Abstract
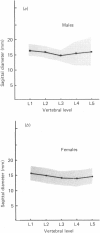
An osteometric study of the anteroposterior diameter of the lumbar vertebral canal and intervertebral foramina of normal adult Nigerians is reported. The results show that the midsagittal diameter of the canal is subject to racial variations, and is determined primarily by the thickness and orientation of the lamina and to a lesser extent by the height of the pedicle. The significance of the findings is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amonoo-Kuofi H. S. Maximum and minimum lumbar interpedicular distances in normal adult Nigerians. J Anat. 1982 Sep;135(Pt 2):225–233. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chynn K. Y., Altman I., Shaw W. I., Finby N. The roentgenographic manifestations and clinical features of lumbar spinal stenosis with special emphasis on the superior articular process. Neuroradiology. 1978;16:378–380. doi: 10.1007/BF00395310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crock H. V. Normal and pathological anatomy of the lumbar spinal nerve root canals. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1981;63B(4):487–490. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.63B4.7298672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS P. R. The thoraco-lumbar mortice joint. J Anat. 1955 Jul;89(3):370–377. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPSTEIN J. A., EPSTEIN B. S., LAVINE L. Nerve rot compression associated with narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1962 May;25:165–176. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.25.2.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein S. The morphometry and pathological anatomy of the lumbar spine in South African negroes and caucasoids with specific reference to spinal stenosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1977 May;59(2):173–180. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.59B2.873978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinck V. C., Clark W. M., Jr, Hopkins C. E. Normal interpediculate distances (minimum and maximum) in children and adults. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1966 May;97(1):141–153. doi: 10.2214/ajr.97.1.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinck V. C., Hopkins C. E., Clark W. M. Sagittal diameter of the lumbar spinal canal in children and adults. Radiology. 1965 Nov;85(5):929–937. doi: 10.1148/85.5.929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. A., Thomson J. L. The narrow lumbar canal. A clinical and radiological review. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1968 Aug;50(3):595–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. L., Smith D. The lumbar spinal canal in children. Part I: The sagittal diameter. Eur J Radiol. 1981 May;1(2):163–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLESINGER E. B., TAVERAS J. M. Factors in the production of cauda equina syndromes in lumbar discs. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1953;3(78TH):263–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERBIEST H. A radicular syndrome from developmental narrowing of the lumbar vertebral canal. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1954 May;36-B(2):230–237. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.36B2.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERBIEST H. Further experiences on the pathological influence of a developmental narrowness of the bony lumbar vertebral canal. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1955 Nov;37-B(4):576–583. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.37B4.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venner R. M., Crock H. V. Clinical studies of isolated disc resorption in the lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1981;63B(4):491–494. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.63B4.6457838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbiest H. Results of surgical treatment of idiopathic developmental stenosis of the lumbar vertebral canal. A review of twenty-seven years' experience. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1977 May;59(2):181–188. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.59B2.141452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]