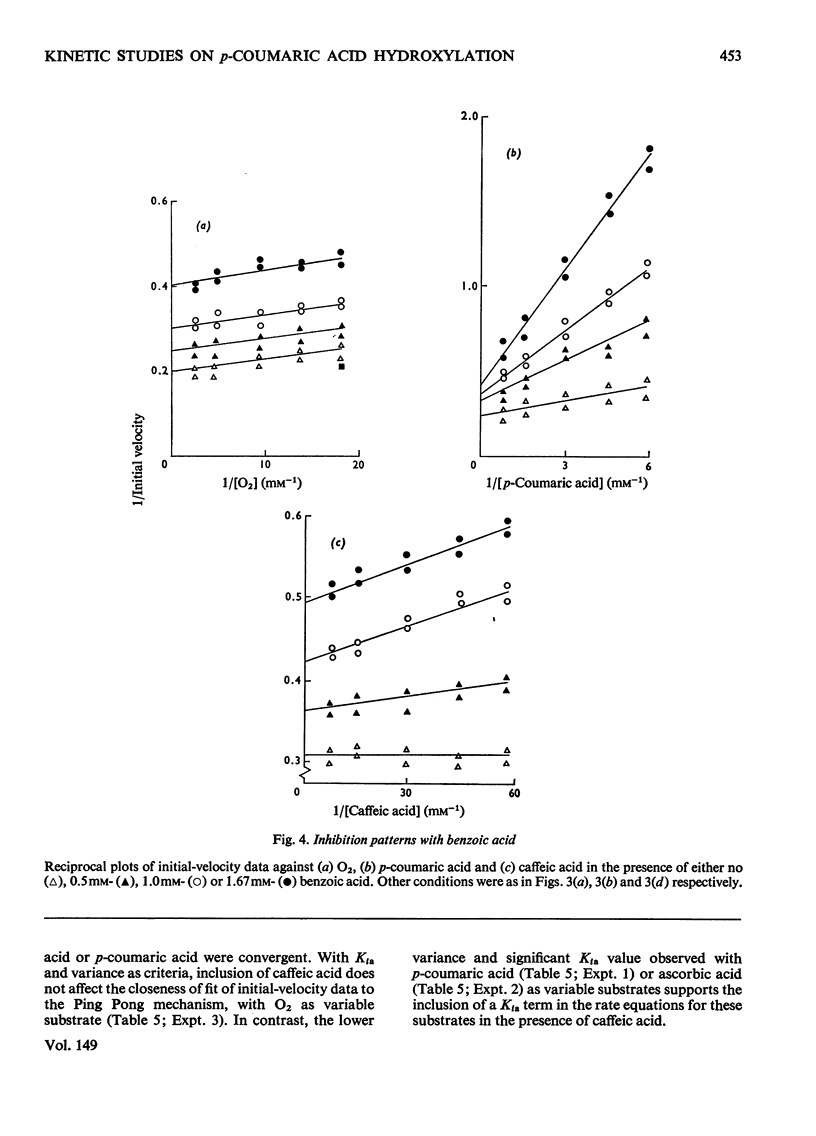
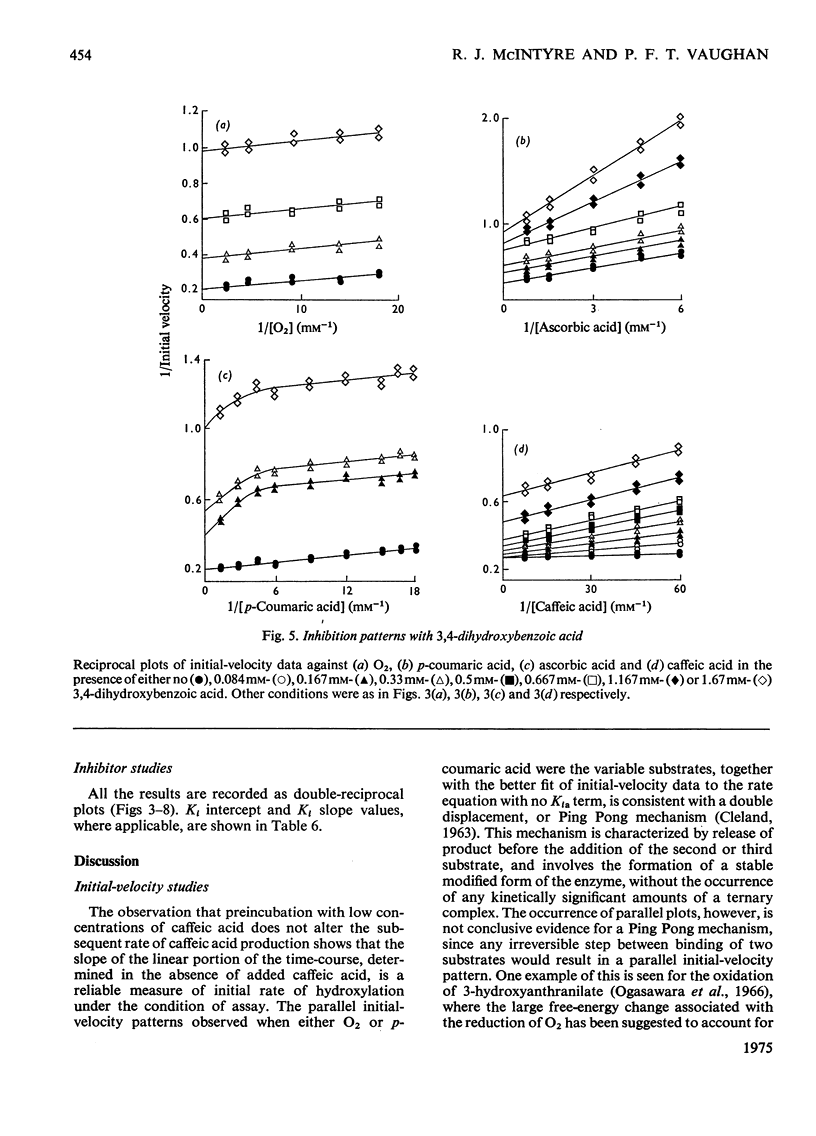
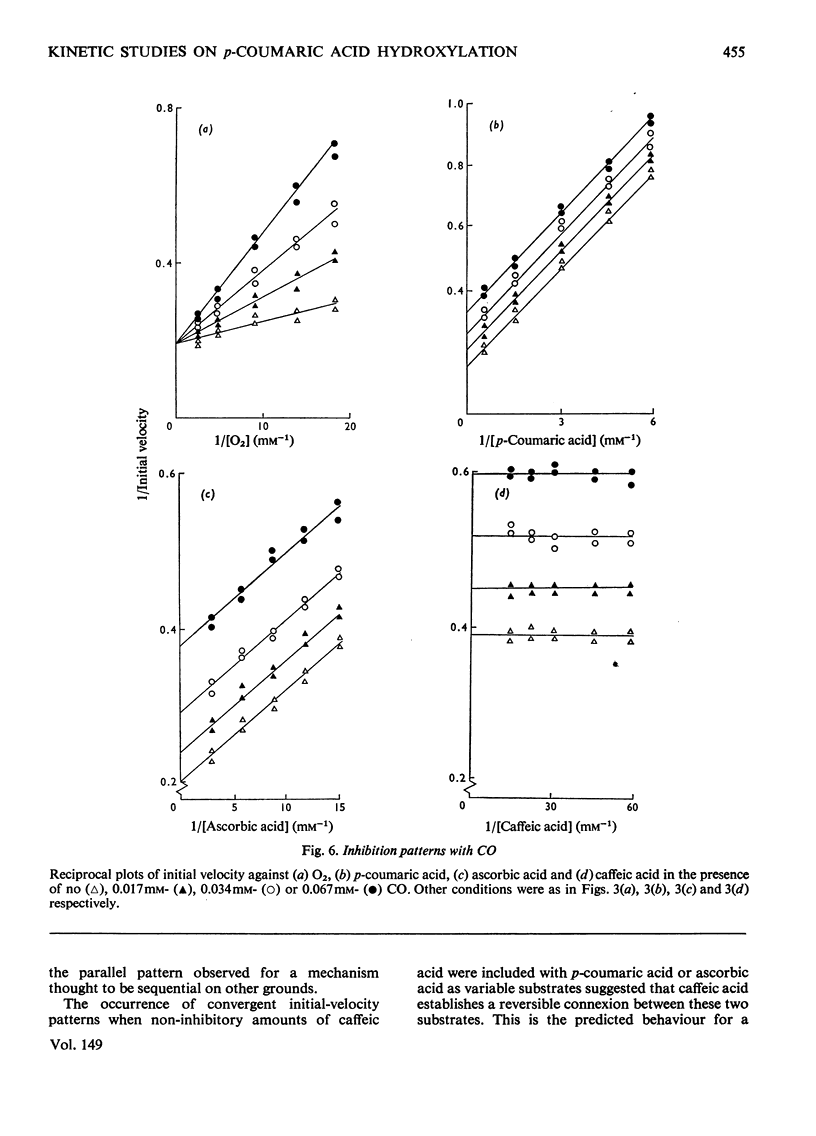
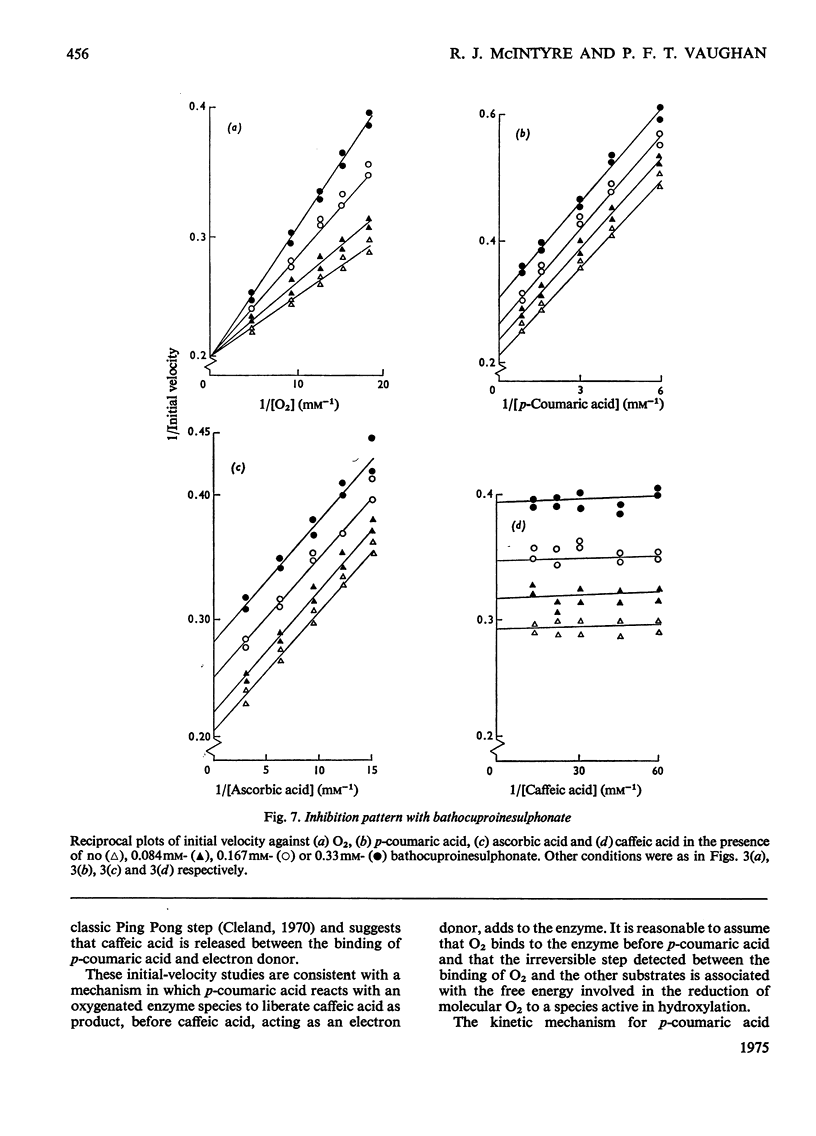
Abstract
1. A spectrophotometric assay is described that enables the hydroxylation of p-coumaric acid to caffeic acid, catalysed by spinach-beet phenolase, to be followed continuously. 2. Initial-velocity and inhibitor studies indicate that the order of substrate addition is oxygen, p-coumaric acid and electron donor, with an irreversible step separating the binding of each substrate. 3. Caffeic acid is most likely to act as electron donor at the active site; other electron donors, such as ascorbic acid, NADH and dimethyltetrahydropteridine, function mainly to recycle cofactor amounts of caffeic acid. 4. A reaction scheme, consistent with these data, is proposed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUTT V. S., HALLAWAY M. The catalysis of ascorbate oxidation by ionic copper and its complexes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Jan;92:24–32. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady F. O., Monaco M. E., Forman H. J., Schutz G., Feigelson P. On the role of copper in activation of and catalysis by tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):7915–7922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLELAND W. W. The kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions with two or more substrates or products. I. Nomenclature and rate equations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jan 8;67:104–137. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91800-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth H. W., Coleman J. E. Physicochemical and kinetic properties of mushroom tyrosinase. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 10;245(7):1613–1625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm H. J. The use of competitive inhibitors in studying the mechanism of action of some enzyme systems utilizing three substrates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jul 11;139(2):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory R. P., Bendall D. S. The purification and some properties of the polyphenol oxidase from tea (Camellia sinensis L.). Biochem J. 1966 Dec;101(3):569–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1010569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolley R. L., Jr, Evans L. H., Makino N., Mason H. S. Oxytyrosinase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):335–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendal L. P. The action of tyrosinase on monophenols. Biochem J. 1949;44(4):442–454. doi: 10.1042/bj0440442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASON H. S. Comparative biochemistry of the phenolase complex. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1955;16:105–184. doi: 10.1002/9780470122617.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane W. D. Application of the sodium diethyldithiocarbamate reaction to the micro-colorimetric determination of copper in organic substances. Biochem J. 1932;26(4):1022–1033. doi: 10.1042/bj0261022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen K. H. Rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase. A method for the measurement of activity, with particular reference to the distinctive features of the enzyme and the pteridine cofactor. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jan;7(3):360–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara N., Gander J. E., Henderson L. M. Purification and properties of 3-hydroxyanthranilate oxygenase from beef kidney. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 10;241(3):613–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierpoint W. S. The enzymic oxidation of chlorogenic acid and some reactions of the quinone produced. Biochem J. 1966 Feb;98(2):567–580. doi: 10.1042/bj0980567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz S. H., Warner M. C. 3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine as the tyrosinase cofactor. Occurrence in melanoma and binding constant. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5308–5314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J., Cooper J. M. Method of determining oxygen concentrations in biological media, suitable for calibration of the oxygen electrode. Anal Biochem. 1970 Feb;33(2):390–399. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph F. B., Purich D. L., Fromm H. J. Coenzyme A-linked aldehyde dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. I. Partial purification, properties, and kinetic studies of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 10;243(21):5539–5545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan P. F., Butt V. S. The action of o-dihydric phenols in the hydroxylation of p-coumaric acid by a phenolase from leaves of spinach beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Biochem J. 1970 Aug;119(1):89–94. doi: 10.1042/bj1190089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan P. F., Butt V. S. The expression of catechol oxidase activity during the hydroxylation of p-coumaric acid by spinach-beet phenolase. Biochem J. 1972 May;127(4):641–647. doi: 10.1042/bj1270641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan P. F., Butt V. S. The hydroxylation of p-coumaric acid by an enzyme from leaves of spinach beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):109–115. doi: 10.1042/bj1130109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan P. F., Butt V. S. The hydroxylation of p-coumaric acid by an enzyme from leaves of spinach beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):109–115. doi: 10.1042/bj1130109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


