Abstract
1. Two methods were used to obtain alpha-mannosidase free from unbound Zn2+, (a) by removal of excess of metal ion from preparations purified in the presence of Zn2+ and (b) by purification under conditions that eliminate the need to add Zn2+. 2. The purified enzyme is homogeneous on ultracentrifugation, polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis and gel chromatography. 3. The molecular weight is estimated to be 230 000. 4. The enzyme contains between 470 and 565 mug of zinc/g of protein, corresponding to between 1.7 and 2 atoms of zinc/enzyme molecule. The contents of other metals are much lower. 5. The enzyme is inactivated by chelating agents and activity is restored by Zn2+. 6. No other metal ion was found to replace Zn2+ with retention of activity. Some bivalent metal ions, e.g. Cu2+, rapidly inactivate the enzyme. 7. The results indicate that jack-bean alpha-mannosidase exists naturally as a zinc-protein complex and may be considered as a metalloenzyme.
Full text
PDF


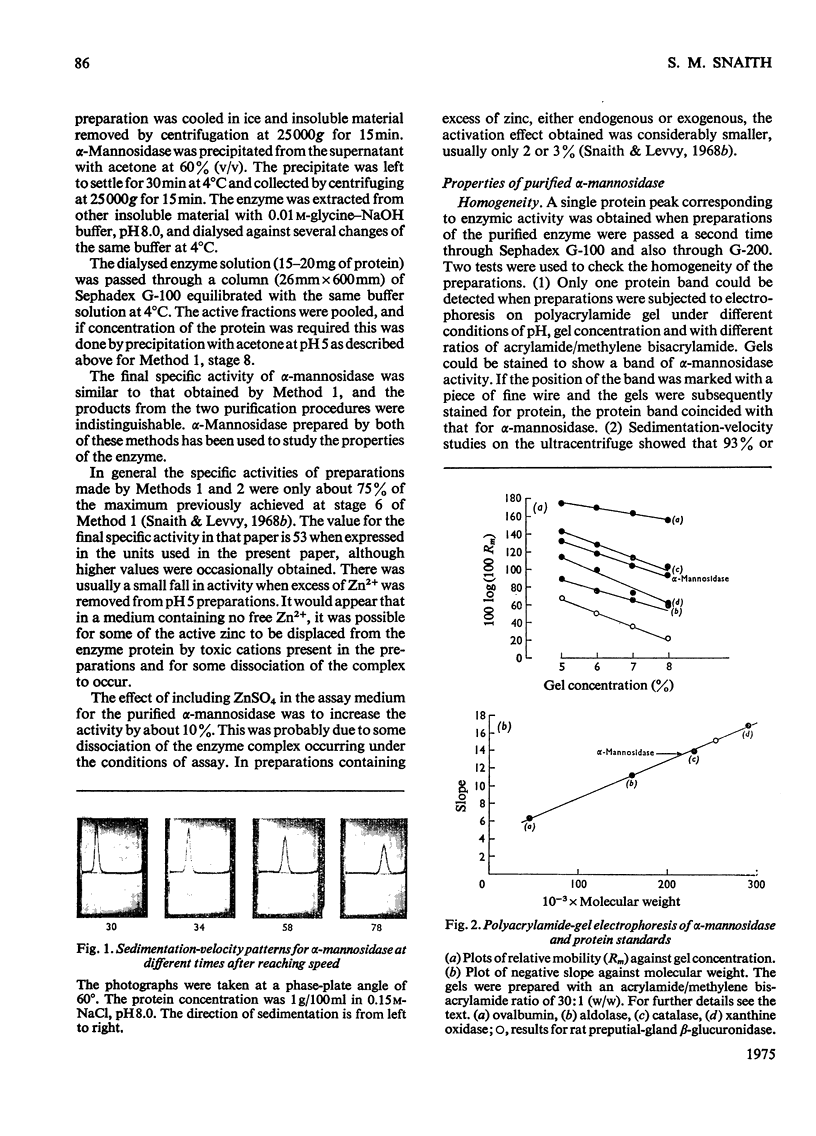

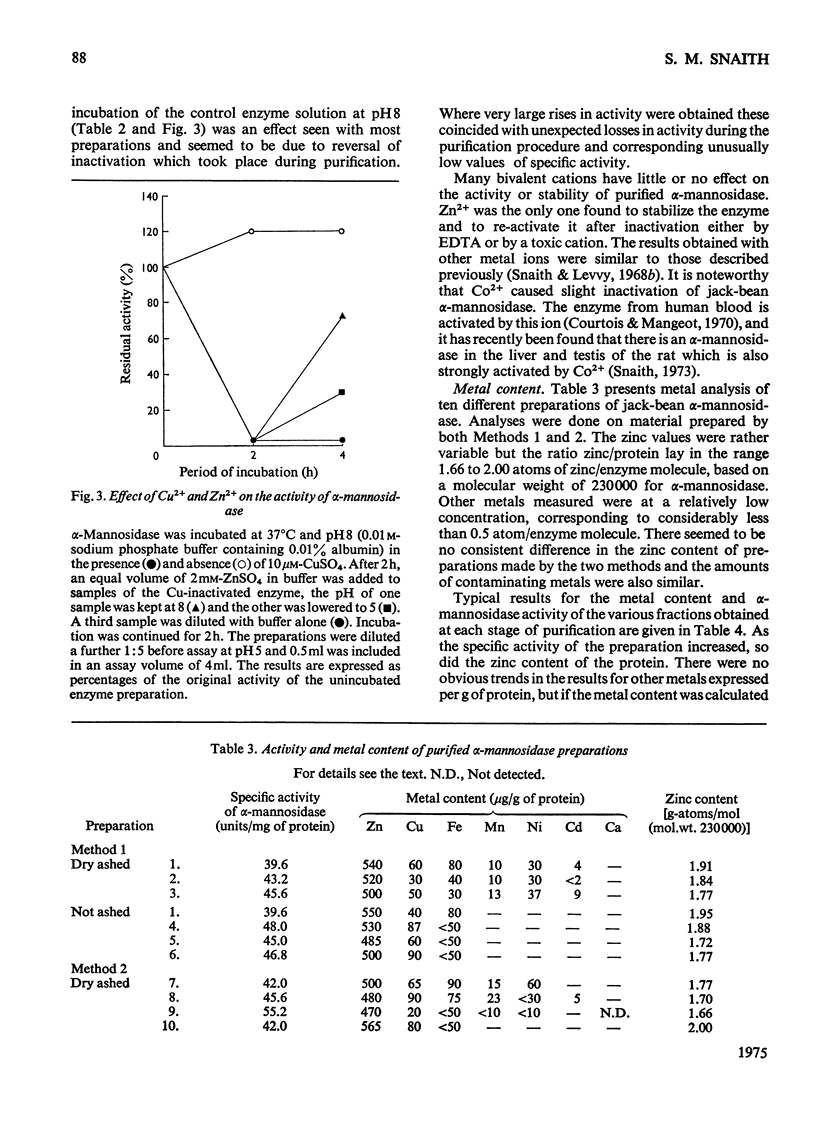
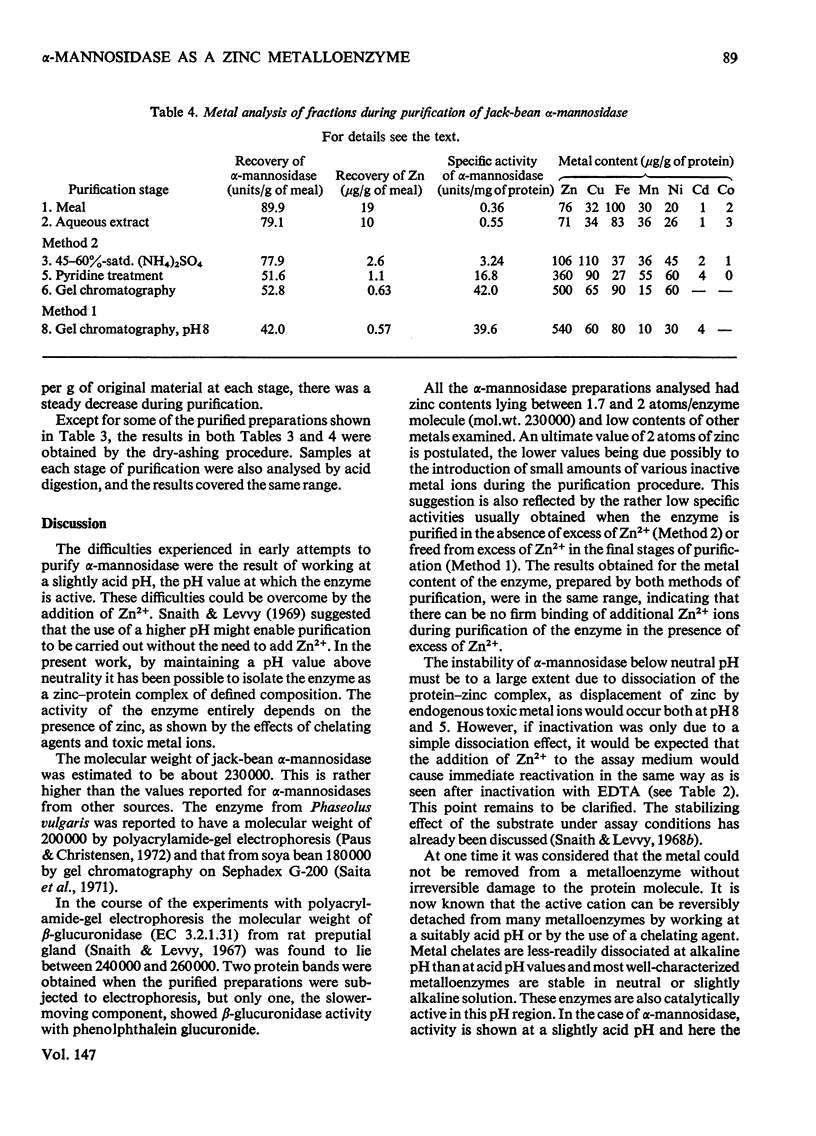

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avila J. L., Convit J. Characterization and properties of alpha-D-mannosidase of human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Sep 14;47(3):335–345. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90265-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois J. E., Mangeot M. Etude de l'alpha-mannosidase du sérum sanguin humain, son activation par le cobalt. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 Jun 1;270(22):2727–2728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumura T., Yamashina I. Purification of alpha-mannosidase from hog kidney and its action on glycopeptides. J Biochem. 1970 Oct;68(4):561–571. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paus E., Christensen T. B. Alpha-mannosidase from Phaseolus vulgaris. Purification and characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Feb 15;25(2):308–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petek F., Villarroya E. Purification et propriétés de l'alpha-mannosidase des graines germées de vicia sativa. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1968;50(4):725–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saita M., Ikenaka T., Matsushima Y. Isolation and characterization of -D-mannosidase from soy bean. J Biochem. 1971 Nov;70(5):827–833. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snaith S. M. Activation by ferrous ions of an alpha-mannosidase in rat testis and liver. Biochem Soc Trans. 1973 Nov;1(6):1266–1267. doi: 10.1042/bst0011266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snaith S. M., Levvy G. A., Hay A. J. Purification and properties of alpha-D-mannosidase from the limpet, Patella vulgata. Biochem J. 1970 Mar;117(1):129–137. doi: 10.1042/bj1170129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snaith S. M., Levvy G. A. Purification and properties of alpha-D-mannosidase from jack-bean meal. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(4):663–670. doi: 10.1042/bj1100663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snaith S. M., Levvy G. A. Purification and properties of alpha-D-mannosidase from rat epididymis. Biochem J. 1969 Aug;114(1):25–33. doi: 10.1042/bj1140025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snaith S. M., Levvy G. A. Purification of beta-glucuronidase from the female-rat preputial gland on Sephadex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;146(2):599–600. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90248-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukeno T., Tarentino A. L., Plummer T. H., Jr, Maley F. Purification and properties of -D- and -D-mannosidases from hen oviduct. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 11;11(8):1493–1501. doi: 10.1021/bi00758a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki I., Kushida H. Studies on mammalian glycosidases. V. Effects of metal ions upon acidic and neutral alpha-glucosidases, beta-galactosidases, and alpha-mannosidases in liver extract of rabbit. J Biochem. 1973 Sep;74(3):627–629. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALLEE B. L. Zinc and metalloenzymes. Adv Protein Chem. 1955;10:317–384. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]