Abstract
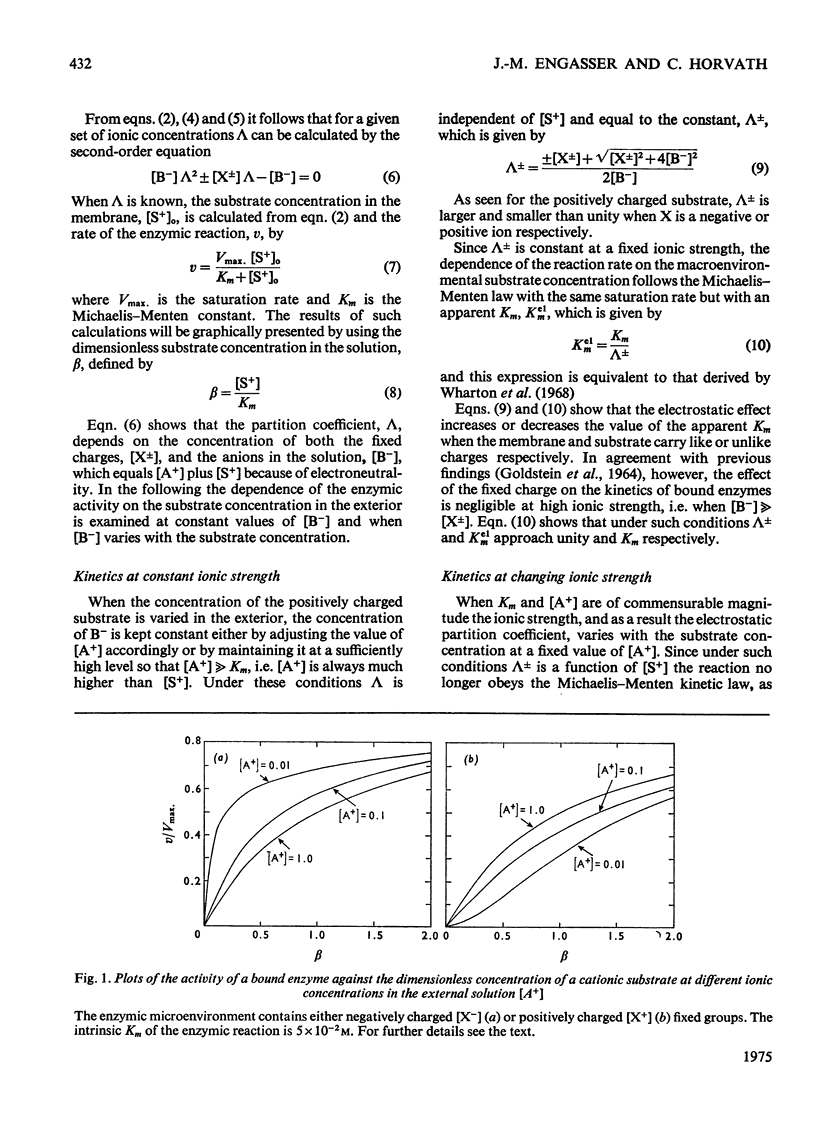
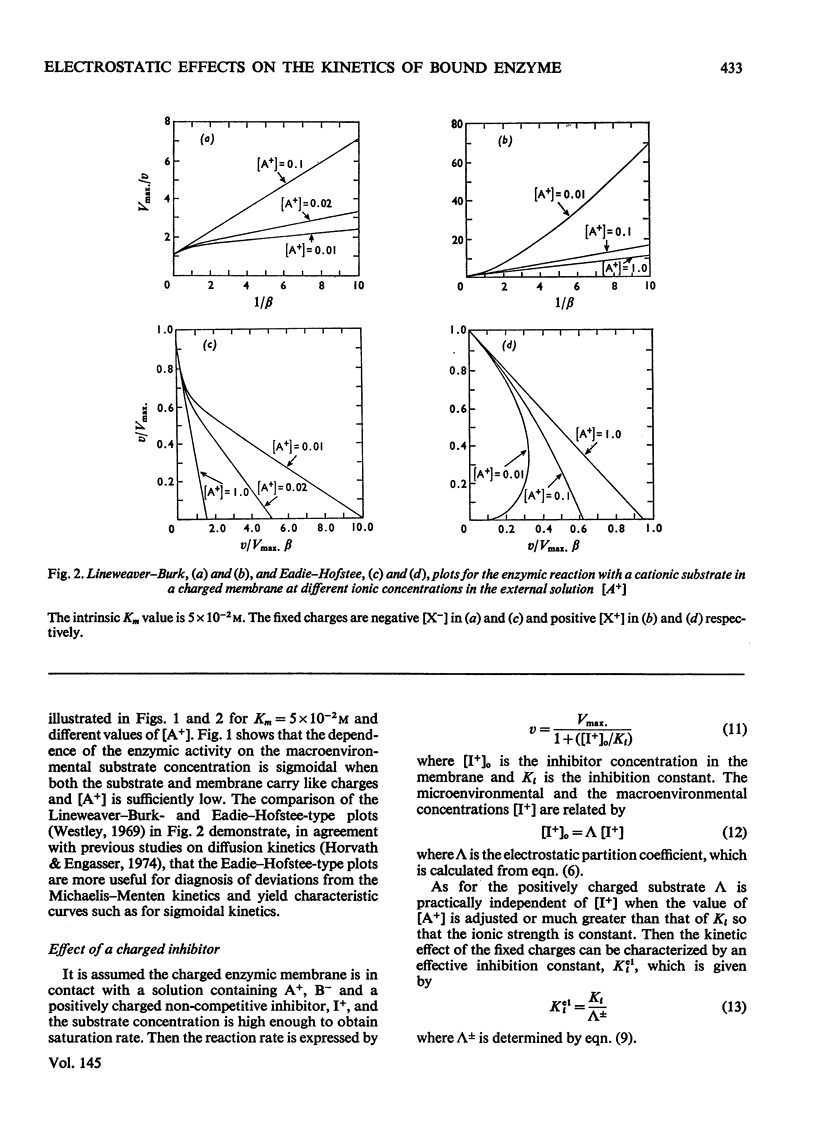
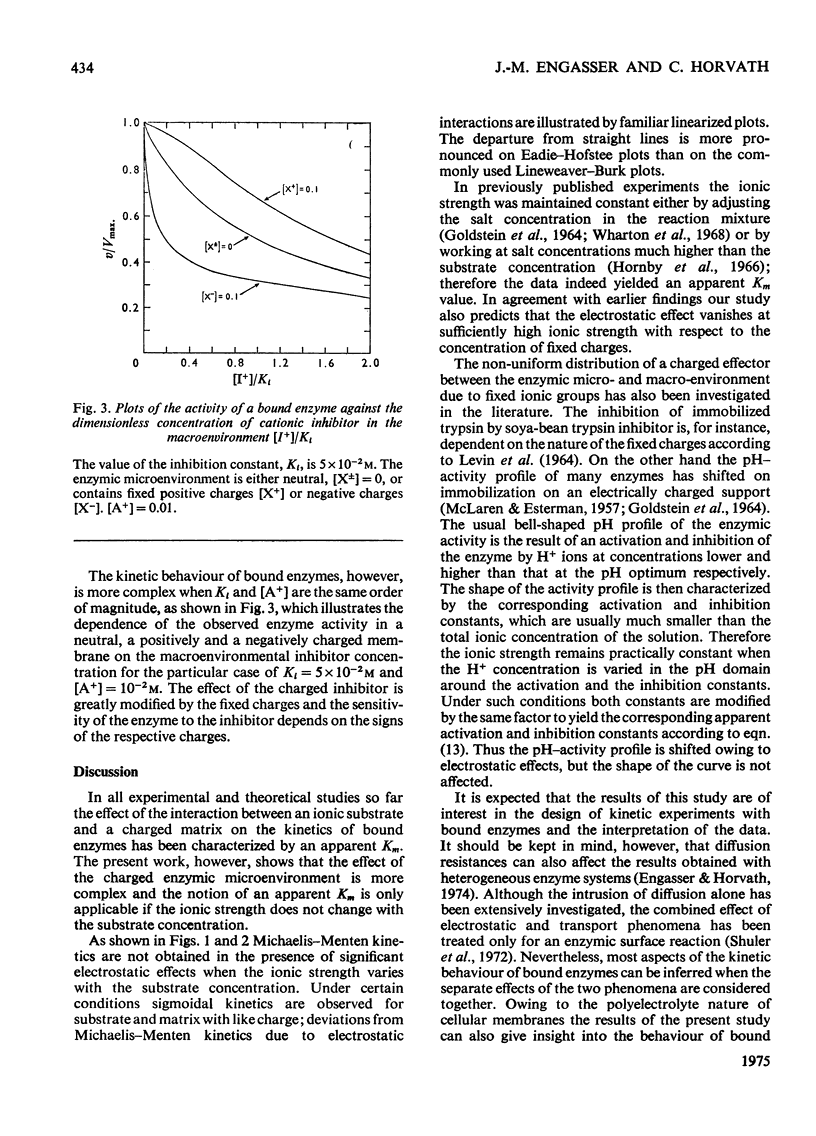
1. The effect of the interaction between the charged matrix and substrate on the kinetic behaviour of bound enzymes was investigated theoretically. 2. Simple expression is derived for the apparent Km. 3. The apparent Km can only be used for the characterization of the electrostatic effect of the ionic strength does not vary with the substrate concentration. 4. The deviations from Michaelis-Menton kinetics are graphically illustrated for cases when the ionic strength varies with the substrate concentration. 5. The inhibition of the bound enzyme by a charged inhibitor at constant ionic strength is characterized by an apparent Ki. 6. When both the inhibitor concentration and the ionic strength change there is no apparent Ki, and the inhibition profile is graphically illustrated for this case. 7. Under certain conditions the electrostatic effects manifest thenselves in a sigmoidal dependence of the enzyme activity on the concentration of the substrate or inhibitor.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Engasser J. M., Horvath C. Effect of internal diffusion in heterogeneous enzyme systems: evaluation of true kinetic parameters and substrate diffusivity. J Theor Biol. 1973 Nov 5;42(1):137–155. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(73)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engasser J. M., Horvath C. Inhibition of bound enzymes. 3. Diffusion enhanced regulatory effect with substrate inhibition. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 10;13(19):3855–3859. doi: 10.1021/bi00716a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN L., LEVIN Y., KATCHALSKI E. A WATER-INSOLUBLE POLYANIONIC DERIVATIVE OF TRYPSIN. II. EFFECT OF THE POLYELECTROLYTE CARRIER ON THE KINETIC BEHAVIOR OF THE BOUND TRYPSIN. Biochemistry. 1964 Dec;3:1913–1919. doi: 10.1021/bi00900a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornby W. E., Lilly M. D., Crook E. M. The preparation and properties of ficin chemically attached to carboxymethylcellulose. Biochem J. 1966 Feb;98(2):420–425. doi: 10.1042/bj0980420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornby W. E., Lilly M. D. Some changes in the reactivity of enzymes resulting from their chemical attachment to water-insoluble derivatives of cellulose. Biochem J. 1968 May;107(5):669–674. doi: 10.1042/bj1070669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath C., Engasser J. M. External and internal diffusion in heterogeneous enzymes systems. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1974 Jul;16(7):909–923. doi: 10.1002/bit.260160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katchalski E., Silman I., Goldman R. Effect of the microenvironment on the mode of action of immobilized enzymes. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1971;34:445–536. doi: 10.1002/9780470122792.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN Y., PECHT M., GOLDSTEIN L., KATCHALSKI E. A WATER-INSOLUBLE POLYANIONIC DERIVATIVE OF TRYPSIN. I. PREPARATION AND PROPERTIES. Biochemistry. 1964 Dec;3:1905–1913. doi: 10.1021/bi00900a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLAREN A. D., ESTERMANN E. F. Influence of pH on the activity of chymotrypsin at a solid-liquid interface. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 May;68(1):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90336-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuler M. L., Aris R., Tsuchiya H. M. Diffusive and electrostatic effects with insolubilized enzymes. J Theor Biol. 1972 Apr;35(1):67–76. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(72)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton C. W., Crook E. M., Brocklehurst K. The nature of the perturbation of the michaelis constant of the bromelain-catalysed hydrolysis of alpha-N-benzoyl-L-arginine ethyl ester consequent upon attachment of bromelain to O-(carboxymethyl)-cellulose. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Dec 5;6(4):572–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


