Abstract
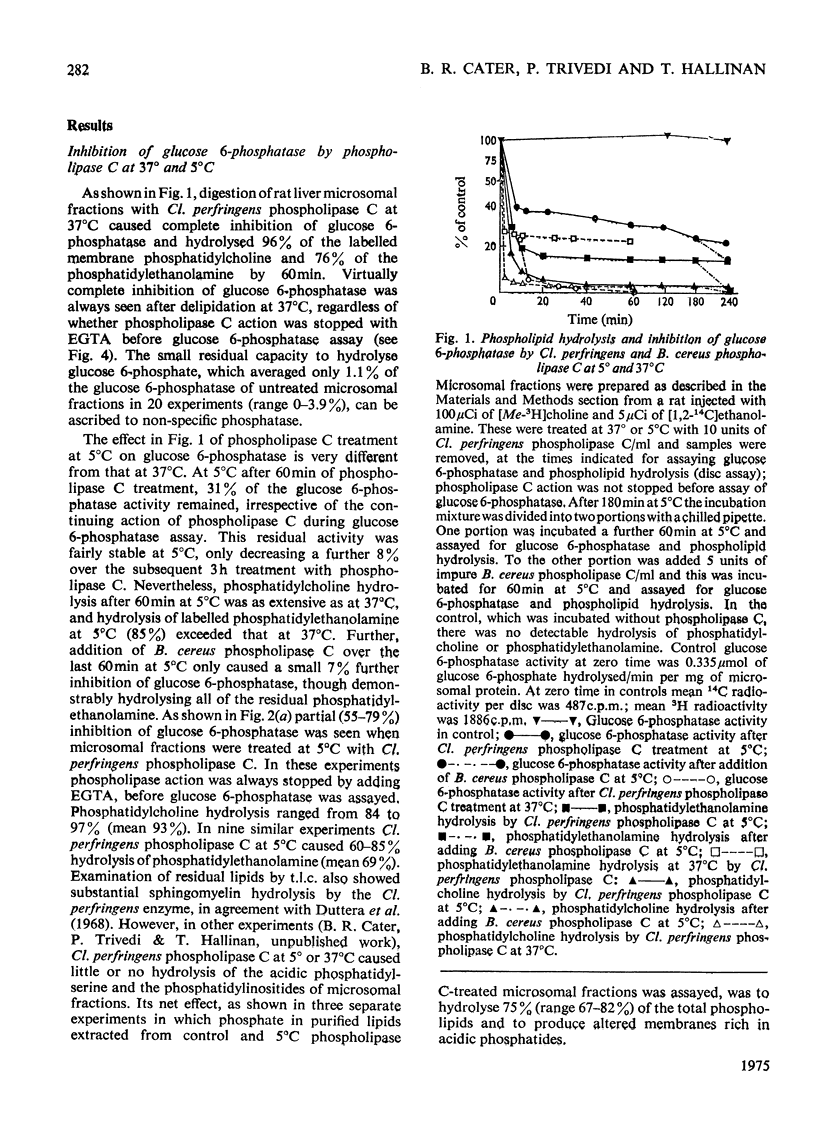
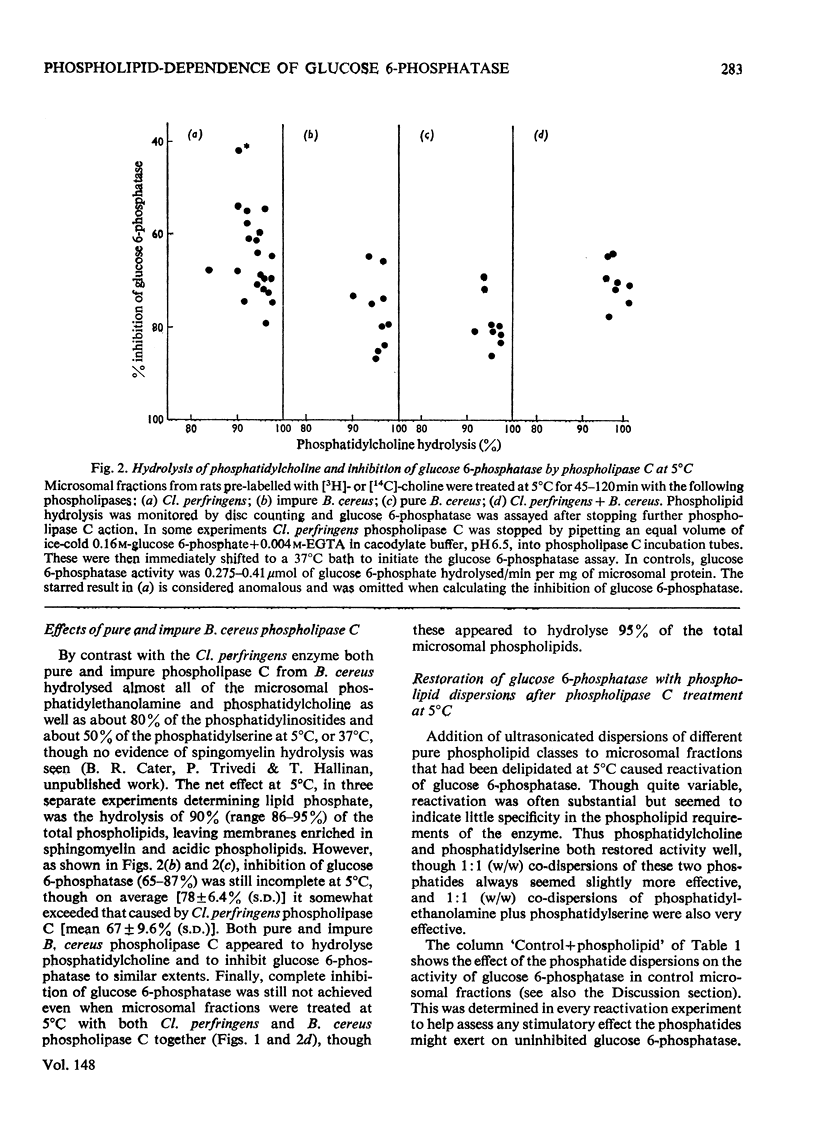
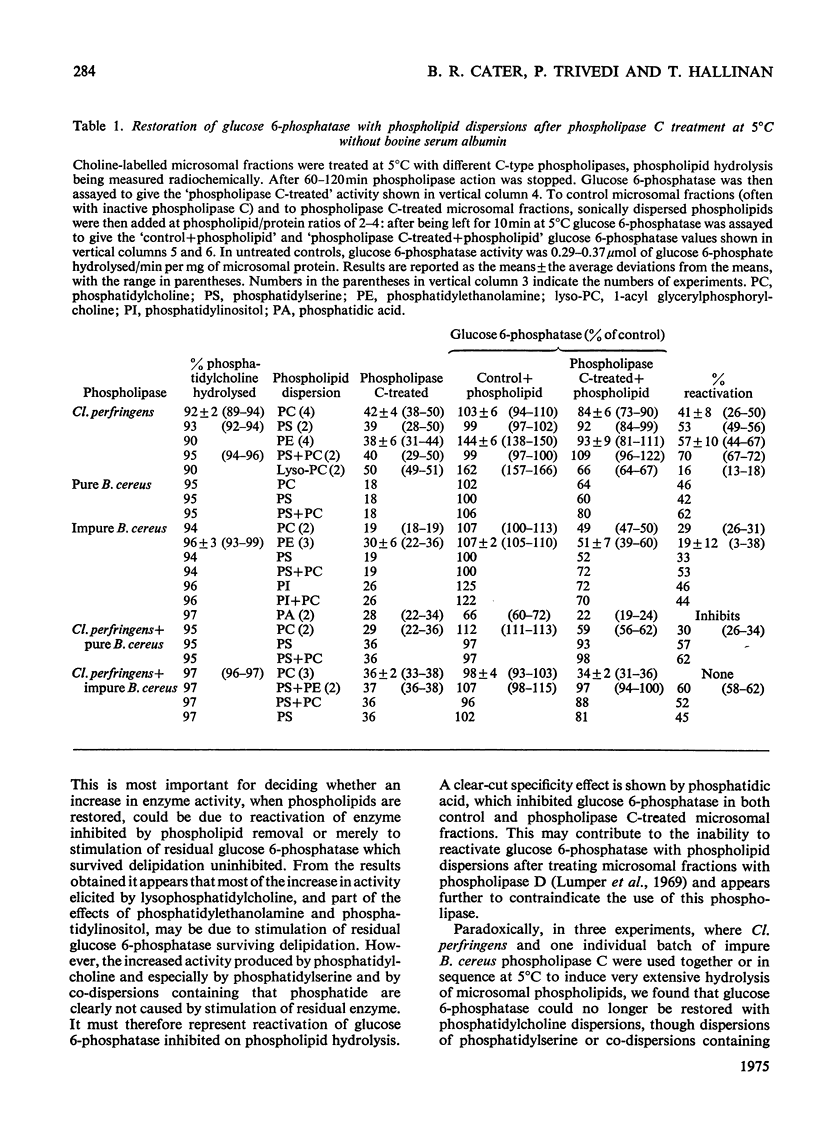
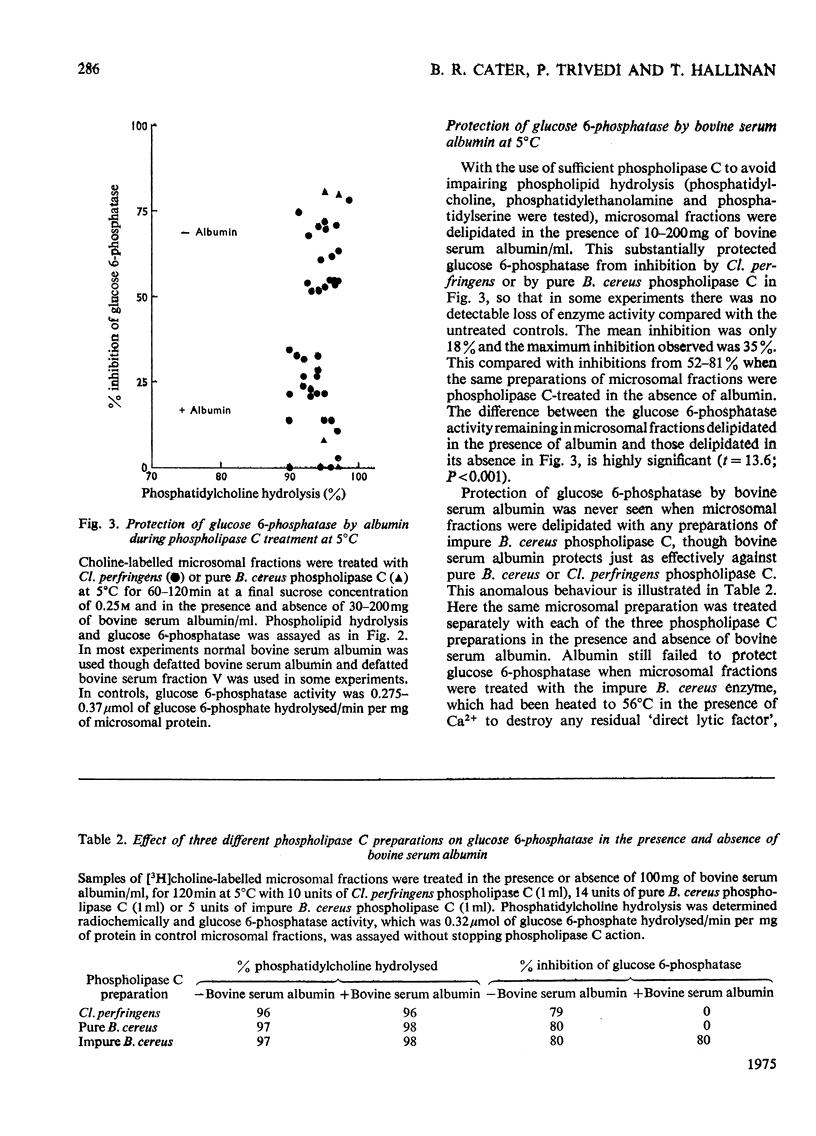
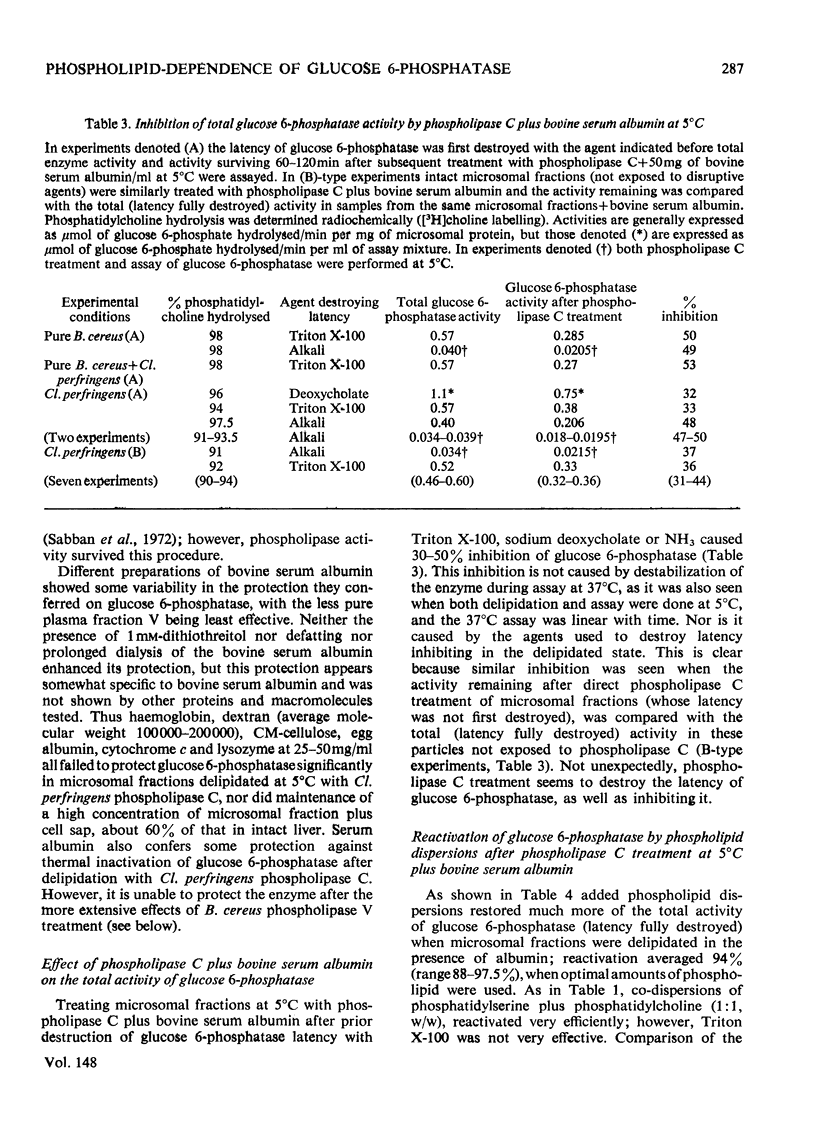
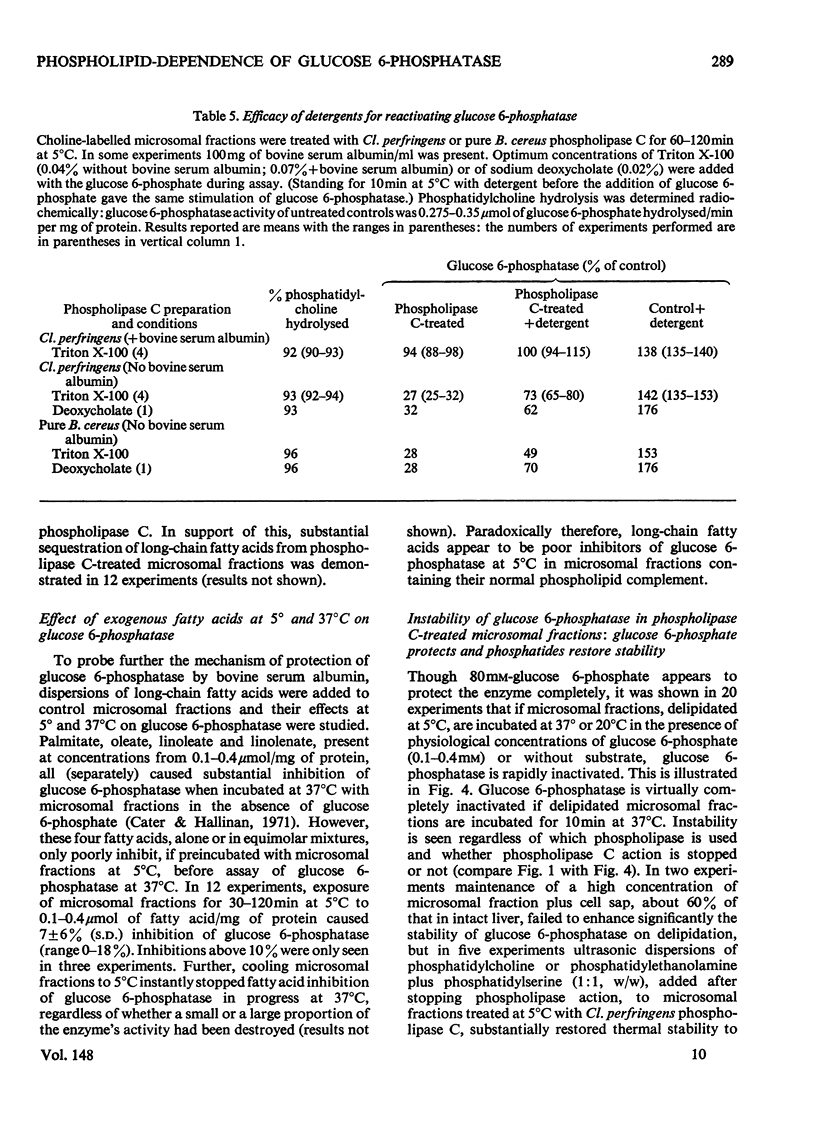
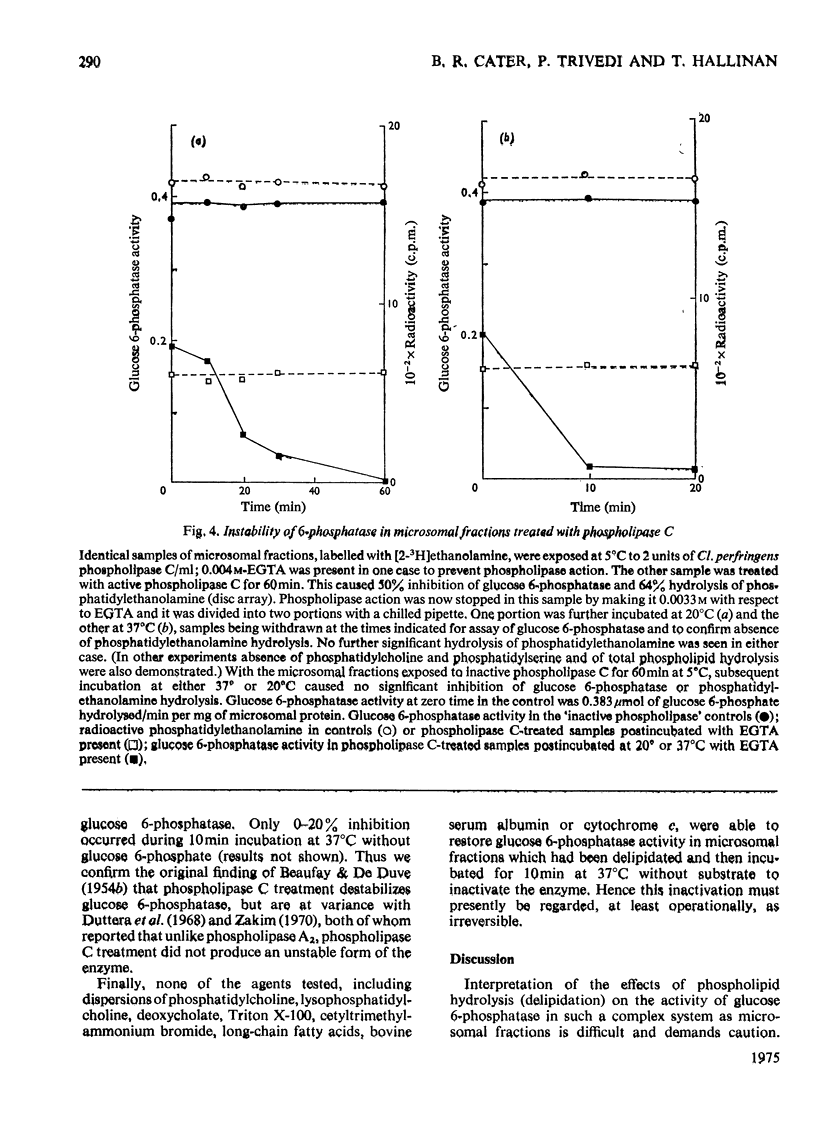
1. Pure or impure C-type phospholipases hydrolysed rat liver microsomal phosphatides in situ at 5 degrees or 37 degrees C. At 5 degrees C mean hydrolysis of total phospholipids was 90% by Bacillus cereus and 75% by Clostridium perfringens (Clostridium welchii) C-type phospholipases. 2. Four degrees of inhibition of glucose 6-phosphatase (D-glucose 6-phosphate phosphohydrolase; EC 3.1.3.9) resulted. (a) At 37 degrees C inhibition was virtually complete and apparently irreversible. (b) At 5 degrees C phospholipase C inhibited 50-87% of the activity expressed by intact control microsomal fractions. (c) Bovine serum albumin present during delipidation alleviated most of this inhibition: at 5 degrees C phospholipase C plus bovine serum albumin inhibited by 0-35% (mean 18%):simultaneous stimulation by the destruction of its latency seems to offset glucose 6-phosphatase inhibition, sometimes completely. (d) If latency was first destroyed, phospholipase C plus bovine serum albumin inhibited 30-50% of total glucose 6-phosphatase activity at 5 degrees C. Only this inhibition is likely largely to reflect the lower availability of phospholipids, essential for maximal enzyme activity, as it is virtually completely reversed by added phospholipid dispersions. Co-dispersions of phosphatidylserine plus phosphatidylcholine (1:1, w/w) were especially effective but Triton X-100 was unable effectively to restore activity. 3. Considerable glucose 6-phosphatase activity survived 240min of treatment with phospholipase C at 5 degrees C, but in the absence of substrate or at physiological glucose 6-phosphate concentrations the delipidated enzyme was completely inactivated within 10min at 37 degrees C. However, 80mM-glucose 6-phosphate stabilized it and phospholipid dispersions substantially restored thermal stability. 4. It is concluded that glucose 6-phosphatase is at least partly phospholipid-dependent, and complete dependence is not excluded. For reasons discussed it is impossible yet to be certain which phospholipid class(es) the enzyme requires for activity.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. J. The estimation of phosphorus. Biochem J. 1940 Jun;34(6):858–865. doi: 10.1042/bj0340858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arion W. J., Carlson P. W., Wallin B. K., Lange A. J. Modifications of hydrolytic and synthetic activities of liver microsomal glucose 6-phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2551–2557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arion W. J., Wallin B. K., Carlson P. W., Lange A. J. The specificity of glucose 6-phosphatase of intact liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2558–2565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEAUFAY H., DE DUVE C. Le système hexose-phosphatasique. IV. Spécificité de la glucose-6-phosphatase. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1954;36(11-12):1525–1537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEAUFAY H., DE DUVE C. Le système hexose-phosphatasique. VI. Essais de démembrement des microsomes porteurs de glucose-6-phosphatase. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1954;36(11-12):1551–1568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaufay H., Amar-Costesec A., Thinès-Sempoux D., Wibo M., Robbi M., Berthet J. Analytical study of microsomes and isolated subcellular membranes from rat liver. 3. Subfractionation of the microsomal fraction by isopycnic and differential centrifugation in density gradients. J Cell Biol. 1974 Apr;61(1):213–231. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cater B. R., Hallina T. Endogenous acylhydrolase breaks down diglyceride in 5 degrees phospholipase C treated rat liver microsomes. Products inhibit glucose 6-phosphohydrolase. FEBS Lett. 1971 Aug 1;16(2):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80352-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cater B. R., Poulter J., Hallinan T. The quantitative dependence of glucose-6-phosphohydrolase upon phospholipids: Effects of phospholipase C at 50 degrees and 370 degrees. FEBS Lett. 1970 Oct;10(5):346–348. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80469-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbeau A., Nachbaur J., Vignais P. M. Enzymic characterization and lipid composition of rat liver subcellular membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 3;249(2):462–492. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman R., Finean J. B., Knutton S., Limbrick A. R. A structural study of the modification of erythrocyte ghosts by phospholipase C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;219(1):81–92. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duttera S. M., Byrne W. L., Ganoza M. C. Studies on the phospholipid requirement of glucose 6-phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2216–2228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuer G., Golberg L. Liver response tests. 8. Factors influencing the activities of liver-microsomal phosphatases. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1967 Nov;5(5):673–690. doi: 10.1016/s0015-6264(67)83219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finean J. B., Martonosi A. The action of phospholipase C on muscle microsomes: a correlation of electron microscope and biochemical data. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jun 1;98(3):547–553. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90151-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland R. C., Cori C. F. Separation of phospholipids from glucose-6-phosphatase by gel chromatography. Specificity of phospholipid reactivation. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 5;11(25):4712–4718. doi: 10.1021/bi00775a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunderson H. M., Nordlie R. C. The fully-active nature of synthetic and hydrolytic activities of glucose-6-phosphatase of intact nuclear membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):601–607. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90755-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurr M. I., Prottey C., Hawthorne J. N. The phospholipids of liver-cell fractions. II. Incorporation of [32P]orthophosphate in vivo in normal and regenerating rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 4;106(2):357–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallinan T., Nagley P., Murty C. N., Bennett J., Grant J. H. The use of radioactive choline as a label for microsomal membranes. II. Studies on membrane-ribosome interaction, subfractionation and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr;173(3):554–563. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinig H. Nuclear membranes from mammalian liver. II. Lipid composition. J Cell Biol. 1970 Aug;46(2):396–402. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.2.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama Y. Studies on microsomal nucleoside diphosphatase of rat hepatocytes. Its purification, intramembranous localization, and turnover. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):2979–2988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. A., Symons A. M., Ancill R. J. Action of anti-inflammatory steroids on the lytic action of phospholipase C and 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid on lysosomes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Jan 15;23(2):467–470. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90441-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumper L., Zubrzycki Z., Staudinger H. Inaktivierung mikrosomaler Enzyme durch Phospholipase D. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969 Feb;350(2):163–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurray W. C., Dawson R. M. Phospholipid exchange reactions within the liver cell. Biochem J. 1969 Mar;112(1):91–108. doi: 10.1042/bj1120091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möllby R., Nord C. E., Wadström T. Biological activities contaminating preparations of phospholipase C ( -toxin) from Clostridium perfringens. Toxicon. 1973 Feb;11(2):139–147. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(73)90075-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabban E., Laster Y., Loyter A. Resolution of the hemolytic and the hydrolytic activities of phospholipase-C preparation from Clostridium perfringens. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 24;28(3):373–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Peterson R. F., Barclay M. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):374–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0900374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snoke R. E., Nordlie R. C. Comparative studies of the responses of rat liver microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase and inorganic pyrophosphate-glucose phosphotransferase to phospholipase C treatment and phospholipid supplementation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 20;258(1):188–205. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90978-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetten M. R., Burnett F. F. Activation of rat-liver microsomal glucose 6-phosphatase, inorganic pyrophosphatase and inorganic pyrophosphate-glucose phosphotransferase by hydroxyl ion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Nov 15;128(2):344–350. doi: 10.1016/0926-6593(66)90181-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetten M. R., Malamed S., Federman M. Activation in vitro of glucose-6-phosphatase, inorganic pyrophosphate-glucose phosphotransferase and related enzymes: relationship to microsomal membrane structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;193(2):260–267. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trump B. F., Duttera S. M., Byrne W. L., Arstila A. U. Membrane structure: lipid-protein interactions in microsomal membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):433–440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin B. K., Arion W. J. The requirement for membrane integrity in the inhibition of hepatic glucose 6-phosphatase by sulfhydryl reagents and taurocholate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Aug 7;48(3):694–699. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90404-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakim D. Regulation of microsomal enzymes by phospholipids. I. The effect of phospholipases and phospholipids on glucose 6-phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):4953–4961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaal R. F., Roelofsen B., Comfurius P., van Deenen L. L. Complete purification and some properties of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 13;233(2):474–479. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90347-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


