr, Basch J. J. Phosphorylation of casein. Role of the golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):8193–8194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Sabatini D. Dissociation of mammalian polyribosomes into subunits by puromycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):390–394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Effect of diphtheria toxin on protein synthesis: inactivation of one of the transfer factors. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):83–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Reimann E. M. Assay of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:287–290. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjardins P. R., Lue P. F., Liew C. C., Gornall A. G. Purification and properties of rat liver nuclear protein kinases. Can J Biochem. 1972 Dec;50(12):1249–1259. doi: 10.1139/o72-170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Hasty M. A. Phosvitin kinase from the liver of the rooster. Purification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6300–6307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard G. A., Traugh J. A., Croser E. A., Traut R. R. Ribosomal proteins from rabbit reticulocytes: number and molecular weights of proteins from ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 15;93(3):391–404. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issinger O. G., Benne R., Hershey J. W., Traut R. R. Phosphorylation in vitro of eukaryotic initiation factors IF-E2 and IF-E3 by protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6471–6474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issinger O. G., Kiefer M. C., Traut R. R. Specificity of ATP-dependent and GTP-dependent protein kinases with respect to ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issinger O. G., Traut R. R. Selective phosphorylation from GTP of proteins L7 and L12 of E. coli 50S ribosomes by a protein kinase from rabbit reticulocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 5;59(3):829–836. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazemie M., Chatterjee S. K., Matthaei H. Studies on rabbit reticulocyte ribosomes, I. Preparation and characterization of ribosomal subunits. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1973 May;354(5):471–480. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1973.354.1.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Froscio M., Rogers A., Murray A. W. Multiple protein kinases from human lymphocytes. Identification enzymes phosphorylating exogenous histon and casein. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;145(2):241–249. doi: 10.1042/bj1450241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer G., Cimadevilla J. M., Hardesty B. Specificity of the protein kinase activity associated with the hemin-controlled repressor of rabbit reticulocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3078–3082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G. Protein kinases. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1972;5:99–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranu R. S., Levin D. H., Delaunay J., Ernst V., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates: characteristics of inhibition of protein synthesis by a translational inhibitor from heme-deficient lysates and its relationship to the initiation factor which binds Met-tRNAf. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2720–2724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranu R. S., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates: purification and initial characterization of the cyclic 3':5'-AMP independent protein kinase of the heme-regulated translational inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4349–4353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodnight R., Lavin B. E. Phosvitin kinase from brain: activation by ions and subcellular distribution. Biochem J. 1964 Oct;93(1):84–91. doi: 10.1042/bj0930084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda M., Yamamura H., Oga Y. Phosphoprotein kinases associated with rat liver chromatin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jan 8;42(1):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90368-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. B. Comparative study of the protein kinase associated with animal viruses. Virology. 1975 Apr;64(2):566–570. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugh J. A., Traut R. R. Characterization of protein kinases from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1207–1212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wålinder O. Calf brain phosvitin kinase. II. Purification and characterization of three different fractions of phosvitin kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 12;293(1):140–149. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wålinder O. Calf brain phosvitin kinase. Purification of the kinase associated with a phosphate-incorporating protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;258(2):411–421. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90233-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]