Abstract
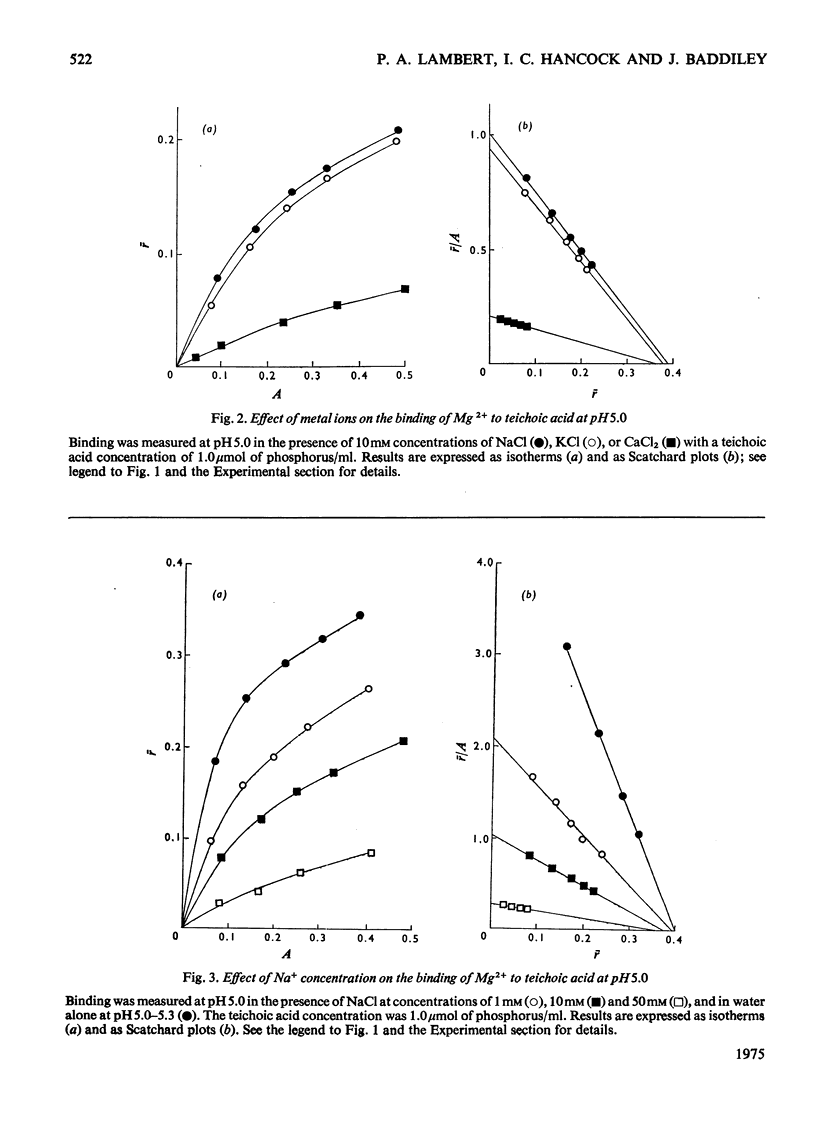
The binding of Mg2+ to the wall teichoic acid of Lactobacillus buchneri N.C.I.B. 8007 was measured by equilibrium dialysis at controlled ionic concentration and pH. In an aqueous solution containing 10mM-NaCl at pH 5.0 one Mg2+ ion was bound for every two phosphate groups of the teichoic acid, with an apparent association constant, Kassoc. = 2.7 x 10(3) M-1. On lowering the pH below the pKa of the phosphate groups the amount of bound Mg2+ decreased concomitantly with decreasing ionization of the phosphate groups. Both the amount of Mg2+ bound to the teichoic acid and the apparent association constants were similar in the presence of 10 mM concentrations of NaCl or KCl but decreased markedly in the presence of 10 mM-CaCl2 because of competition between Ca2+ and Mg2+ for the binding sites. A similar effect was found when the concentration of NaCl was increased from 0 to 50 mM. The results are discussed in relation to the function of teichoic acid in the walls of Gram-positive bacteria.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARCHIBALD A. R., ARMSTRONG J. J., BADDILEY J., HAY J. B. Teichoic acids and the structure of bacterial walls. Nature. 1961 Aug 5;191:570–572. doi: 10.1038/191570a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald A. R., Baddiley J., Heptinstall S. The alanine ester content and magnesium binding capacity of walls of Staphylococcus aureus H grown at different pH values. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 16;291(3):629–634. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald A. R., Baddiley J., Heptinstall S. The distribution of the glucosyl substituents along the chain of the teichoic acid in walls of Lactobacillus buchneri N.C.I.B. 8007. Biochem J. 1969 Jan;111(2):245–246. doi: 10.1042/bj1110245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddiley J., Hancock I. C., Sherwood P. M. X-ray photoelectron studies of magnesium ions bound to the cell walls of gram-positive bacteria. Nature. 1973 May 4;243(5401):43–45. doi: 10.1038/243043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddiley J. Teichoic acids in cell walls and membranes of bacteria. Essays Biochem. 1972;8:35–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., Birdsell D. C. Interaction of concanavalin A with the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):652–658. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.652-658.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., McDannel M. L., Streips U. N., Birdsell D. C., Young F. E. Polyelectrolyte nature of bacterial teichoic acids. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):606–615. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.606-615.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C., Tempest D. W. Influence of culture pH on the content and composition of teichoic acids in the walls of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Nov;73(2):395–402. doi: 10.1099/00221287-73-2-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C. The anionic polymers in the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis var. niger grown in phosphorus-limiting environments supplemented with increasing concentrations of sodium chloride. Biochem J. 1971 Jan;121(2):349–351. doi: 10.1042/bj1210349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C. The wall content and composition of Bacillus substilis var. niger grown in a chemostat. Biochem J. 1970 Jul;118(3):367–373. doi: 10.1042/bj1180367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heptinstall S., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. Teichoic acids and membrane function in bacteria. Nature. 1970 Feb 7;225(5232):519–521. doi: 10.1038/225519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. H., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. The function of teichoic acids in cation control in bacterial membranes. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;132(1):83–93. doi: 10.1042/bj1320083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meers J. L., Tempest D. W. The influence of growth-limiting substrate and medium NaCl concentration on the synthesis of magnesium-binding sites in the walls of Bacillus subtilis var. niger. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Nov;63(3):325–331. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-3-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou L. T., Chatterjee A. N., Young F. E., Marquis R. E. The physiology of teichoic acid deficient staphylococci. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Nov;19(11):1393–1399. doi: 10.1139/m73-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou L. T., Marquis R. E. Electromechanical interactions in cell walls of gram-positive cocci. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):92–101. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.92-101.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN H. A modified ninhydrin colorimetric analysis for amino acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Mar;67(1):10–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw N., Baddiley J. The teichoic acid from the walls of Lactobacillus buchneri N.C.I.B. 8007. Biochem J. 1964 Nov;93(2):317–321. doi: 10.1042/bj0930317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slabyj B. M., Panos C. Teichoic acid of a stabilized L-form of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):934–942. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.934-942.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



