Abstract
1. A soluble enzyme system which oxidizes benzene to cis-1,2-dihydroxycyclohexa-3,5-diene (cis-benzene glycol) was obtained from a species of Pseudomonas grown on benzene as the major carbon source. 2. The system was shown to consist of three protein components. Two of these were non-haem-iron proteins of molecular weight approx. 21,000 and approx. 186,000 and the other was a flavoprotein of molecular weight approx. 60,000. 3. Fe2+ and NADH were essential cofactors for benzene oxidation.
Full text
PDF
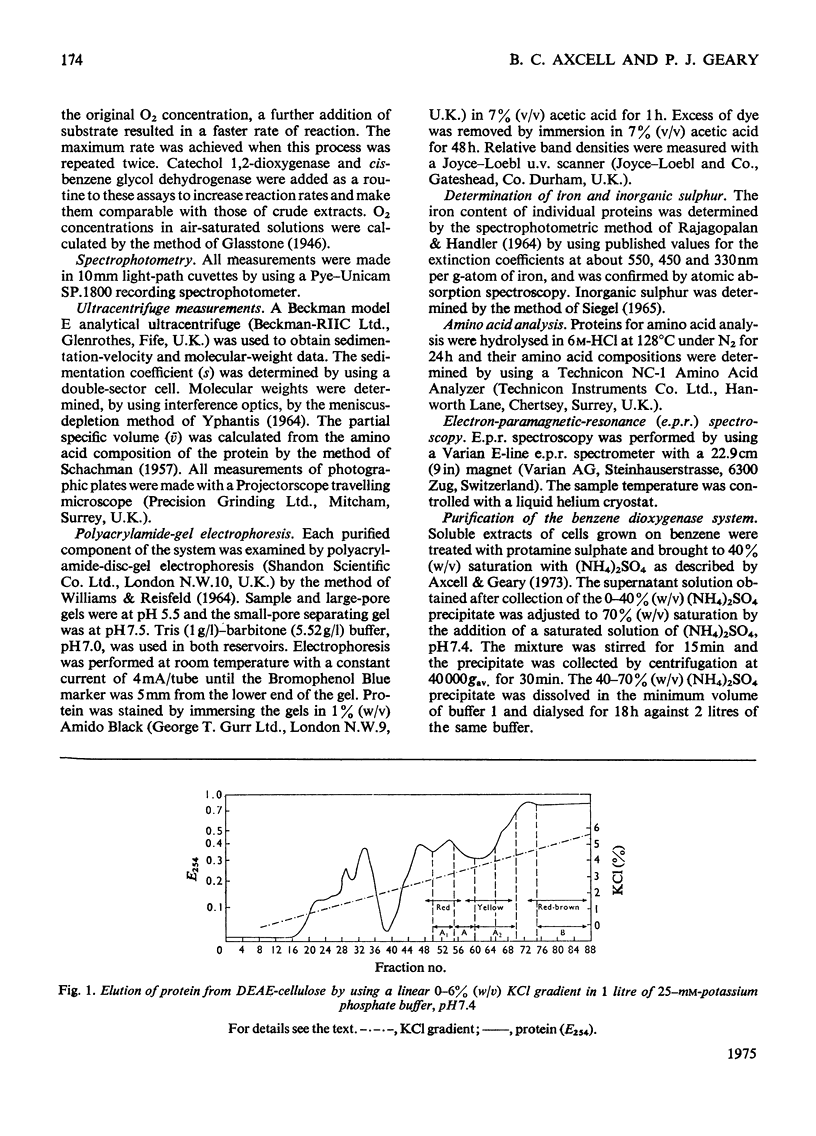

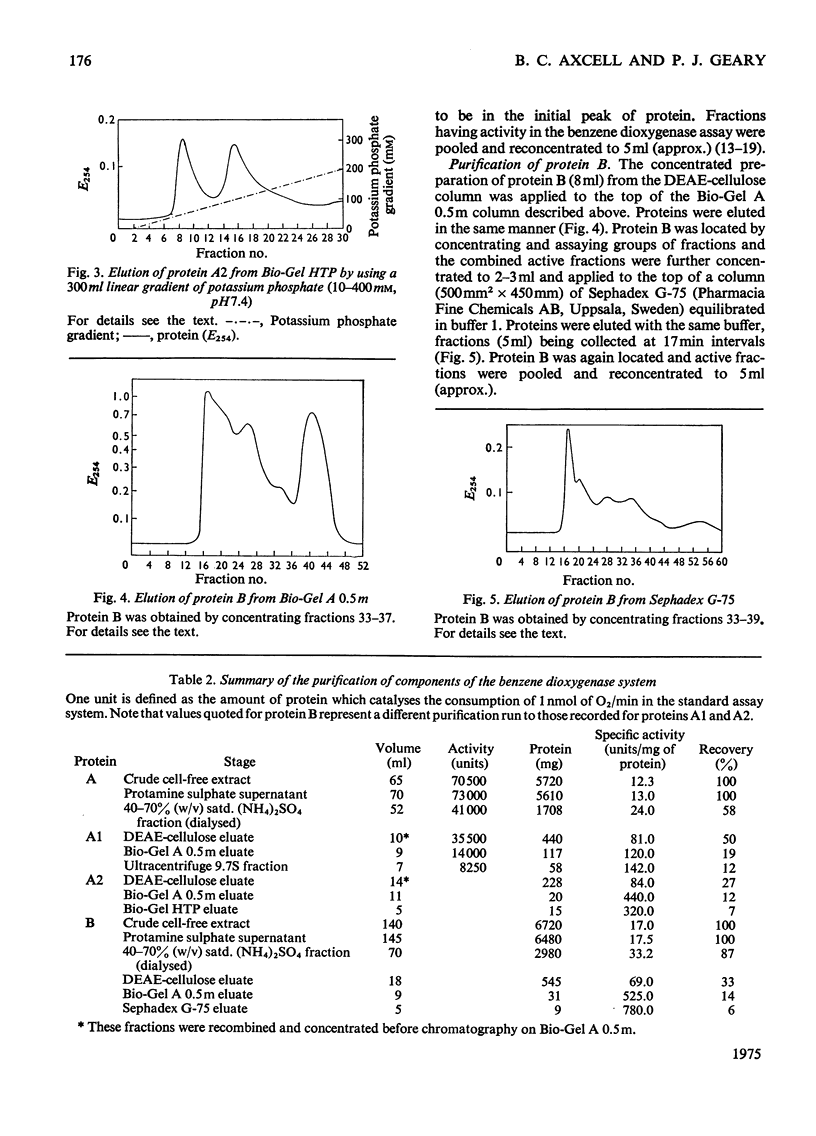
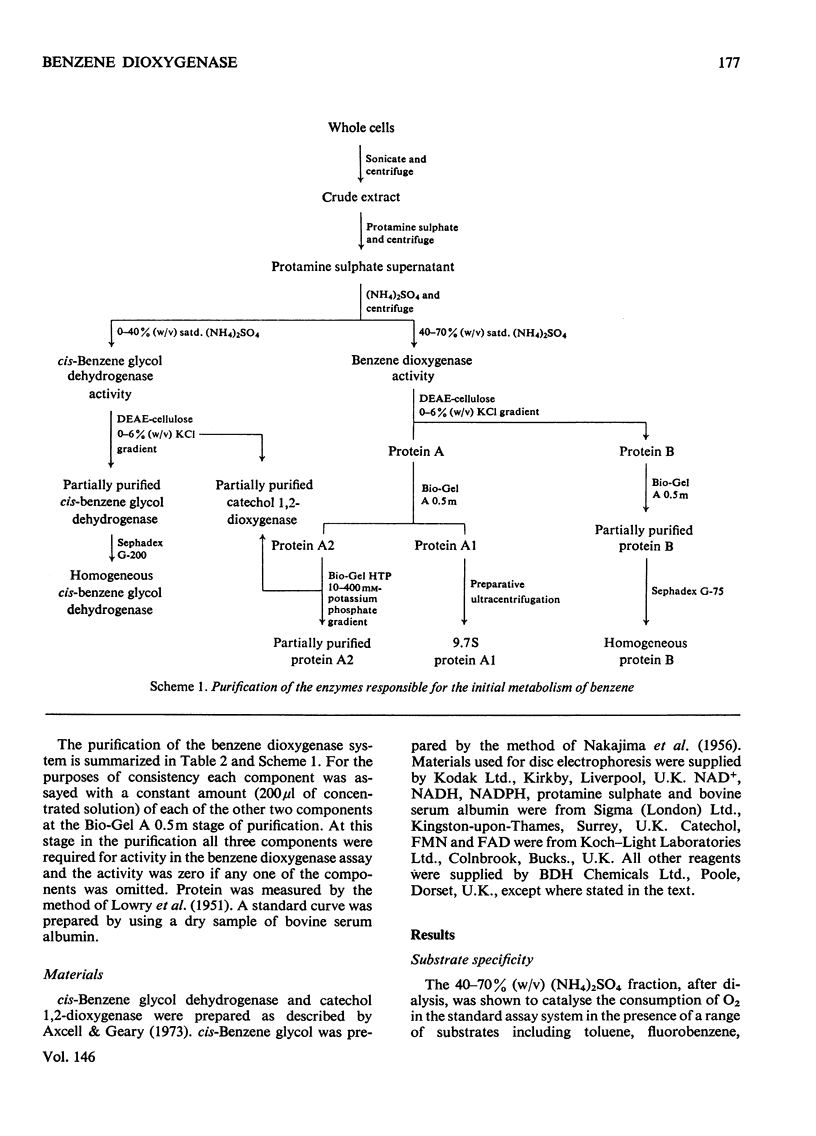

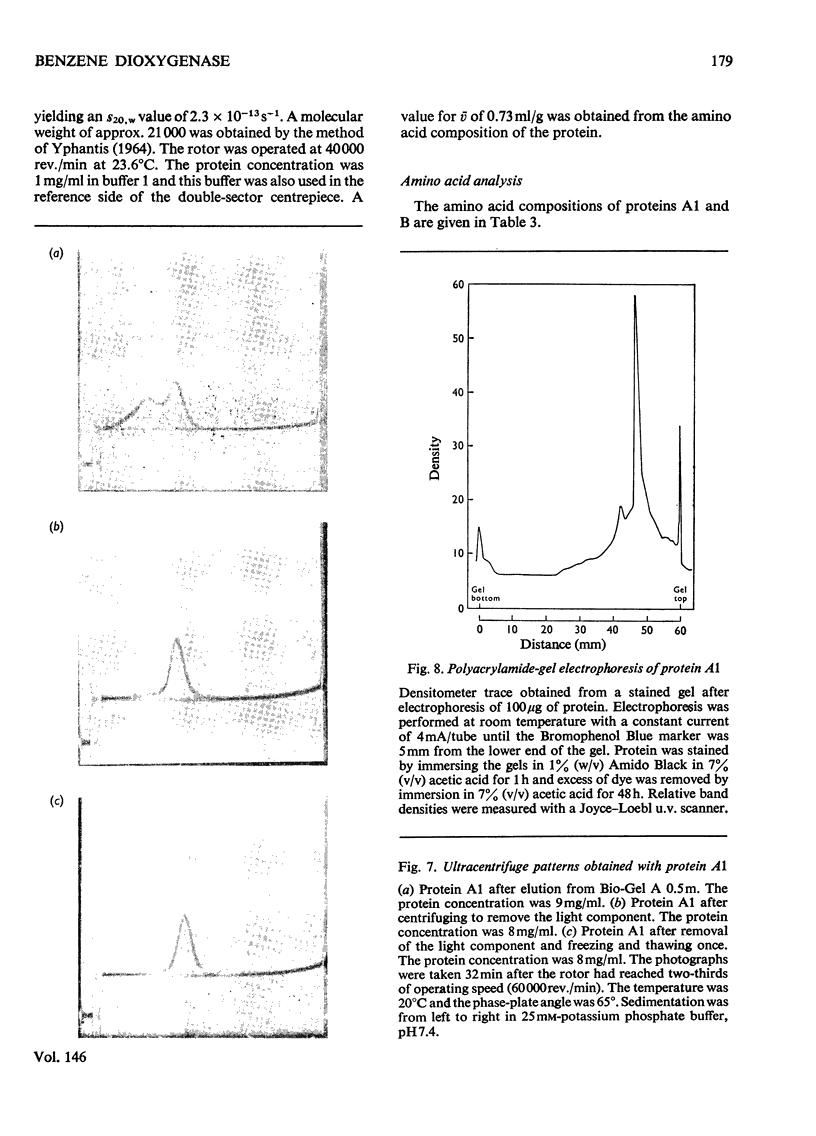


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axcell B. C., Geary P. J. The metabolism of benzene by bacteria. Purification and some properties of the enzyme cis-1,2-dihydroxycyclohexa-3,5-diene (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) oxidoreductase (cis-benzene glycol dehydrogenase). Biochem J. 1973 Dec;136(4):927–934. doi: 10.1042/bj1360927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhardt F. H., Ruf H. H., Staudinger H. Pufification of a 4-methoxybenzoate O-demethylase from Pseudomonas putida. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Aug;352(8):1091–1099. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1971.352.2.1091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Cardini G. E., Maseles F. C., Kallio R. E. Incorporation of oxygen-18 into benzene by Pseudomonas putida. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 31;9(7):1631–1635. doi: 10.1021/bi00809a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Koch J. R., Kallio R. E. Oxidative degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by microorganisms. I. Enzymatic formation of catechol from benzene. Biochemistry. 1968 Jul;7(7):2653–2662. doi: 10.1021/bi00847a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Högn T., Jaenicke L. Benzene metabolism of Moraxella species. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Oct;30(2):369–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAJAGOPALAN K. V., HANDLER P. THE ABSORPTION SPECTRA OF IRON-FLAVOPROTEINS. J Biol Chem. 1964 May;239:1509–1514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEGEL L. M. A DIRECT MICRODETERMINATION FOR SULFIDE. Anal Biochem. 1965 Apr;11:126–132. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS D. E., REISFELD R. A. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS IN POLYACRYLAMIDE GELS: EXTENSION TO NEW CONDITIONS OF PH AND BUFFER. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:373–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



