Abstract
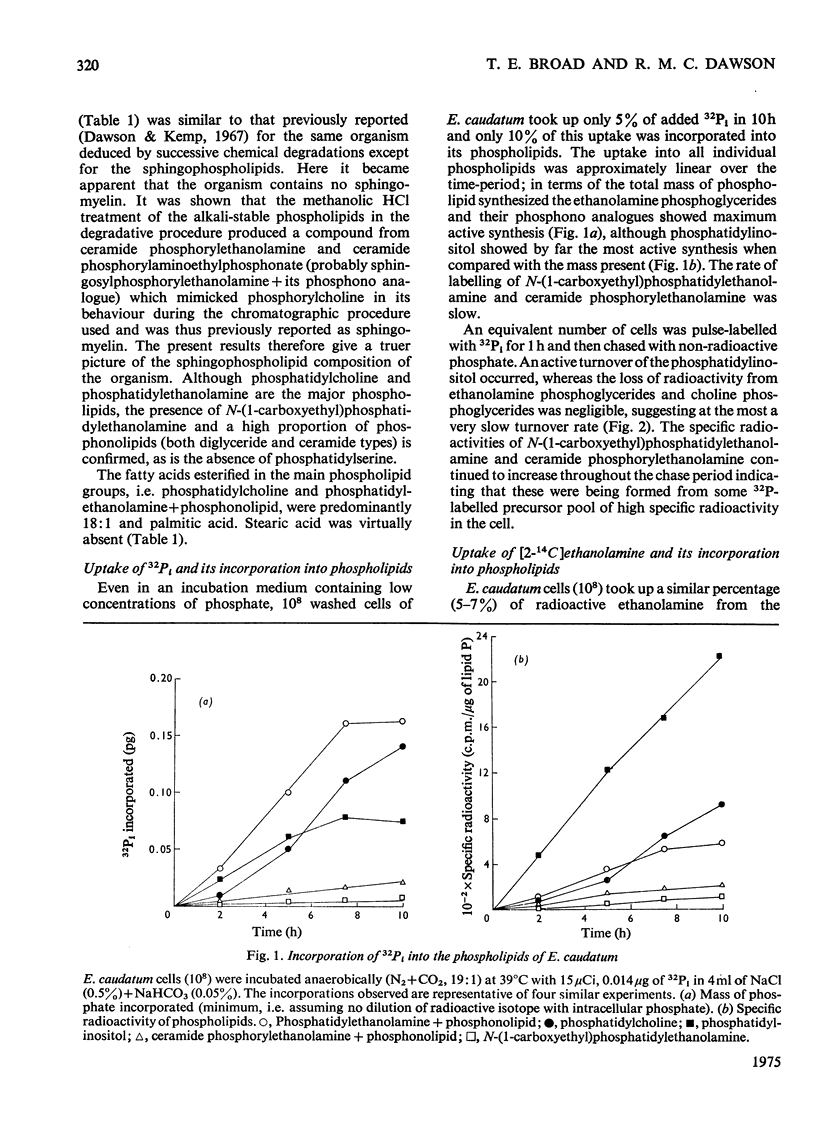
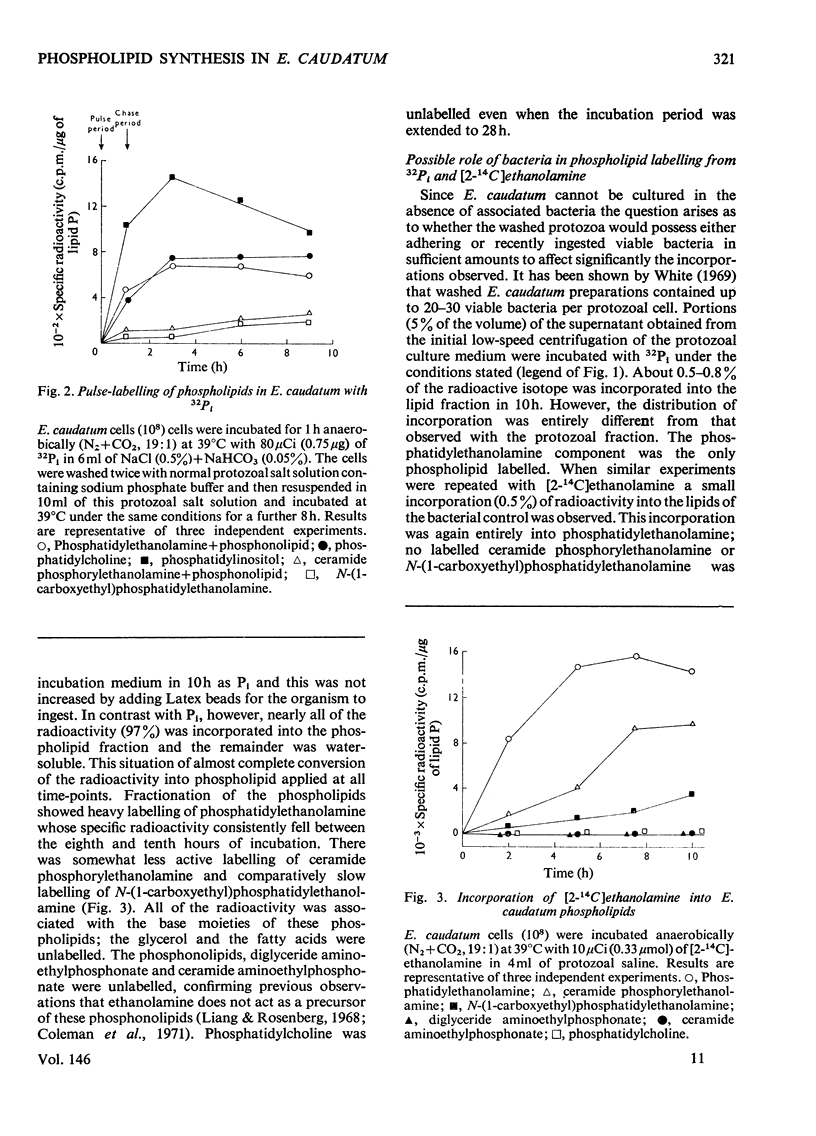
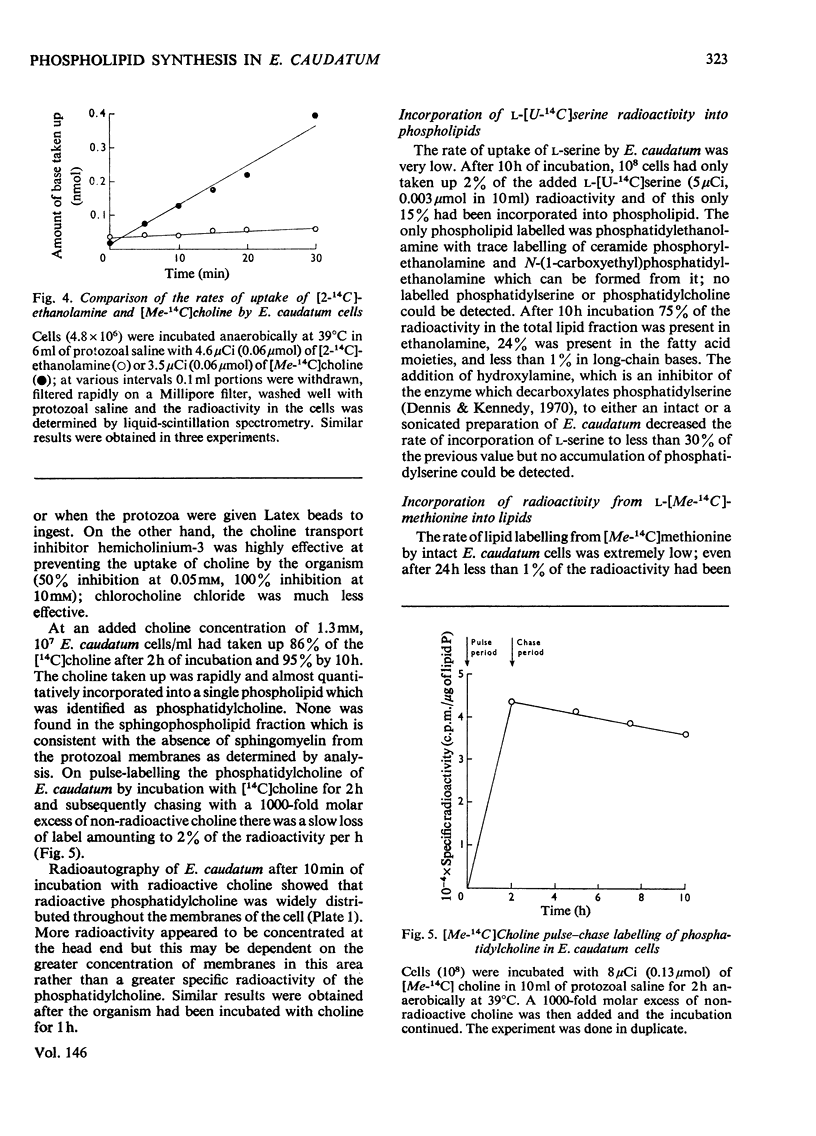
1. The anaerobic rumen protozoon Entodinium caudatum was incubated either intact or with various radioactive precursors of phospholipids after ultrasonication. 2. Pulse-chase experiments showed a rapid turnover of phosphatidylinositol and much slower turnovers of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. 3. E. caudatum imbibed choline very rapidly; this was immediately and exclusively converted into phosphatidylcholine which was shown by radioautography after 10 min to be distributed throughout the cell membranes. 4. Phosphatidylcholine was synthesized through a phosphorylcholine-CDP-choline pathway, the methylation or base-exchange pathways not being present. 5. Under suitable conditions [Me-14C]choline can be substantially (50-60%) converted into CDP-choline by sonicated E. caudatum and this provides an excellent method of preparing this biosynthetic intermediary. 6. [2-14C]Ethanolamine was taken up much less readily than choline. The former was incorporated into phosphatidylethanolamine by the CDP-ethanolamine pathway. 7. Doubly labelled [32P]phosphatidyl[2-3H]ethanolamine was converted into ceramide phosphorylethanolamine and N-(1-carboxyethyl)phosphatidyl-ethanolamine, without change in the isotopic ratio. Ceramide phosphoryl [2-14C]-ethanolamine was converted into phsophatidylethanolamine. 8. Palmitic acid, oleic acid and linoleic acid were taken by E. caudatum cells and incorporated into phospholipids. By contrast, although stearic acid was taken up it was hardly incorporated into phospholipids.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANSELL G. B., DOHMEN H. The metabolism of individual phospholipids in the rat brain during hypoglycaemia, anaesthesia and convulsions. J Neurochem. 1957;2(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1957.tb12346.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
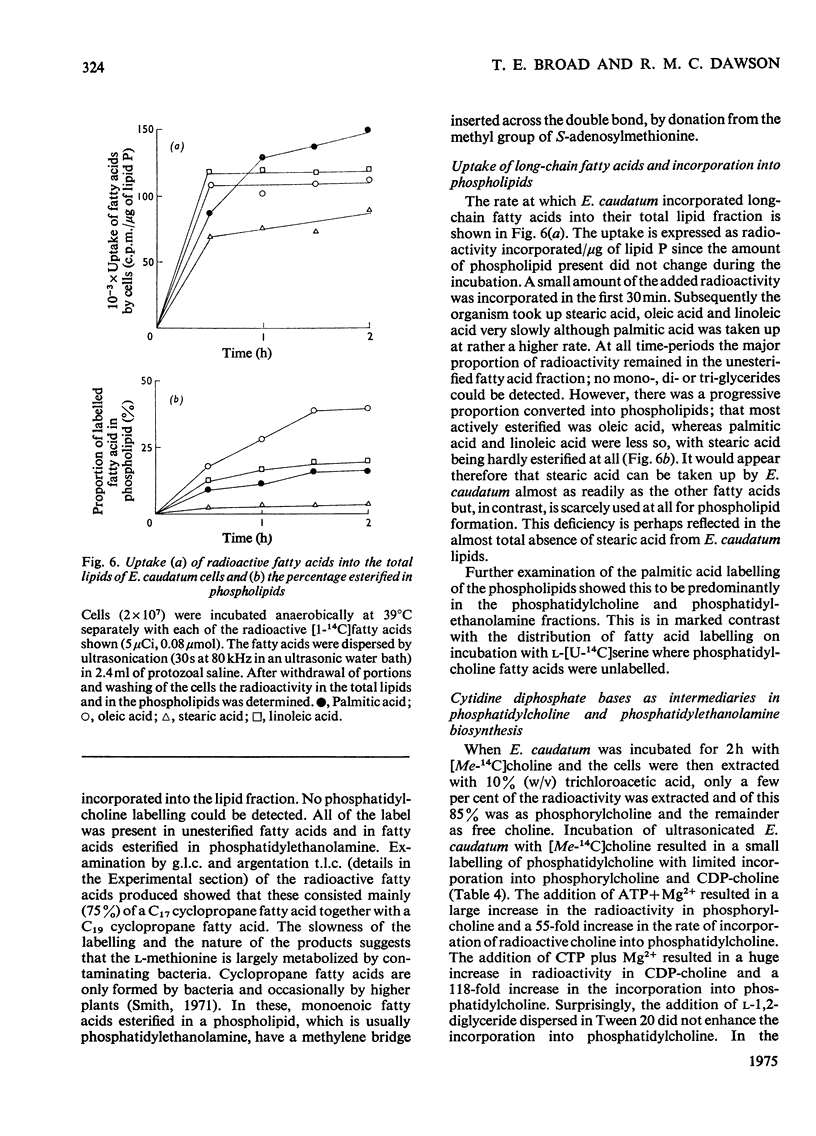
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCKERHOFF H. BREAKDOWN OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS IN MILD ALKALINE HYDROLYSIS. J Lipid Res. 1963 Jan;4:96–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broad T. E., Dawson R. M. Formation of ceramide phosphorylethanolamine from phosphatidylethanolamine in the rumen protozoon Entodinium caudatum (Short Communication). Biochem J. 1973 Jun;134(2):659–662. doi: 10.1042/bj1340659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLEMAN G. S. The cultivation of sheep rumen oligotrich protozoa in vitro. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Apr;22:555–563. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-2-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLEMAN G. S. The preparation and survival of almost bacteria-free suspensions of Entodinium caudatum. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Jun;28:271–281. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-2-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chlapowski F. J., Band R. N. Assembly of lipids into membranes in Acanthamoeba palestinensis. I. Observations on the specificity and stability of choline- 14 C and glycerol- 3 H as labels for membrane phospholipids. J Cell Biol. 1971 Sep;50(3):625–633. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie W. W., Holman R. T. Mass spectrometry of lipids. I. Cyclopropane fatty acid esters. Lipids. 1966 May;1(3):176–182. doi: 10.1007/BF02531869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman G. S., Kemp P., Dawson R. M. The catabolism of phosphatidylethanolamine by the rumen protozoon Entodinium caudatum and its conversion into the N-(1-carboxyethyl) derivative. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(1):97–104. doi: 10.1042/bj1230097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman G. S. The metabolism of starch, maltose, glucose and some other sugars by the rumen ciliate Entodinium caudatum. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Aug;57(3):303–332. doi: 10.1099/00221287-57-3-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. The incorporation of labelled phosphate into the phosphoglycerides of intact rat liver. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):552–555. doi: 10.1042/bj0610552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Kemp P. The aminoethylphosphonate-containing lipids of rumen protozoa. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):837–842. doi: 10.1042/bj1050837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis E. A., Kennedy E. P. Enzymatic synthesis and decarboxylation of phosphatidylserine in Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Lipid Res. 1970 Sep;11(5):394–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Koch M. A. Biosynthesis of sphingomyelin. Transfer of phosphorylcholine from phosphatidylcholine to erythro-ceramide in a cell-free system. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1973 Dec;354(12):1661–1665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Marggraf W. D., Koch M. A., Anderer F. A. Evidence for a new biosynthetic pathway of sphingomyelin in SV 40 transformed mouse cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1345–1352. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAVER R. C., SWEELEY C. C. METHODS FOR METHANOLYSIS OF SPHINGOLIPIDS AND DIRECT DETERMINATION OF LONG-CHAIN BASES BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Apr;42:294–298. doi: 10.1007/BF02540132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungalwala F. B., Freinkel N., Dawson R. M. The metabolism of phosphatidylinositol in the thyroid gland of the pig. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(1):19–33. doi: 10.1042/bj1230019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp P., Dawson R. M. Isolation of a new phospholipid, phosphatidyl-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-alanine, from rumen protozoa. Biochem J. 1969 Jul;113(3):555–558. doi: 10.1042/bj1130555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp P., Dawson R. M. Isomerization of linolenic acid by rumen micro-organisms. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(3):477–478. doi: 10.1042/bj1090477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp P., Dawson R. M., Klein R. A. A new bacterial sphingophospholipid containing 3-aminopropane-1,2-diol. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(1):221–227. doi: 10.1042/bj1300221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang C. R., Rosenberg H. The biosynthesis of the carbon-phosphorus bond in Tetrahymena. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 11;156(2):437–439. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90283-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lust G., Daniel L. J. The biosynthesis of the methyl groups of choline in Ochromonas malhamensis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Mar;113(3):603–608. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90237-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. K., Dawson R. M. Can mitochondria and synaptosomes of guinea-pig brain synthesize phospholipids? Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(4):805–821. doi: 10.1042/bj1260805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarles R. H., Dawson R. M. The hydrolysis of monolayers of phosphatidyl(Me-14C)choline by phospholipase D. Biochem J. 1969 Jul;113(4):697–705. doi: 10.1042/bj1130697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock R. C. Incorporation of 14 C-labelled non-lipid precursors into lipid of Plasmodium knowlesi in vitro. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1971 Nov 15;40(3):657–669. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(71)90141-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. D., Law J. H. Phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 10;202(1):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90225-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. A., Jr Studies of membrane formation in Tetrahymena pyriformis. I. Rates of phospholipid biosynthesis. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):2015–2022. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipton C. L., Swords M. D. Biosynthesis of phosphatidylcholine in Euglena gracilis. J Protozool. 1966 Aug;13(3):469–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1966.tb01941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman M. D., Radin N. S. The enzymatic formation of sphingomyelin from ceramide and lecithin in mouse liver. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1506–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaskovsky V. E., Kostetsky E. Y. Modified spray for the detection of phospholipids on thin-layer chromatograms. J Lipid Res. 1968 May;9(3):396–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. F., Scott T. W., Dawson R. M. The hydrogenation of unsaturated fatty acids in the ovine digestive tract. Biochem J. 1964 Jul;92(1):60–68. doi: 10.1042/bj0920060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. W. Viable bacteria inside the rumen ciliate Entodinium caudatum. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Jun;56(3):403–408. doi: 10.1099/00221287-56-3-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



