Abstract
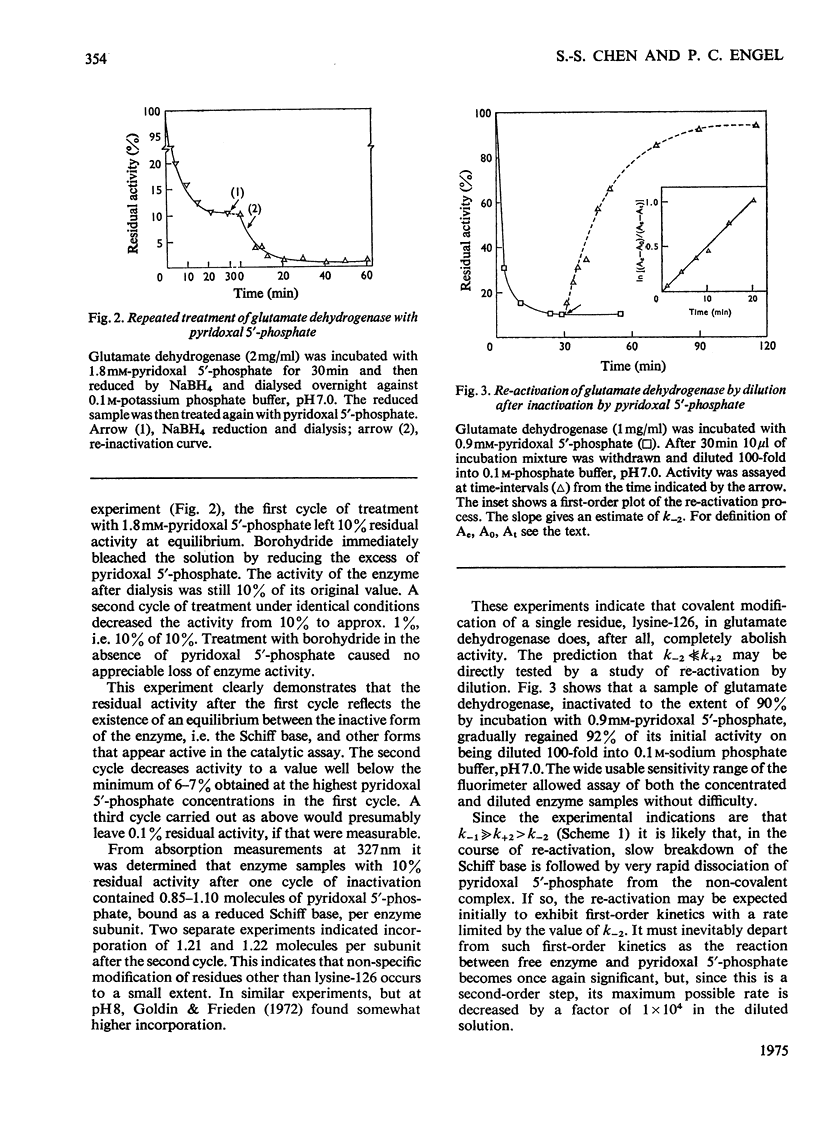
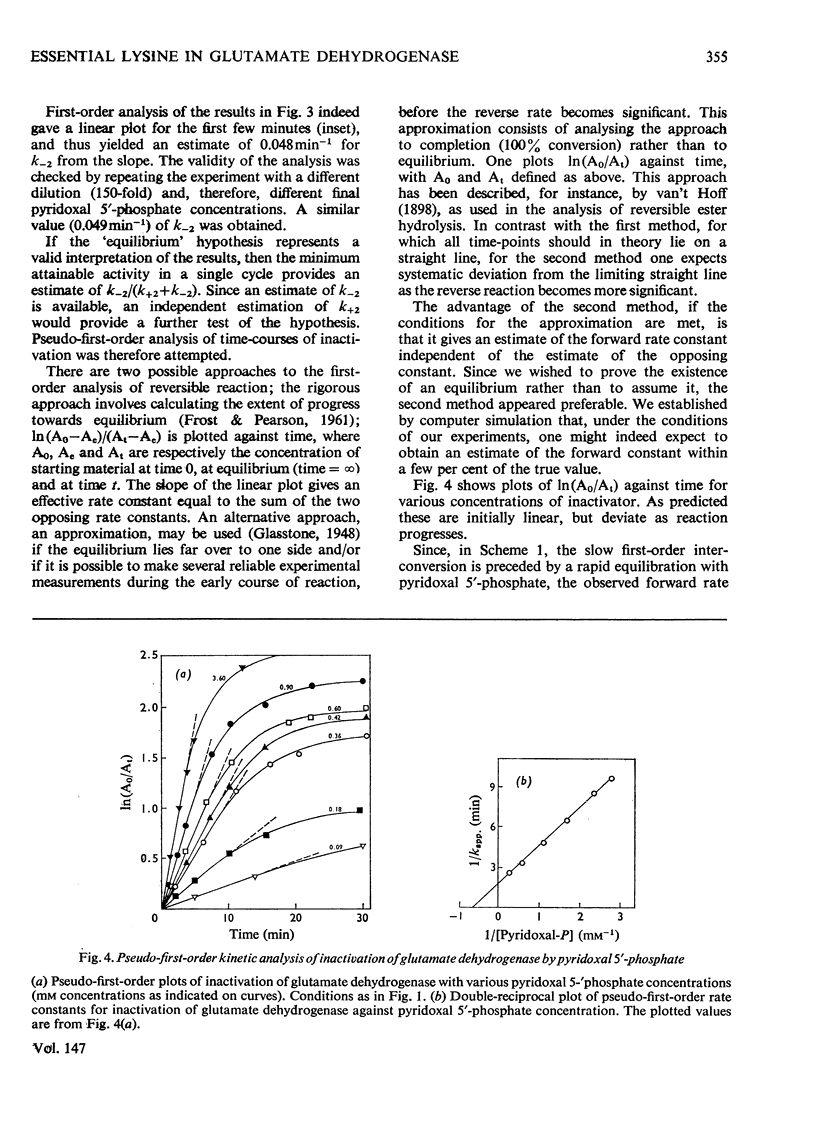
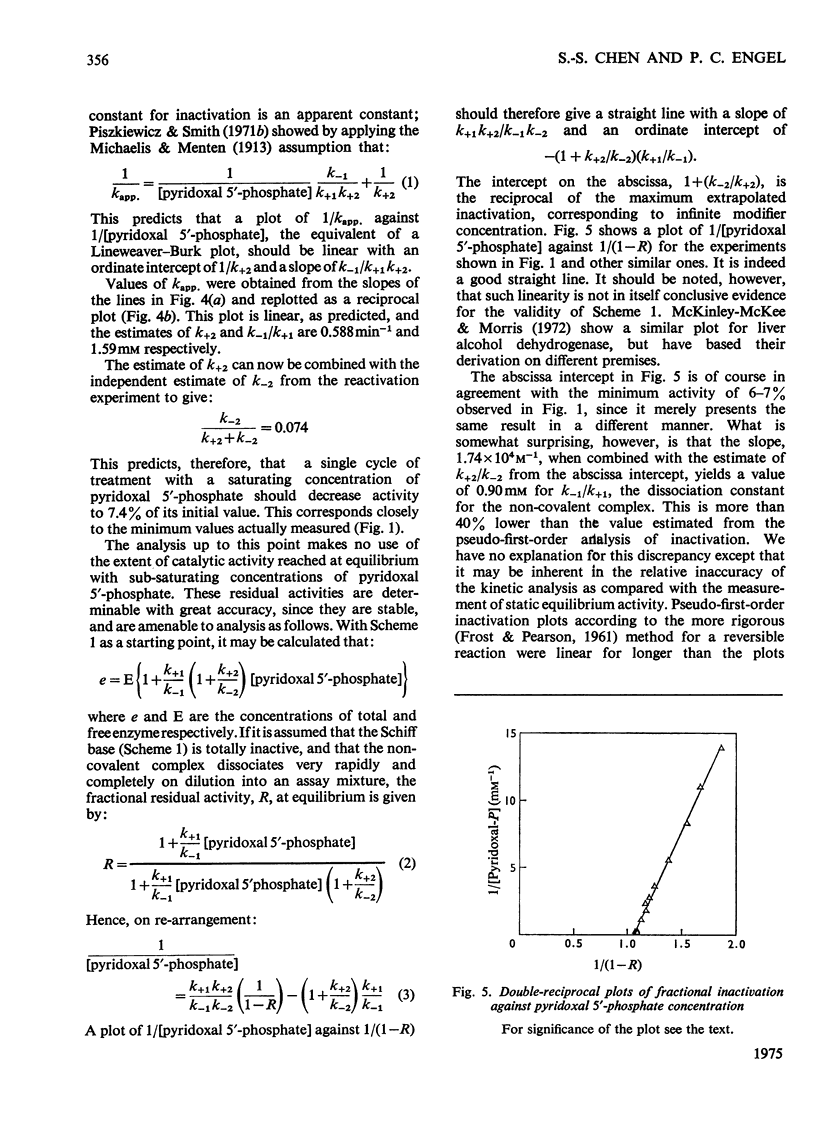
1. The activity of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase incubated with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate declined to a steady value reached within 30--60 min. The residual activity depended on the concentration of modifier up to about 5 mM. Above this concentration, however, no further inactivation was produced. The minimum activity obtainable in such incubations was 6--7% of the initial value. 2. Km values of the modified enzyme were unaltered, whereas Vmax. was decreased. 3. Activity was fully regained on dialysis against 0.1 M-potassium phosphate buffer. 4. Reduction with borohydride rendered the inactivation permanent but did not alter its extent. 5. Enzyme permanently inactivated in this way to the extent of 90% and dialysed was re-treated with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. In this second cycle activity declined from 10 to 1% of the original activity. 6. This strongly suggests that the failure to achieve complete inactivation in a single cycle reflects a reversible equilibrium between inactive Schiff base, i.e. covalently modified enzyme, and a non-covalent complex. 7. The re-inactivation reaction occurring on dilution was demonstrated directly and a first-order rate constant obtained (0.048 min-1). This, in conjunction with an estimate of the forward rate constant for Schiff-base formation, obtained by approximate pseudo-first-order analysis of inactivation at varied modifier concentrations, gives a predicted minimum activity very close to that actually obtained in a single cycle of treatment. 8. The dissociation constant of the non-covalent complex is given by two methods as 0.90 and 1.59mM. 9. The results indicate that covalent modification with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate completely abolishes the activity of glutamate dehydrogenase.
Full text
PDF

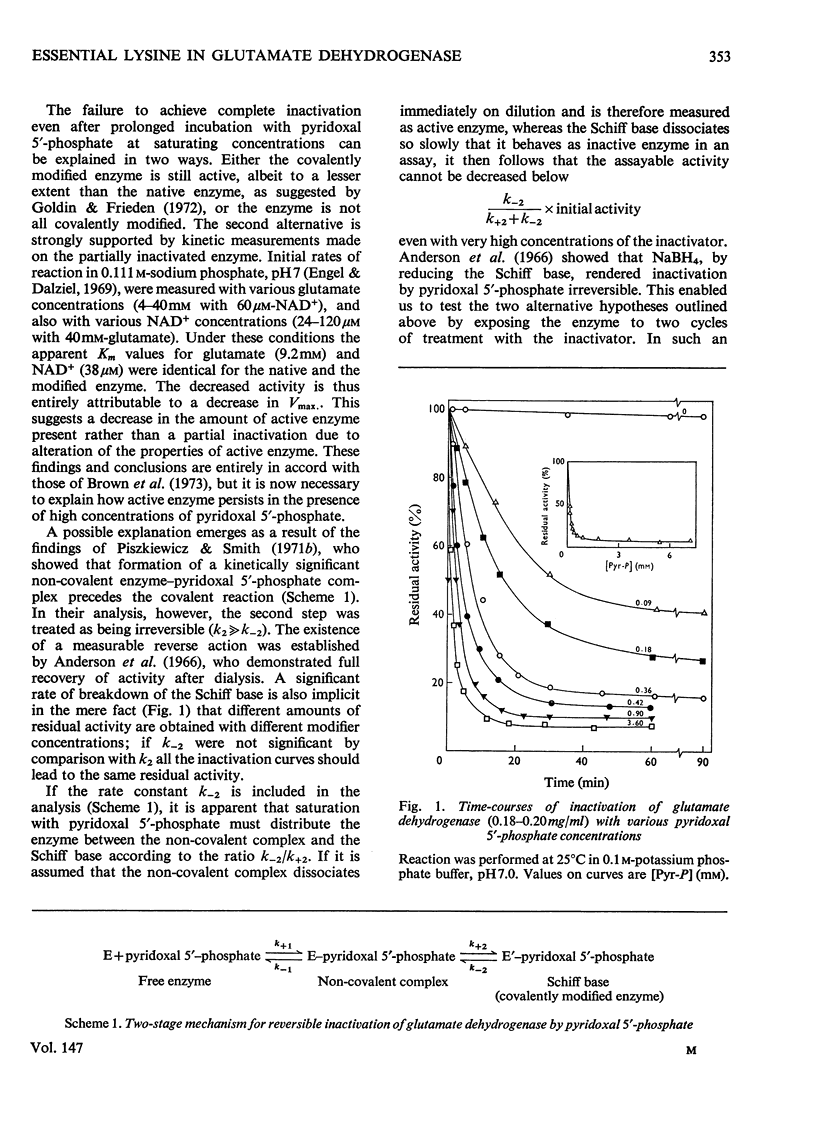


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B. M., Anderson C. D., Churchich J. E. Inhibition of glutamic dehydrogenase by pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. Biochemistry. 1966 Sep;5(9):2893–2900. doi: 10.1021/bi00873a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A., Culver J. M., Fisher H. F. Mechanism of inactivation of L-glutamate dehydrogenase by pyridoxal and pyridoxal phosphate. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 23;12(22):4367–4373. doi: 10.1021/bi00746a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffee C. J., Bradshaw R. A., Goldin B. R., Frieden C. Identification of the sites of modification of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase reacted with trinitrobenzenesulfonate. Biochemistry. 1971 Sep 14;10(19):3516–3526. doi: 10.1021/bi00795a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALZIEL K. Kinetic studies of liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1962 Aug;84:244–254. doi: 10.1042/bj0840244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Prisco G. Tyrosyl and lysyl residues involved in the reactivity of catalytic and regulatory sites of crystalline beef liver glutamate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1971 Feb 16;10(4):585–589. doi: 10.1021/bi00780a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan R. R., Dalziel K. Active centre equivalent weight of glutamate dehydrogenase from dry weight determinations and spectrophotometric titrations of abortive complexes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Oct;250(1):47–50. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel P. C., Dalziel K. Kinetic studies of glutamate dehydrogenase with glutamate and norvaline as substrates. Coenzyme activation and negative homotropic interactions in allosteric enzymes. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(4):621–631. doi: 10.1042/bj1150621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin B. R., Frieden C. The effect of pyridoxal phosphate modification on the catalytic and regulatory properties of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2139–2144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook J. J., Jeckel R. A peptide containing a reactive lysyl group from ox liver glutamate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1969 Mar;111(5):689–694. doi: 10.1042/bj1110689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook J. J., Roberts P. A., Wallis R. B. The site at which 4-iodoacetamidosalicylate reacts with glutamate dehydrogenases. Biochem J. 1973 May;133(1):165–171. doi: 10.1042/bj1330165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm A. D., Radda G. K. Allosteric transitions of glutamate dehydrogenase. Nature. 1968 Aug 31;219(5157):947–949. doi: 10.1038/219947a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm A. D., Radda G. K. The reaction of glutamate dehydrogenase with 4-iodoacetamido salicylic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Sep;15(3):555–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley-McKee J. S., Morris D. L. The lysines in liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Chemical modification with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate and methyl picolinimidate. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jun 23;28(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01877.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piszkiewicz D., Landon M., Smith E. L. Bovine liver flutamate dehydrogenase. Sequence of a hexadecapeptide containing a lysyl residue reactive with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 25;245(10):2622–2626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piszkiewicz D., Smith E. L. Bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase. Equilibria and kinetics of inactivation by pyridoxal. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4538–4544. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veronese F. M., Piszkiewicz D., Smith E. L. Inactivation of bovine glutamate dehydrogenase by carbamyl phosphate and cyanate. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):754–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis R. B., Holbrook J. J. The effect of modifying lysine-126 on the physical, catalytic and regulatory properties of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1973 May;133(1):173–182. doi: 10.1042/bj1330173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


