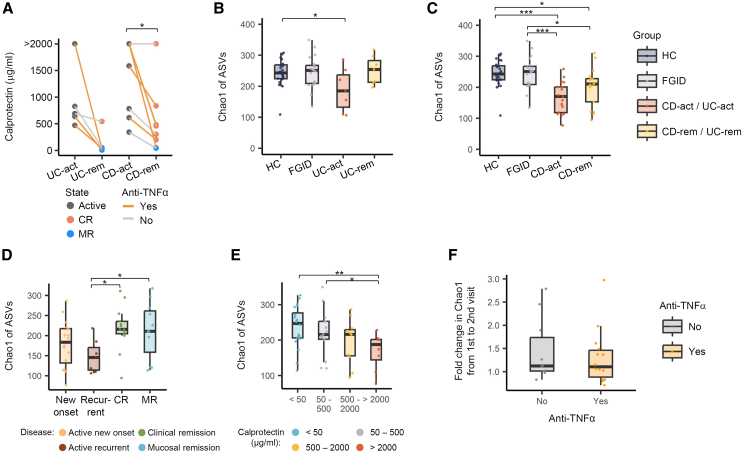
Figure 2.
Gut microbiota alpha diversity of patients with UC and CD compared to healthy controls and patients with functional gastrointestinal diseases
(A) The fecal calprotectin concentration of the patients was measured at diagnosis (UC-act, CD-act) and remission (UC-rem, CD-rem). The remission state was further categorized into CR and MR based on endoscopic examination findings. Data points are shown in different colors, and the subset of patients who received anti-TNF-α treatment can be distinguished by line color. Fecal calprotectin concentration data included five patients with UC and nine patients with CD. Paired Wilcoxon test: CD-rem vs. CD-act, p = 0.022; UC-rem vs. UC-act, p = 0.063. (BE) Chao1 richness index calculated from read counts per 16S ASV.
(B) Comparison among HC and patients with FGID, UC-act, and UC-rem.
(C) Comparison among HC and patients with FGID, CD-act, and CD-rem.
(D) Comparison among patients with IBD based on diagnostic status. Active IBD states were further classified into new-onset and recurrent types. Remission states were classified into clinical and mucosal. Wilcoxon test: CR vs. recurrent IBD, 1.5-fold, p = 0.01; MR vs. recurrent IBD, 1.4-fold, p = 0.04.
(E) Comparison within IBD patients based on fecal calprotectin levels. Wilcoxon test: very high vs. low, p = 0.006; very high vs. low-mid, p = 0.03.
(F) Fold changes in ASV Chao1 index from active to remission state divided by patient usage of the anti-TNF-α agent. Significance of the difference was tested by Wilcoxon’s signed rank test. The pairs of groups with values of p < 0.05 are indicated by horizontal brackets. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Boxplots in (B–F) represent interquartile range, along with the individual data points shown as dots. A full table of statistical values is available as Table S1. Anti-TNF-α, anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha; ASV, amplicon sequence variant; CD, Crohn disease; CD-act, active CD; CD-rem, remission CD; CR, clinical remission; FGID, functional gastrointestinal disease; HC, healthy controls; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; MR, mucosal remission; UC, ulcerative colitis; UC-act, active UC; UC-rem, remission UC.