Abstract
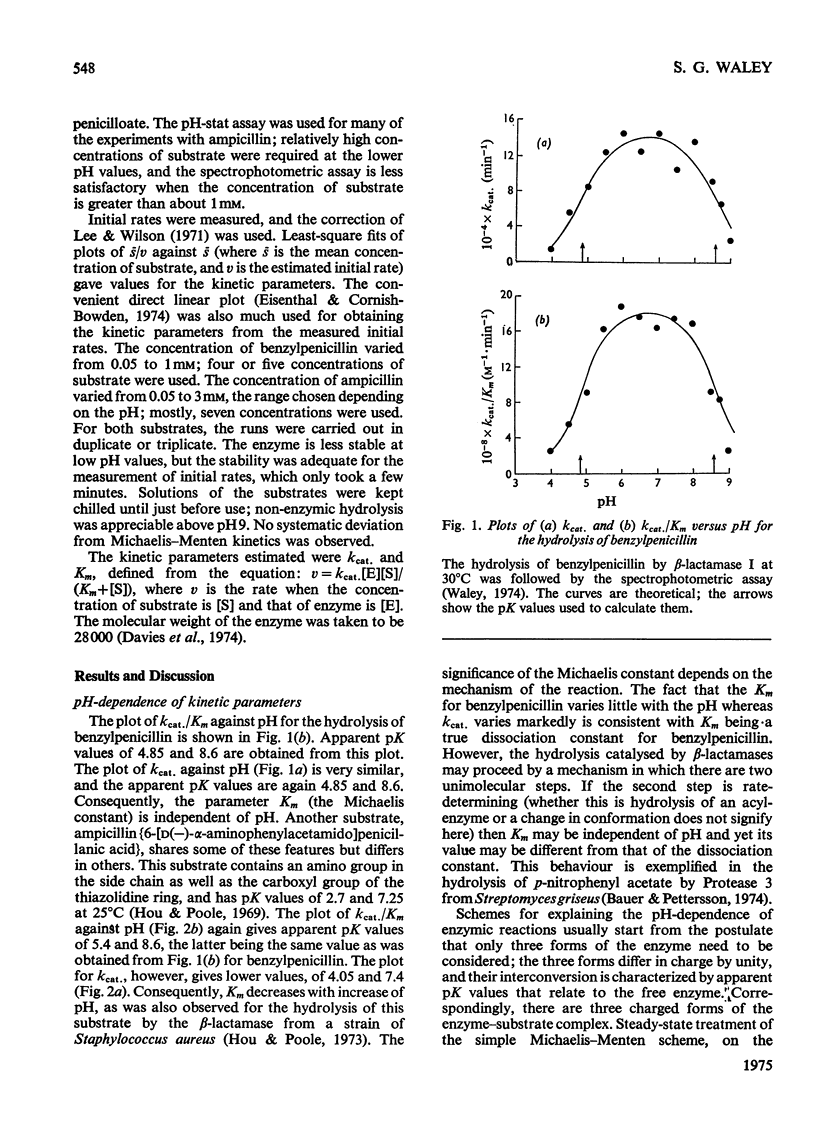
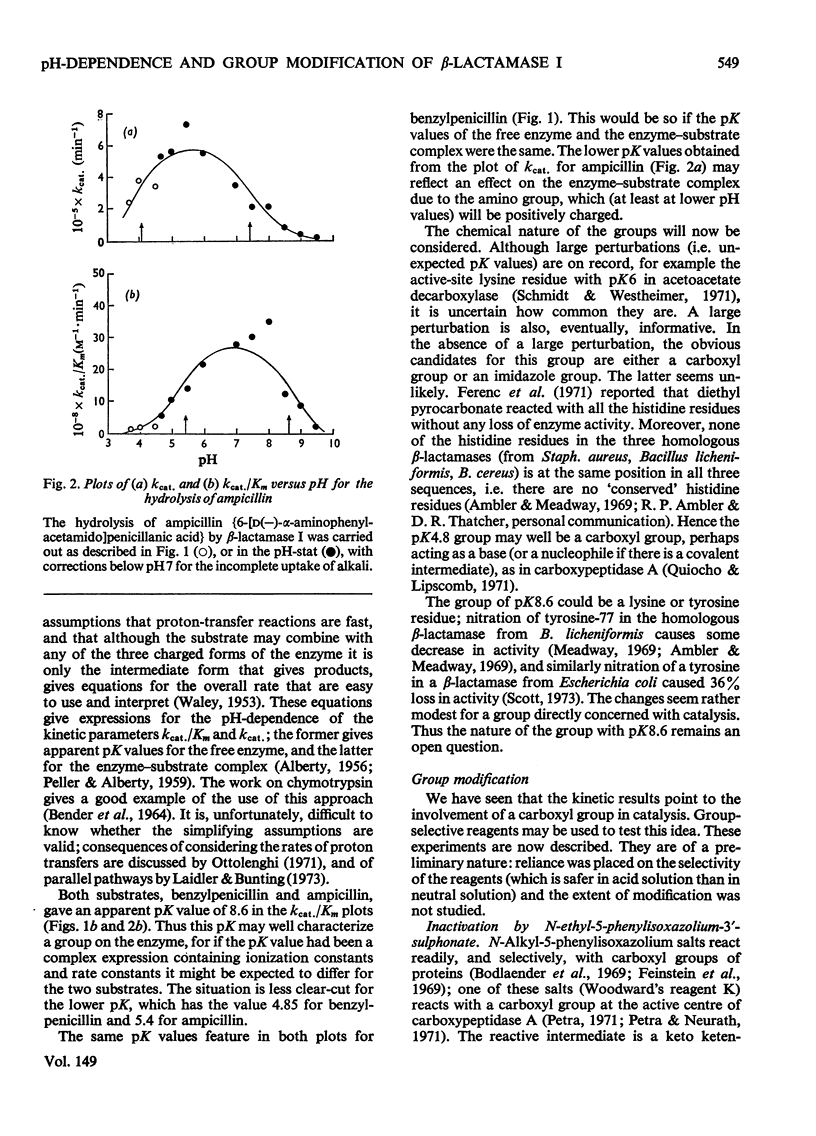
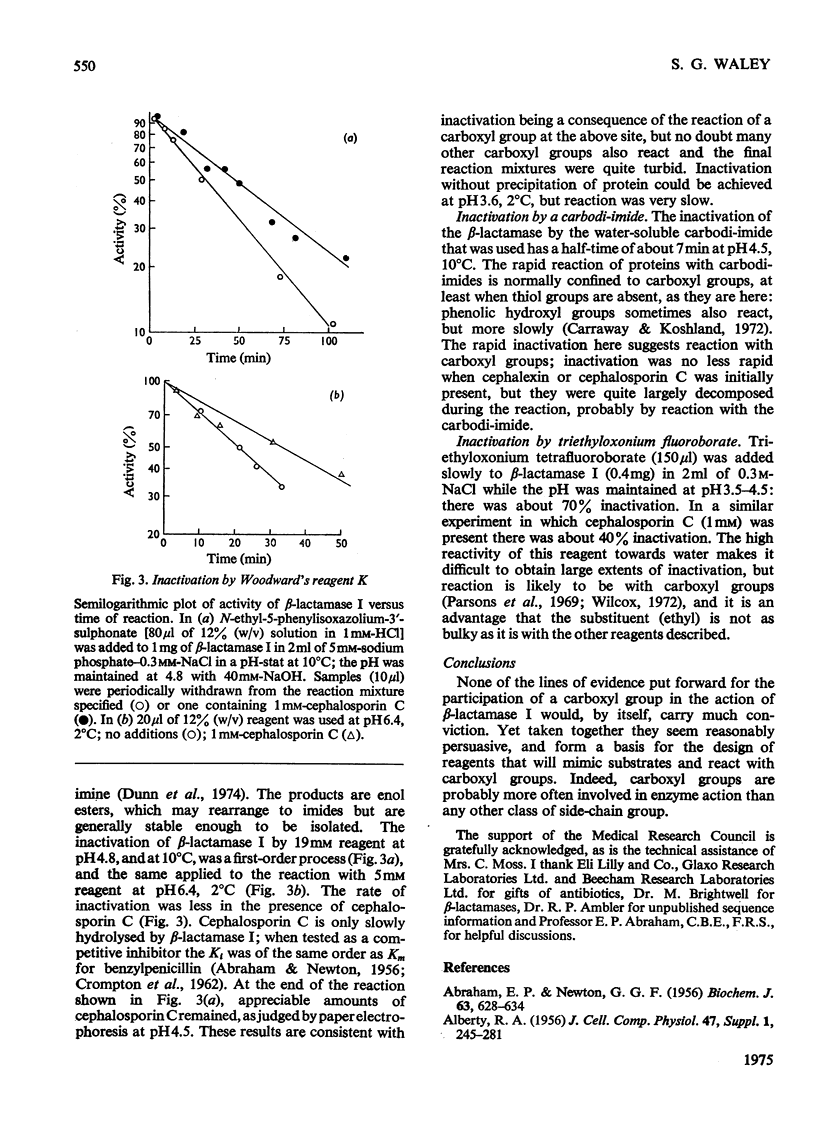
The pH-dependence of the kinetic parameters for the hydrolysis of the beta-lactam ring by beta-lactamase I (penicillinase, EC 3.5.2.6) was studied. Benzylpenicillin and ampicillin (6-[D(-)-alpha-aminophenylacetamido]penicillanic acid) were used. Both kcat. and kcat./Km for both substrates gave bell-shaped plots of parameter versus pH. The pH-dependence of kcat./Km for the two substrates gave the same value (8.6) for the higher apparent pK, and so this value may characterize a group on the free enzyme; the lower apparent pK values were about 5(4.85 for benzylpenicillin, 5.4 for ampicillin). For benzylpenicillin both kcat. and kcat./Km depended on pH in exactly the same way. The value of Km for benzylpenicillin was thus independent of pH, suggesting that ionization of the enzyme's catalytically important groups does not affect binding of this substrate. The pH-dependence of kcat. for ampicillin differed, however, presumably because of the polar group in the side chain. The hypothesis that the pK5 group is a carboxyl group was tested. Three reagents that normally react preferentially with carboxyl groups inactivated the enzyme: the reagents were Woodward's reagent K, a water-soluble carbodi-imide, and triethyloxonium fluoroborate. These findings tend to support the idea that a carboxylate group plays a part in the action of beta-lactamase I.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAHAM E. P., NEWTON G. G. A comparison of the action of penicillinase on benzylpenicillin and cephalosporin N and the competitive inhibition of penicillinase by cephalosporin C. Biochem J. 1956 Aug;63(4):628–634. doi: 10.1042/bj0630628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P., Meadway R. J. Chemical structure of bacterial penicillinases. Nature. 1969 Apr 5;222(5188):24–26. doi: 10.1038/222024a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer C. A., Pettersson G. Effect of pH on the catalytic activity of Streptomyces griseus protease 3. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 15;45(2):469–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodlaender P., Feinstein G., Shaw E. The use of isoxazolium salts for carboxyl group modification in proteins. Trypsin. Biochemistry. 1969 Dec;8(12):4941–4949. doi: 10.1021/bi00840a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROMPTON B., JAGO M., CRAWFORD K., NEWTON G. G., ABRAHAM E. P. Behaviour of some derivatives of 7-aminocephalosporanic acid and 6-aminopenicillanic acidas substrates, inhibitors and inducers of penicillinases. Biochem J. 1962 Apr;83:52–63. doi: 10.1042/bj0830052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEPUE R. H., MOAT A. G., BONDI A. THE RELATION BETWEEN PENICILLIN STRUCTURE AND PENICILLINASE ACTIVITY. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Sep;107:374–381. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90293-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. B., Abraham E. P. Separation, purification and properties of beta-lactamase I and beta-lactamase II from Bacillus cereus 569/H/9. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;143(1):115–127. doi: 10.1042/bj1430115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. M., Anfinsen C. B. Kinetics of Woodward's Reagent K hydrolysis and reaction with staphylococcal nuclease. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3717–3723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenthal R., Cornish-Bowden A. The direct linear plot. A new graphical procedure for estimating enzyme kinetic parameters. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):715–720. doi: 10.1042/bj1390715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein G., Bodlaender P., Shaw E. The modification of essential carboxylic acid side chains of trypsin. Biochemistry. 1969 Dec;8(12):4949–4955. doi: 10.1021/bi00840a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenc I., Mile I., Csányi V. The role of the histidine side chains in the catalytic activity of B. cereus expopenicillinase. Acta Biochim Biophys Acad Sci Hung. 1971;6(1):5–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou J. P., Poole J. W. Kinetics of -lactamase inactivation of penicillins I: effect of side-chain structure, ionic strength, pH, and temperature. J Pharm Sci. 1973 May;62(5):783–788. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600620516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou J. P., Poole J. W. The amino acid nature of ampicillin and related penicillins. J Pharm Sci. 1969 Dec;58(12):1510–1515. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600581219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. J., Wilson I. B. Enzymic parameters: measurement of V and Km. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 22;242(3):519–522. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90144-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottolenghi P. The effects of hydrogen ion concentration on the simplest steady-state enzyme systems. Biochem J. 1971 Jul;123(3):445–453. doi: 10.1042/bj1230445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons S. M., Jao L., Dahlquist F. W., Borders C. L., Jr, Racs J., Groff T., Raftery M. A. The nature of amino acid side chains which are critical for the activity of lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1969 Feb;8(2):700–712. doi: 10.1021/bi00830a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patil G. V., Day R. A. Involvement of a carboxyl group in the active site of Bacillus cereus 569-H penicillinse ( -lactamase I). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 15;293(2):490–496. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pétra P. H. Modification of carboxyl groups in bovine carboxypeptidase A. I. Inactivation of the enzyme by N-ethyl-5-phenylisoxazolium-3'-sulfonate (Woodward's reagent K). Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 17;10(17):3163–3170. doi: 10.1021/bi00793a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pétra P. H., Neurath H. Modification of carboxyl groups in bovine carboxypeptidase A. II. Chemical identification of a functional glutamic acid residue and other reactive groups. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 17;10(17):3171–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiocho F. A., Lipscomb W. N. Carboxypeptidase A: a protein and an enzyme. Adv Protein Chem. 1971;25:1–78. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60278-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt D. E., Jr, Westheimer F. H. PK of the lysine amino group at the active site of acetoacetate decarboxylase. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 30;10(7):1249–1253. doi: 10.1021/bi00783a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALEY S. G. Some aspects of the kinetics of enzymic reactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Jan;10(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90206-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waley S. G. A spectrophotometric assay of beta-lactamase action on penicillins. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):789–790. doi: 10.1042/bj1390789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


