Abstract
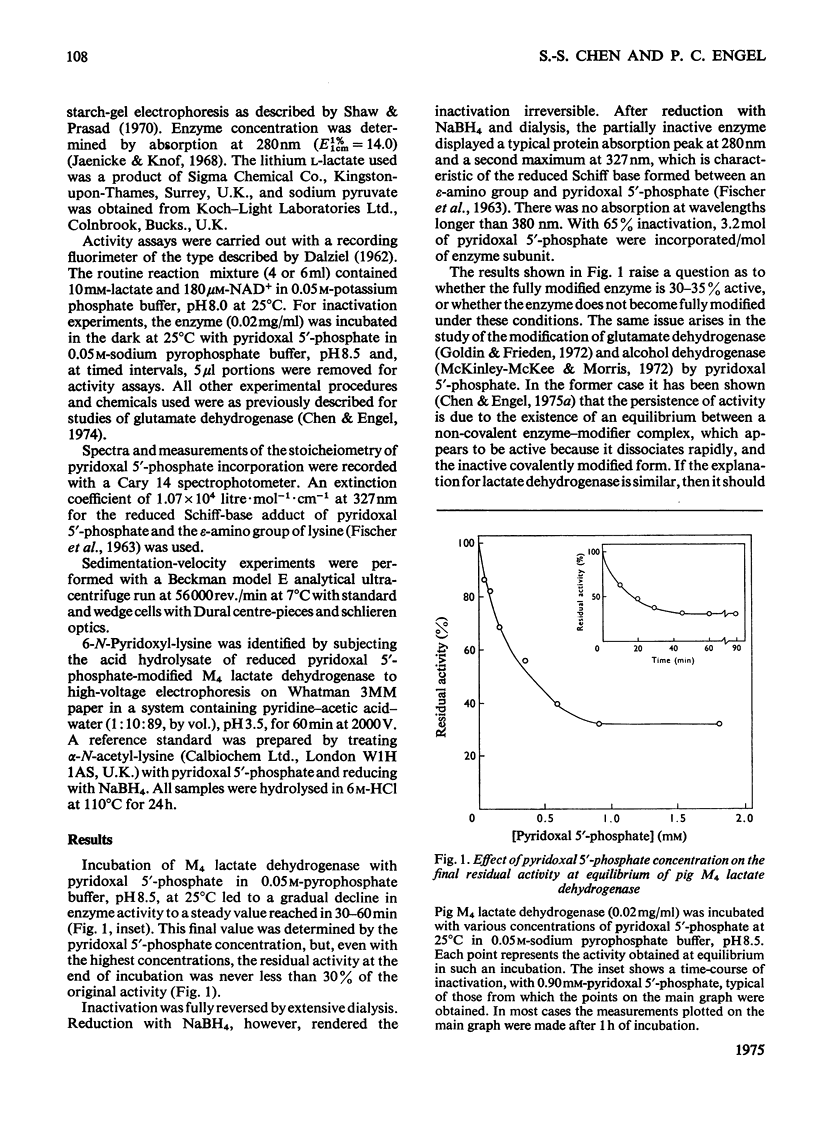
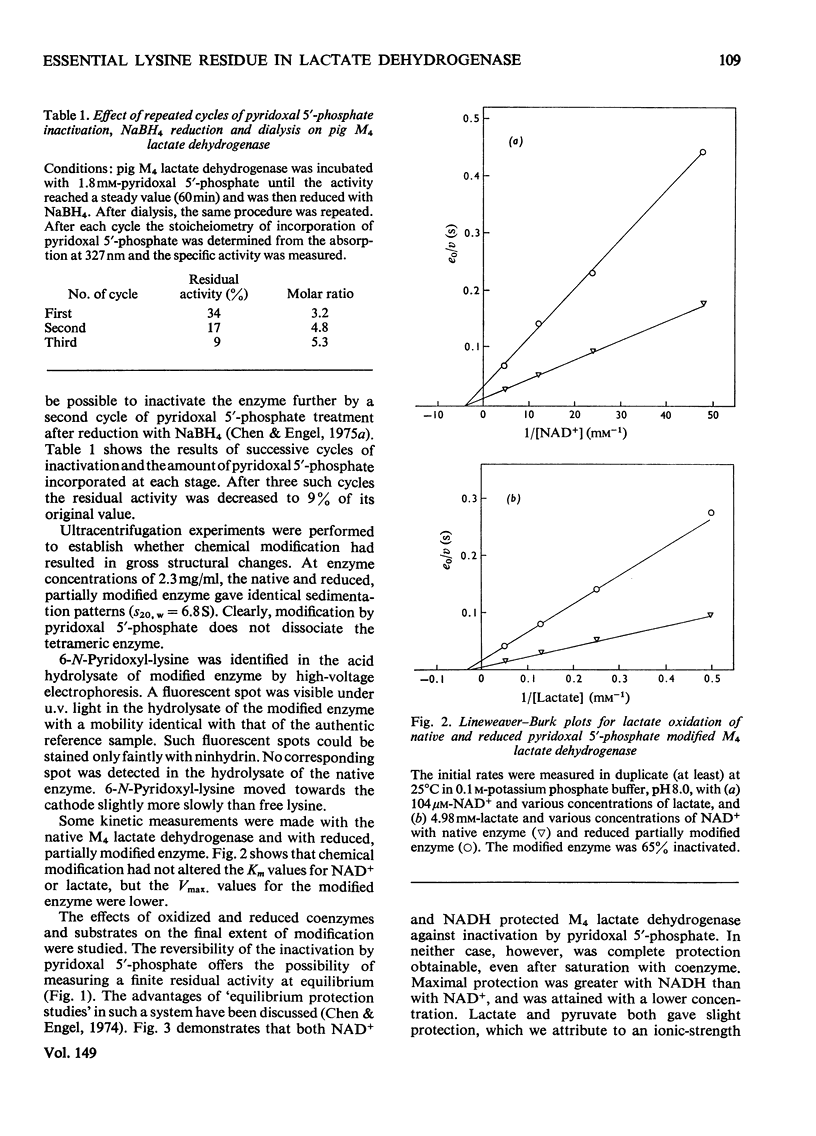
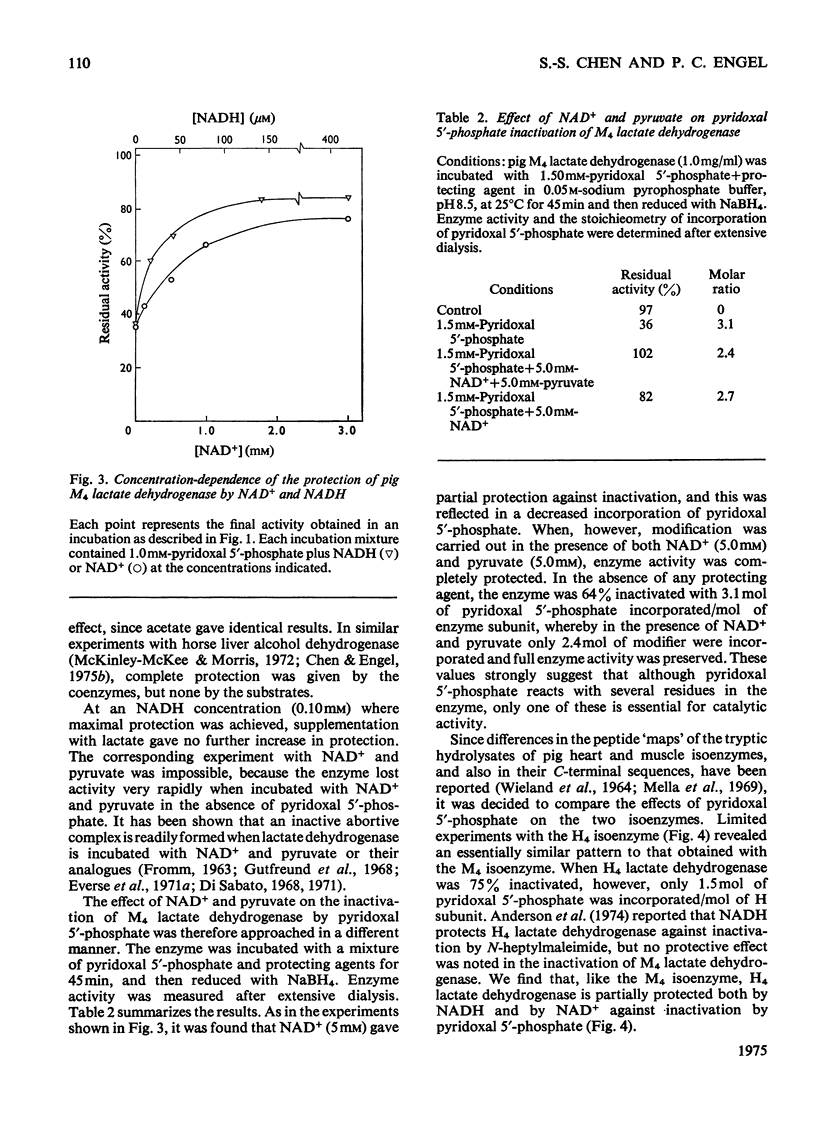
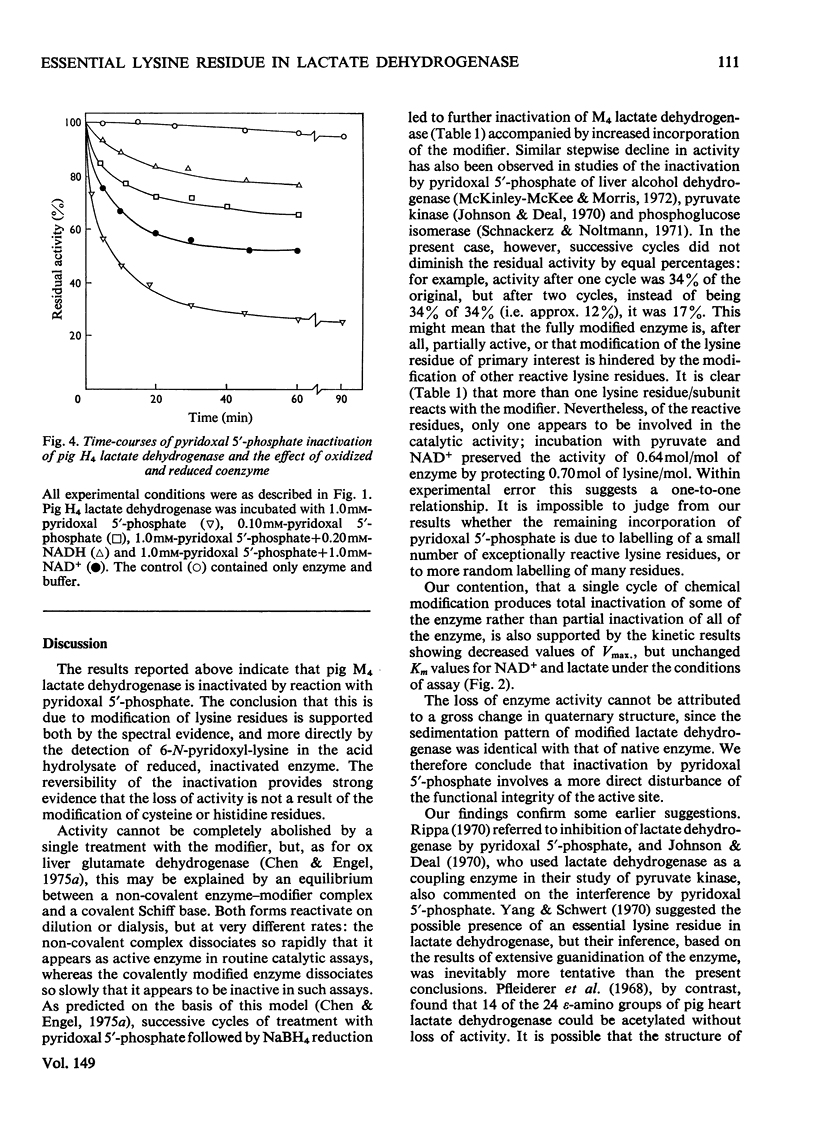
1. Pig M4 lactate dehydrogenase treated in the dark with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate at pH8.5 and 25 degrees C loses activity gradually. The maximum inactivation was 66%, and this did not increase with concentrations of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate above 1 mM. 2. Inactivation may be reversed by dialysis or made permanent by reducing the enzyme with NaBH4. 3. Spectral evidence indicates modification of lysine residues, and 6-N-pyridoxyl-lysine is present in the hydrolsate of inactivated, reduced enzyme. 4. A second cycle of treatment with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate and NaBH4 further decreases activity. After three cycles only 9% of the original activity remains. 5. Apparent Km values for lactate and NAD+ are unaltered in the partially inactivated enzyme. 6. These results suggest that the covalently modified enzyme is inactive; failure to achieve complete inactivation in a single treatment is due to the reversibility of Schiff-base formation and to the consequent presence of active non-covalently bonded enzyme-modifier complex in the equilibrium mixture. 7. Although several lysine residues per subunit are modified, only one appears to be essential for activity: pyruvate and NAD+ together (both 5mM) completely protect against inactivation, and there is a one-to-one relationship between enzyme protection and decreased lysine modification. 8. NAD+ or NADH alone gives only partial protection. Substrates give virtually none. 9. Pig H4 lactate dehydrogenase is also inactivated by pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. 10. The possible role of the essential lysine residue is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. J., Buehner M., Chandrasekhar K., Ford G. C., Hackert M. L., Liljas A., Rossmann M. G., Smiley I. E., Allison W. S., Everse J. Structure-function relationships in lactate dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1968–1972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams M. J., Ford G. C., Liljas A., Rossmann M. G. Atomic co-ordinates for dogfish M4 apo-lactate dehydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jul 2;53(1):46–51. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91398-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. M., Anderson C. D., Churchich J. E. Inhibition of glutamic dehydrogenase by pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. Biochemistry. 1966 Sep;5(9):2893–2900. doi: 10.1021/bi00873a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. M., Vercellotti S. V., Fisher T. L. Maleimideinactivation of lactate dehydrogenase isozymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 20;350(1):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90211-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold L. J., Jr, Kaplan N. O. The structure of the abortive diphosphopyridine nucleotide-pyruvate-lactate dehydrogenase ternary complex as determined by proton magnetic resonance analysis. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):652–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal K. M., Smith E. L. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-specific glutamate dehydrogenase of Neurospora. I. Isolation, subunits, amino acid composition, sulfhydryl groups, and identification of a lysine residue reactive with pyridoxal phosphate and N-ethylmaleimide. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6002–6008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A., Culver J. M., Fisher H. F. Mechanism of inactivation of L-glutamate dehydrogenase by pyridoxal and pyridoxal phosphate. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 23;12(22):4367–4373. doi: 10.1021/bi00746a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brändén C. I., Eklund H., Nordström B., Boiwe T., Söderlund G., Zeppezauer E., Ohlsson I., Akeson A. Structure of liver alcohol dehydrogenase at 2.9-angstrom resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2439–2442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buehner M., Ford G. C., Moras D., Olsen K. W., Rossman M. G. D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: three-dimensional structure and evolutionary significance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3052–3054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. S., Engel P. C. Inactivation of nicotinamide--adenine dinucleotide-linked dehydrogenases by pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. Biochem Soc Trans. 1975;3(1):80–82. doi: 10.1042/bst0030080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. S., Engel P. C. The equilibrium position of the reaction of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase with pyridoxal5'-phosphate. A demonstration that covalent modification with this reagent completely abolishes catalytic activity. Biochem J. 1975 May;147(2):351–358. doi: 10.1042/bj1470351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S., Engel P. C. Protection of glutamate dehydrogenase by nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide against reversible inactivation by pyridoxal 5'-phosphate as a sensitive indicator of conformational change induced by substrates and substrate analogues. Biochem J. 1974 Dec;143(3):569–574. doi: 10.1042/bj1430569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALZIEL K. Kinetic studies of liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1962 Aug;84:244–254. doi: 10.1042/bj0840244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISABATO G., KAPLAN N. O. THE ROLE OF THE SULFHYDRYL GROUPS OF LACTIC DEHYDROGENASES. Biochemistry. 1963 Jul-Aug;2:776–781. doi: 10.1021/bi00904a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Sabato G. Complexes of chicken heart lactic dehydrogenase with coenzymes and substrates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Nov 25;33(4):688–695. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Sabato G. On the nature of the lactic dehydrogenase-oxidized coenzyme-pyruvate complex. Biochemistry. 1971 Feb 2;10(3):395–401. doi: 10.1021/bi00779a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson J. E., Noltmann E. A. The effect of pH and temperature on the kinetic parameters of phosphoglucose isomerase. Participation of histidine and lysine in a proposed dual function mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1401–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel P. C., Chen S. S. The nature of inhibition and inactivation of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase by pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. Biochem Soc Trans. 1975;3(1):78–80. doi: 10.1042/bst0030078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel P. C., Dalziel K. Kinetic studies of glutamate dehydrogenase. The reductive amination of 2-oxoglutarate. Biochem J. 1970 Jul;118(3):409–419. doi: 10.1042/bj1180409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everse J., Barnett R. E., Thorne C. J., Kaplan N. O. The formation of ternary complexes by diphosphopyridine nucleotide-dependent dehydrogenases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Apr;143(2):444–460. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90230-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everse J., Kaplan N. O. Lactate dehydrogenases: structure and function. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1973;37:61–133. doi: 10.1002/9780470122822.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROMM H. DETERMINATION OF DISSOCIATION CONSTANTS OF COENZYMES AND ABORTIVE TERNARY COMPLEXES WITH RABBIT MUSCLE LACTATE DEHYDROGENASE FROM FLUORESCENCE MEASUREMENTS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Sep;238:2938–2944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. C., Plaut G. W. Functional groups of diphosphopyridine nucleotide linked isocitrate dehydrogenase from bovine heart. II. Studies of an active amino group by reaction with aldehydes. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 1;13(1):52–59. doi: 10.1021/bi00698a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forcina B. G., Ferri G., Zapponi M. C., Ronchi S. Identification of lysines reactive with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate in glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jun 29;20(4):535–540. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin B. R., Frieden C. The effect of pyridoxal phosphate modification on the catalytic and regulatory properties of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2139–2144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutfreund H., Cantwell R., McMurray C. H., Criddle R. S., Hathaway G. The kinetics of the reversible inhibition of heart lactate dehydrogenase through the formation of the enzyme-oxidized nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide-pyruvate compounds. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(3):683–687. doi: 10.1042/bj1060683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook J. J., Gutfreund H. Approaches to the study of enzyme mechanisms lactate dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1973 Apr 15;31(2):157–169. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook J. J., Ingram V. A. Ionic properties of an essential histidine residue in pig heart lactate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;131(4):729–738. doi: 10.1042/bj1310729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenicke R., Knof S. Molecular weight and quaternary structure of lactic dehydrogenase. 3. Comparative determination by sedimentation analysis, light scattering and osmosis. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Apr 3;4(2):157–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00187.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. S., Deal W. C., Jr Inactivation of tetrameric rabbit muscle pyruvate kinase by specific binding of 2 to 4 moles of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 25;245(2):238–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLAR D. B., SCHWERT G. W. LACTIC DEHYDROGENASE. IX. EFFECT OF PHOTO-OXIDATION UPON ACTIVITY AND COMPLEX FORMATION. J Biol Chem. 1963 Oct;238:3249–3255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley-McKee J. S., Morris D. L. The lysines in liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Chemical modification with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate and methyl picolinimidate. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jun 23;28(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01877.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mella K., Torff H. J., Fölsche E. T., Pfleiderer G. Die Carboxyl-terminale Aminosäuresequenz der Lactat-Dehydrogenase aus Schweineherz. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969 Jan;350(1):28–34. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1969.350.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PESCE A., MCKAY R. H., STOLZENBACH F., CAHN R. D., KAPLAN N. O. THE COMPARATIVE ENZYMOLOGY OF LACTIC DEHYDROGENASES. I. PROPERTIES OF THE CRYSTALLINE BEEF AND CHICKEN ENZYMES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jun;239:1753–1761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfleiderer G., Holbrook J. J., Zaki L., Jeckel D. The reactivities of the lysine, cysteine and tyrosine residues of pig heart lactate dehydrogenase in the presence of sulphite. FEBS Lett. 1968 Aug;1(3):129–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(68)80039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piszkiewicz D., Landon M., Smith E. L. Bovine liver flutamate dehydrogenase. Sequence of a hexadecapeptide containing a lysyl residue reactive with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 25;245(10):2622–2626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piszkiewicz D., Smith E. L. Bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase. Equilibria and kinetics of inactivation by pyridoxal. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4538–4544. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronchi S., Zapponi M. C., Ferri G. Inhibition by pyridoxal-phosphate of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Apr;8(3):325–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWERT G. W., TAKENAKA Y. Lactic dehydrogenase. III. Mechanism of the reaction. J Biol Chem. 1956 Nov;223(1):157–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato F., Takagi Y., Shikita M. 20 -hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase of porcine testes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):815–823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnackerz K. D., Noltmann E. A. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate as a site-specific protein reagent for a catalytically critical lysine residue in rabbit muscle phosphoglucose isomerase. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 21;10(26):4837–4843. doi: 10.1021/bi00802a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwert G. W., Miller B. R., Peanasky R. J. Lactic dehydrogenase. X. A re-evaluation of the effects of pH upon the kinetics of the reaction. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 25;242(14):3245–3252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C. R., Prasad R. Starch gel electrophoresis of enzymes--a compilation of recipes. Biochem Genet. 1970 Apr;4(2):297–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00485780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein E., Sulebele G. Equilibrium kinetic study of the catalytic mechanism of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1973 May 22;12(11):2164–2172. doi: 10.1021/bi00735a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIELAND T., GEORGOPOULOS D., KAMPE H., WACHSMUTH E. D. ANALYTISCHER BEWEIS DER HYBRIDNATUR VON ISOZYMEN DER LACTATDEHYDROGENASE. Biochem Z. 1964 Nov 6;340:483–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINER A. D., SCHWERT G. W. Lactic dehydrogenase. IV. The influence of pH on the kinetics of the reaction. J Biol Chem. 1958 Apr;231(2):1065–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINER A. D., SCHWERT G. W. Lactic dehydrogenase. VII. Fluorescence spectra of ternary complexes of lactic dehydrogenase, reduced diphosphopyridine nucleotide, and carboxylic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 May;234(5):1155–1161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woenckhaus C., Berghäuser J., Pfleiderer G. Markierung essentieller Aminosäurereste der Lactat-Dehydrogenase aus Schweineherz mit (Carbonyl-14C)3-(2-Brom-acetyl)-pyridin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969 Apr;350(4):473–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang P. C., Schwert G. W. Lactate dehydrogenase. XI. Effects of guanidination upon the properties of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):4886–4893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZEWE V., FROMM H. J. Kinetic studies of rabbit muscle lactate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1668–1675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapponi M. C., Ferri G., Forcina B. G., Ronchi S. Reaction of rabbit muscle apo-glyceraldehyde-3-P-dehydrogenase with pyridoxal-5'-phosphate. FEBS Lett. 1973 May 1;31(3):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


