Abstract
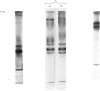
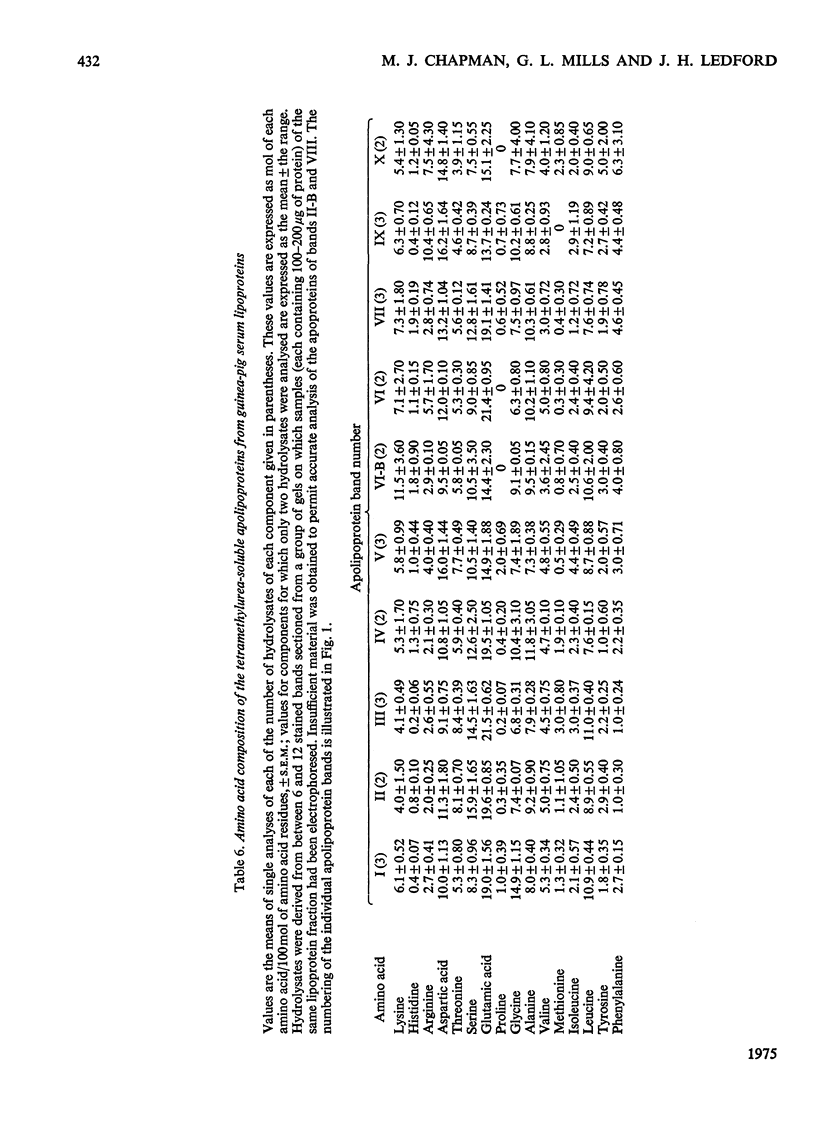
1. Very-low-density (VLD), low-density (LD) and high-density (HD) lipoproteins were isolated by sequential ultracentrifugation from the serum of male guinea pigs fed on a diet containing 3--4% fat. The apoproteins of these lipoproteins (apo-VLD, apo-LD and apo-HD lipoproteins) were studied after delipidation with organic solvents or extraction with tetramethylurea. 2. The major apolipoprotein of LD lipoprotein isolated by gel filtration was found to closely resemble apolipoprotein B of human serum in its chemical and physical properties. Electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel showed that this apoprotein consisted of a number of polypeptides. 3. Tetramethylurea precipitated an apoprotein from guinea-pig serum lipoproteins that is probably the apolipoprotein B-like component. This apoprotein accounted for about 80% of the apo-LD lipoprotein, about 55% of the apo-VLD lipoprotein and about 50% of the apo-HD lipoprotein. 4. The distribution of apolipoproteins soluble in tetramethylurea was determined by densitometric scanning of stained polyacrylamide disc gels. 5. A glycine-rich component of high electrophoretic mobility (band I) and a triplet of soluble apolipoproteins (bands II-IV) were present in both VLD and LD lipoprotein classes. These components constituted a higher proportion of the tetramethylurea-soluble apoproteins of VLD lipoprotein (60--80%) than of LD lipoprotein (40--55%). 6. Small amounts (10--15%) of a component of intermediate mobility, which contained traces of half-cystine, were also present in both VLD and LD lipoproteins. 7. A group of soluble components of basic character (bands VI-X), present as minor components of VLD lipoprotein (10--20%), constituted a major proportion (30--45%) of the soluble apoproteins of LD lipoprotein. Two of these apoproteins were rich in lysine, and two of lower electrophoretic mobility were rich in arginine. 8. The pattern of tetramethylurea-soluble apoproteins in HD lipoprotein was distinguished by the presence of two polypeptides of low electrophoretic mobility as its predominant components. One of these components, band VI, resembled the A-I apolipoprotein of man in both its amino acid profile and in its electrophoretic mobility. The second major component, band VI-B, was rich in lysine and resembled the C-I apolipoprotein of man in amino acid composition. 9. The soluble components of bands I and IX were analogous in physicochemical properties to the R-X1 and R-X2 (high-arginine polypeptide) peptides of human serum lipoproteins respectively.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bersot T. P., Brown W. V., Levy R. I., Windmueller H. G., Fredrickson D. S., LeQuire V. S. Further characterization of the apolipoproteins of rat plasma lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1970 Aug 18;9(17):3427–3433. doi: 10.1021/bi00819a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bier D. M., Havel R. J. Activation of lipoprotein lipase by lipoprotein fractions of human serum. J Lipid Res. 1970 Nov;11(6):565–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmer T., Havel R. J., Long J. A. Physiological fatty liver and hyperlipemia in the fetal guinea pig: chemical and ultrastructural characterization. J Lipid Res. 1972 May;13(3):371–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. V., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Studies of the proteins in human plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5687–5694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camejo G. Structural studies of rat plasma lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3228–3241. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaldi R. A., Vanderkooi G. The low polarity of many membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):930–932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman M. J., Mills G. L., Taylaur C. E. Lipoprotein particles from the Golgi apparatus of guinea-pig liver. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(4):779–787. doi: 10.1042/bj1280779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman M. J., Mills G. L., Taylaur C. E. The effect of a lipid-rich diet on the properties and composition of lipoprotein particles from the Golgi apparatus of guinea-pig liver. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;131(2):177–185. doi: 10.1042/bj1310177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein C., Lim C. T., Scanu A. M. The serum high density lipoproteins of Macacus rhesus. II. Isolation, purification, and characterization of their two major polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7653–7660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Bilheimer D., Lindgren F., Levy R. I. On the apoprotein composition of human plasma very low density lipoprotein subfractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 21;260(2):329–333. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidge N. The isolation and properties of pig plasma lipoproteins and partial characterisation of their apoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 25;295(1):258–273. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishbein W. N. Quantitative densitometry of 1-50 g protein in acrylamide gel slabs with Coomassie blue. Anal Biochem. 1972 Apr;46(2):388–401. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson D. S., Lux S. E., Herbert P. N. The apolipoproteins. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1972;26(0):25–56. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-7547-0_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloster J., Fletcher R. F. Quantitative analysis of serum lipids with thin-layer chromatography. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Feb;13(2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90298-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotto A. M., Brown W. V., Levy R. I., Birnbaumer M. E., Fredrickson D. S. Evidence for the identity of the major apoprotein in low density and very low density lipoproteins in normal subjects and patients with familial hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1486–1494. doi: 10.1172/JCI106945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Fielding C. J., Olivecrona T., Shore V. G., Fielding P. E., Egelrud T. Cofactor activity of protein components of human very low density lipoproteins in the hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipoproteins lipase from different sources. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 24;12(9):1828–1833. doi: 10.1021/bi00733a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Kashyap M. L. Interchange of apolipoproteins between chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins during alimentary lipemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):32–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI107171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert P. N., Windmueller H. G., Bersot T. P., Shulman R. S. Characterization of the rat apolipoproteins. I. The low molecular weight proteins of rat plasma high density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5718–5724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. L. Hydrolysis of proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1965;20:37–107. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60388-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston L. L. Amino acid analysis of stained bands from polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Baker H. N., Taunton O. D., Smith L. C., Garner C. W., Gotto A. M., Jr A comparison of the major apolipoprotein from pig and human high density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2639–2644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janado M., Martin W. G., Cook W. H. Separation and properties of pig-serum lipoproteins. Can J Biochem. 1966 Aug;44(8):1201–1209. doi: 10.1139/o66-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas A. Physicochemical properties of bovine serum high density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7767–7772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P. A rapid electrophoretic technique for identification of subunit species of apoproteins in serum lipoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jun;53(2):350–364. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P., Richards E. G., Havel R. J. Subunit heterogeneity in human serum beta lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1075–1082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitany R. A., Zebrowski E. J. A high resolution PAS stain for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga S., Bolis L., Scanu A. M. Isolation and characterization of subunit polypeptides from apoproteins of rat serum lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 25;236(2):416–430. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90222-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga S., Horwitz D. L., Scanu A. M. Isolation and properties of lipoproteins from normal rat serum. J Lipid Res. 1969 Sep;10(5):577–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostner G., Alaupovic P. Studies of the composition and structure of plasma lipoproteins. Separation and quantification of the lipoprotein families occurring in the high density lipoproteins of human plasma. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 29;11(18):3419–3428. doi: 10.1021/bi00768a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp K., Wiegandt H. Studies on the B-protein of human serum beta-lipoprotein using SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1973 Mar;354(3):262–266. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1973.354.1.262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills G. L., Chapman M. J., McTaggart F. Some effects of diet on guinea pig serum lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 23;260(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIRENBERG M. W., MATTHAEI J. H. The dependence of cell-free protein synthesis in E. coli upon naturally occurring or synthetic polyribonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Oct 15;47:1588–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.10.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puppione D. L., Sardet C., Yamanaka W., Ostwald R., Nichols A. V. Plasma lipoproteins of cholesterol-fed guinea pigs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 16;231(2):295–301. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90142-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarfordt S. H., Nathans A., Dowdee M., Hilderman H. L. Heterogeneity of human very low density lipoproteins by gel filtration chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1972 Jul;13(4):435–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Hansma H., Ostwald R. Characterization of guinea pig plasma lipoproteins: the appearance of new lipoproteins in response to dietary cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 1972 Sep;13(5):624–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore B., Shore V. Isolation and characterization of polypeptides of human serum lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4510–4516. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore V. G., Shore B., Hart R. G. Changes in apolipoproteins and properties of rabbit very low density lipoproteins on induction of cholesteremia. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 9;13(8):1579–1585. doi: 10.1021/bi00705a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solyom A., Bradford R. H., Furman R. H. Apolipoprotein and lipid distribution in canine serum lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 16;229(2):471–483. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90208-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whayne T. F., Jr, Felts J. M. Activation of lipoprotein lipase. Comparative study of man and other mammals. Circ Res. 1970 May;26(5):545–551. doi: 10.1161/01.res.26.5.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whayne T. F., Jr, Felts J. M. Activation of lipoprotein lipase. Effects of rat serum lipoprotein fractions and heparin. Circ Res. 1970 Dec;27(6):941–951. doi: 10.1161/01.res.27.6.941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]