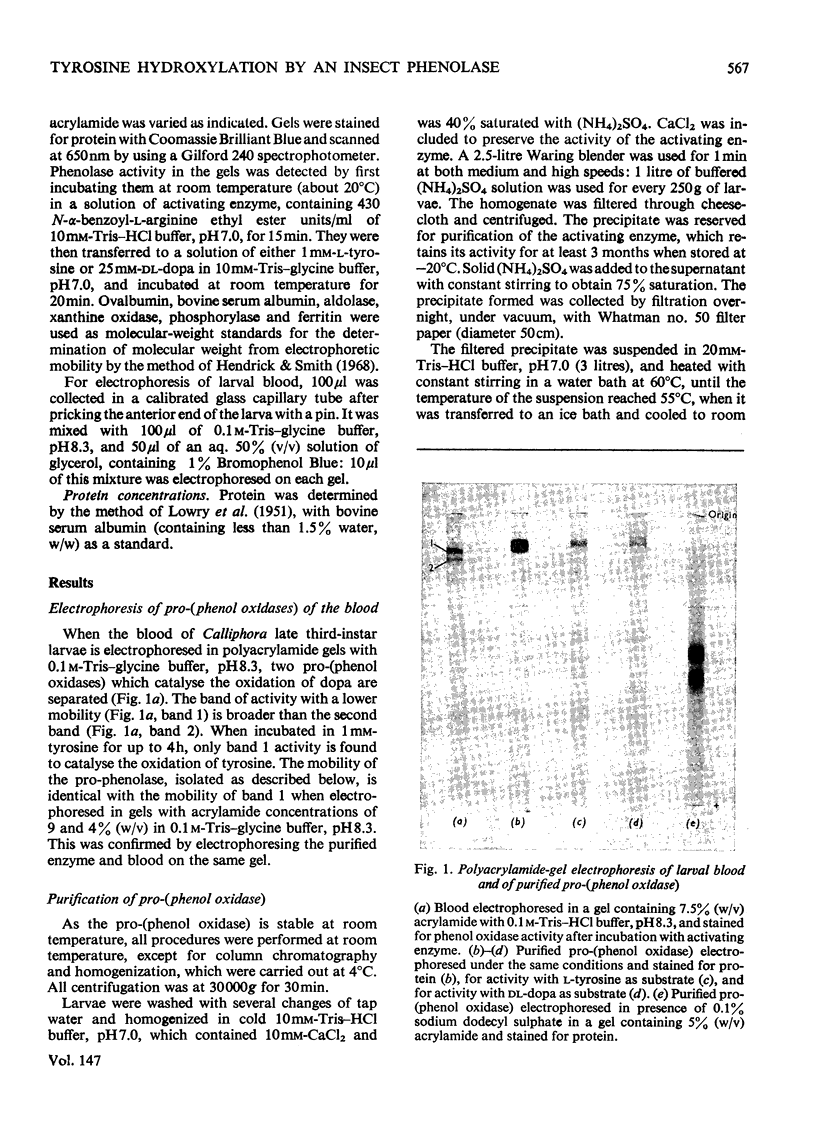
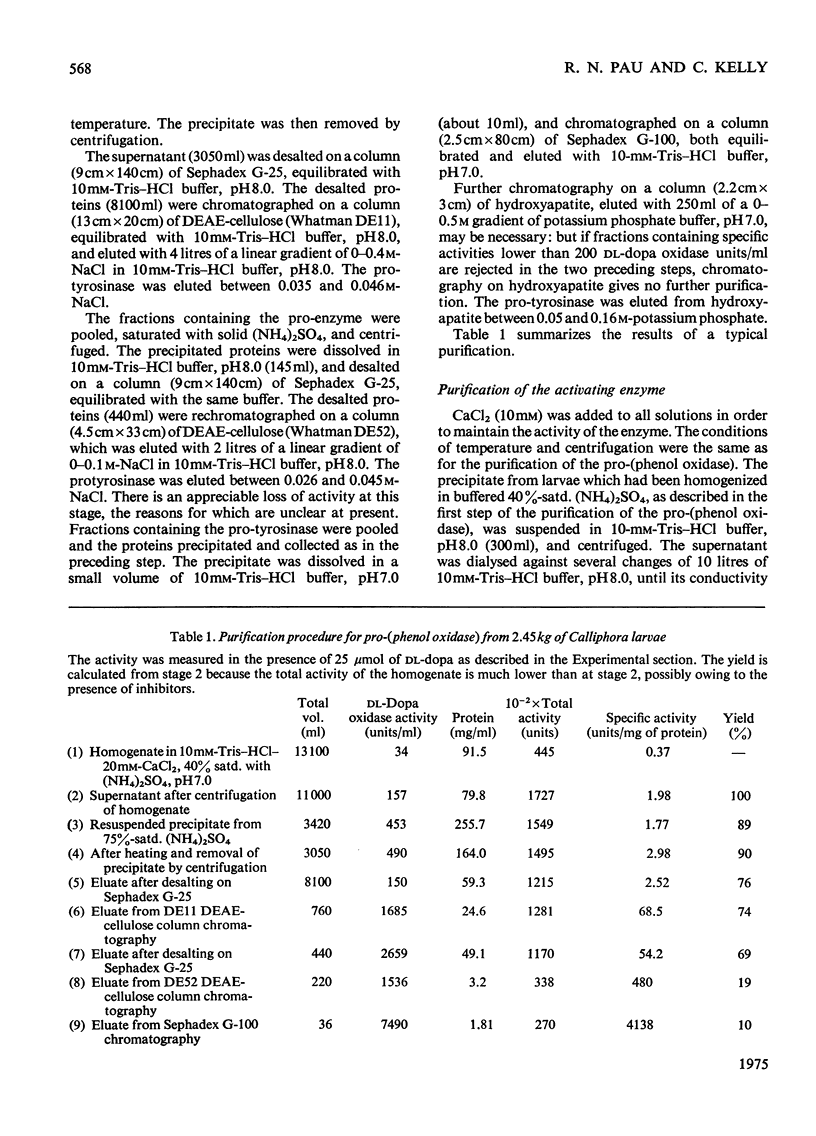
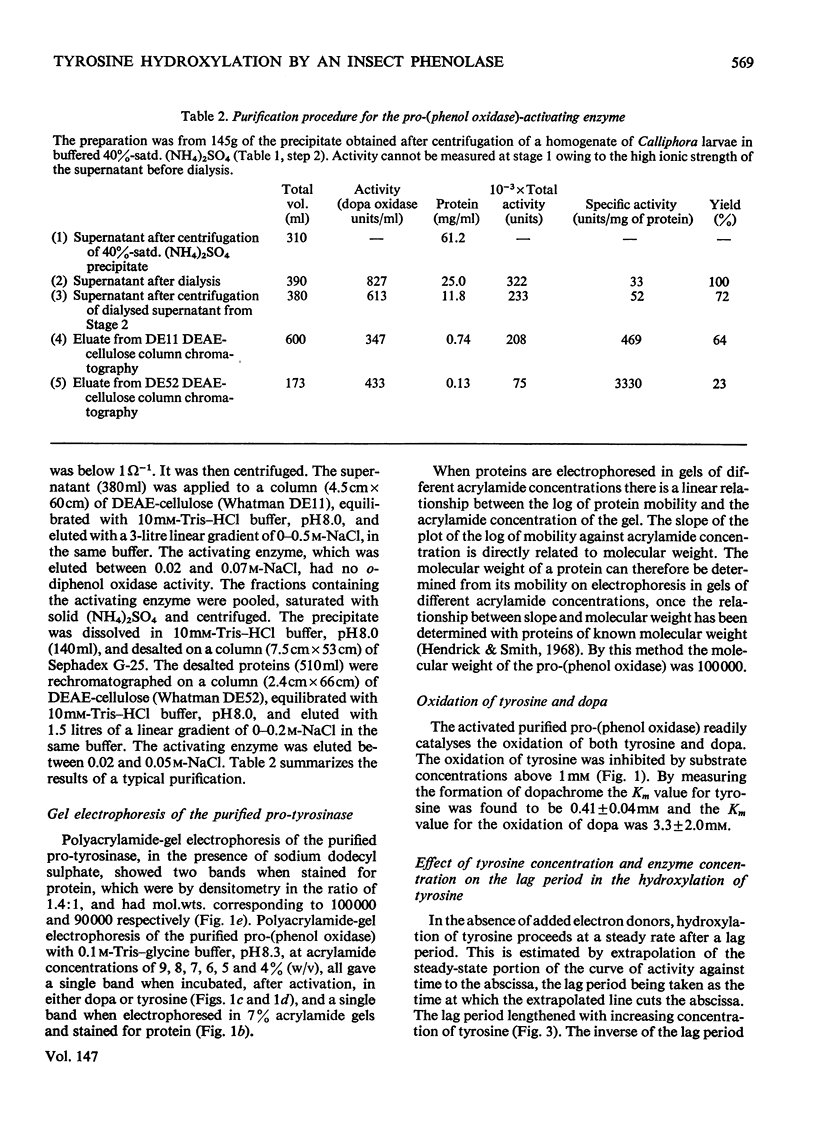
Abstract
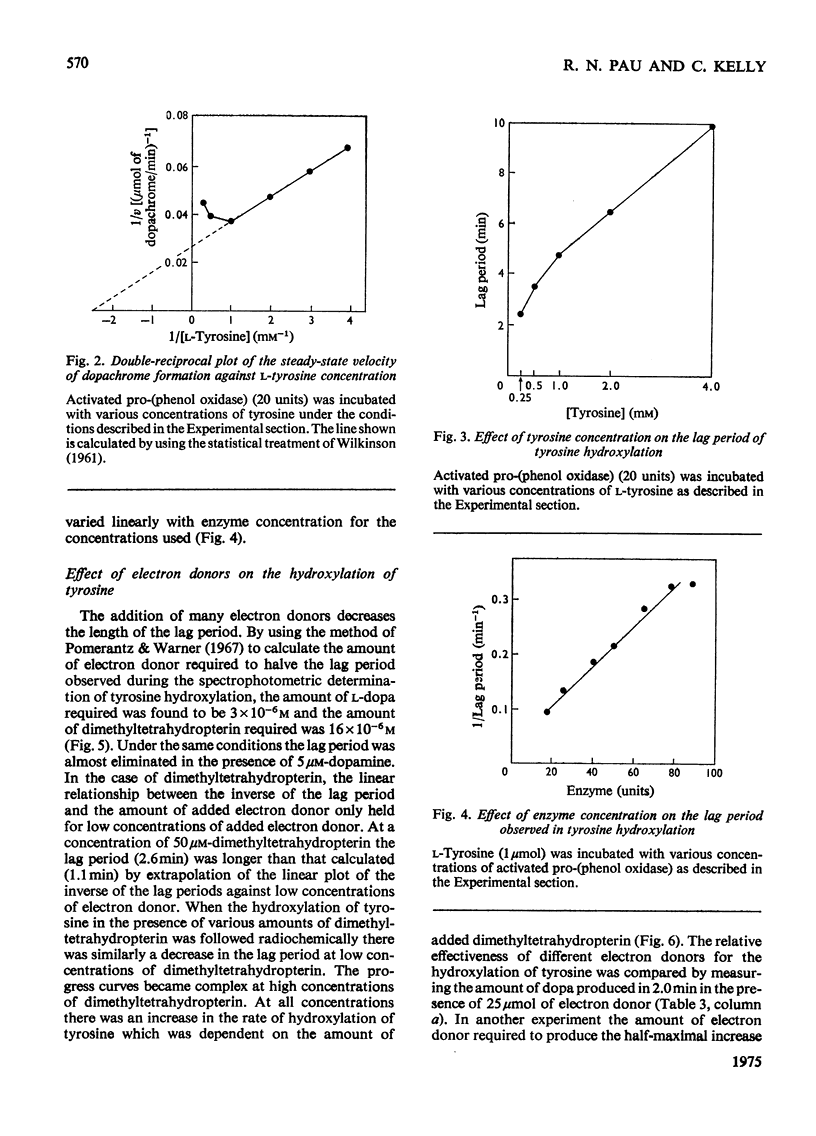
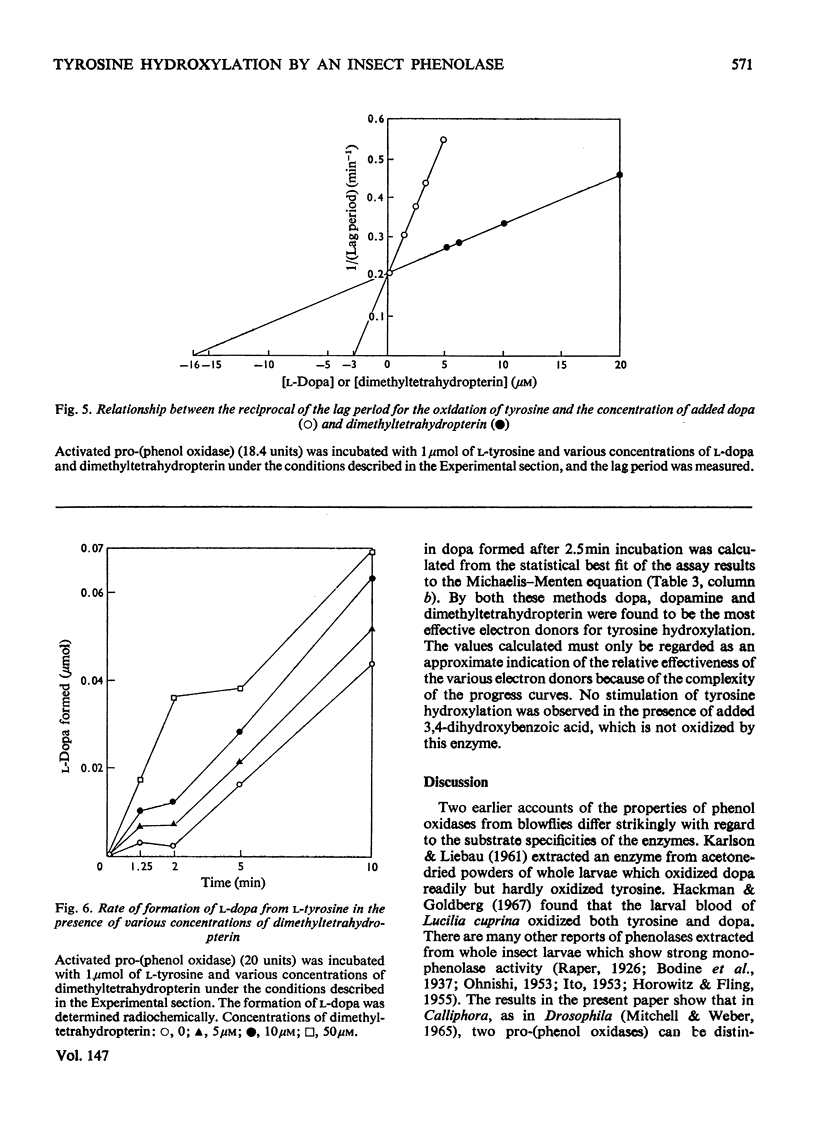
1. Two pro-(phenol oxidase) were distinguished when the blood of late-third-instar larvae of Calliphora erythrocephala was electrophoresed in polyacrylamide gels with Tris-glycine buffer, pH 8.3. One pro-(phenol oxidase), after activation by an enzyme readily catalyses the oxidation of both L-tyrosine and L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-dopa). The second enzyme catalyses the oxidation of L-dopa but not of L-tyrosoine. 2. One of the pro-(phenol oxidases) was purified over 2000-fold from homogenates of whole larvae. This enzyme, after activation, catalyses the oxidation of both dopa and tyrosine. On electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gels with Tris-glycine buffer, pH 8.3, it has the same mobility as the enzyme in the blood which catalyses the oxidation of both tyrosine and dopa. 3. The pro-(phenol oxidase)-activating enzyme was purified over 100-fold from homogenates of whole larvae. 4. The oxidation of L-tyrosine, in the presence of the activated purified phenol oxidase, reached a steady maximum rate after a lag period that was directly related to tyrosine concentration and inversely related to enzyme concentration. 5. The effect of the addition of electron donors on the lag period was studied. Dopa, dopamine (3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) and 2-amino-4-hydroxy-6,7-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropteridine are the most effective hydrogen donors. 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid, the oxidation of which was not catalysed by the activated pro-(phenol oxidase), did not affect the lag period.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashida M. Purification and characterization of pre-phenoloxidase from hemolymph of the silkworm Bombyx mori. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jun;144(2):749–762. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90383-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohke K. Studies on prephenoloxidase-activating enzyme from cuticle of the silkworm Bombyx mori. I. Activation reaction by the enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jul;157(1):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90406-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C., Raper H. S. The accumulation of l-3:4-dihydroxyphenylalanine in the tyrosinase-tyrosine reaction. Biochem J. 1937 Dec;31(12):2162–2170. doi: 10.1042/bj0312162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLING M., HOROWITZ N. H., HEINEMANN S. F. The isolation and properties of crystalline tyrosinase from Neurospora. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jun;238:2045–2053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARLSON P., LIEBAU H. [On tyrosine metabolism of insects. V. Preparation in a pure state, crystallization and substrate specificity of o-diphenol oxidase from Calliphora erythrocephala]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1961 Nov 24;326:135–143. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1961.326.1.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL H. K., WEBER U. M. DROSOPHILA PHENOL OXIDASES. Science. 1965 May 14;148(3672):964–965. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3672.964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munn E. A., Bufton S. F. Purification and properties of a phenol oxidase from the blowfly Calliphora erythrocephala. Eur J Biochem. 1973 May;35(1):3–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGATSU T., LEVITT M., UDENFRIEND S. TYROSINE HYDROXYLASE. THE INITIAL STEP IN NOREPINEPHRINE BIOSYNTHESIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2910–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi E., Dohke K., Ashida M. Activation of prephenoloxidase. II. Activation by alpha-chymotrypsin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Jul;139(1):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz S. H. The tyrosine hydroxylase activity of mammalian tyrosinase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 10;241(1):161–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz S. H., Warner M. C. 3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine as the tyrosinase cofactor. Occurrence in melanoma and binding constant. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5308–5314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raper H. S. The Tyrosinase-Tyrosine Reaction: Production of l-3.4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine from Tyrosine. Biochem J. 1926;20(4):735–742. doi: 10.1042/bj0200735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWEIGER A., KARLSON P. [On tyrosine metabolism by insects. X. Activation of prephenoloxidase and the activator enzyme]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1962 Nov 15;329:210–221. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1962.329.1.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEKERIS C. E., MERGENHAGEN D. PHENOLOXIDASE SYSTEM OF THE BLOWFLY, CALLIPHORA ERYTHROCEPHALA. Science. 1964 Jul 3;145(3627):68–69. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3627.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan P. F., Butt V. S. The hydroxylation of p-coumaric acid by an enzyme from leaves of spinach beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):109–115. doi: 10.1042/bj1130109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]