Abstract
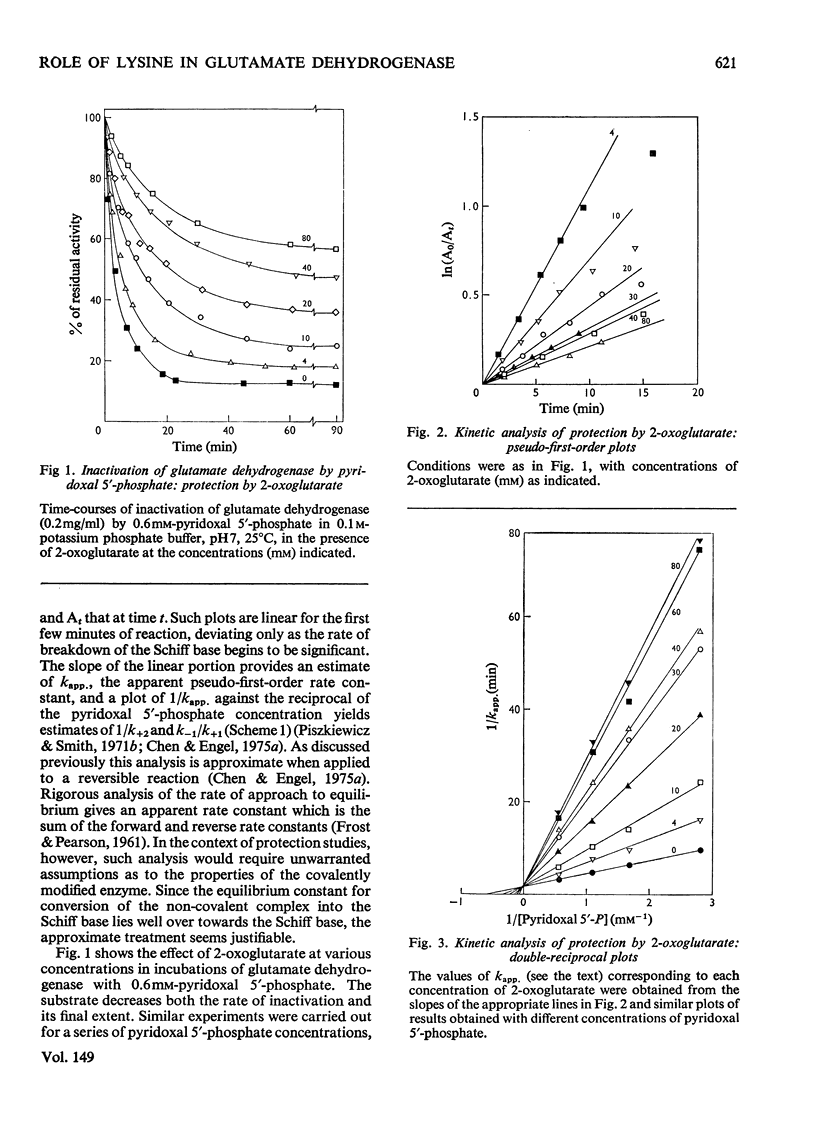
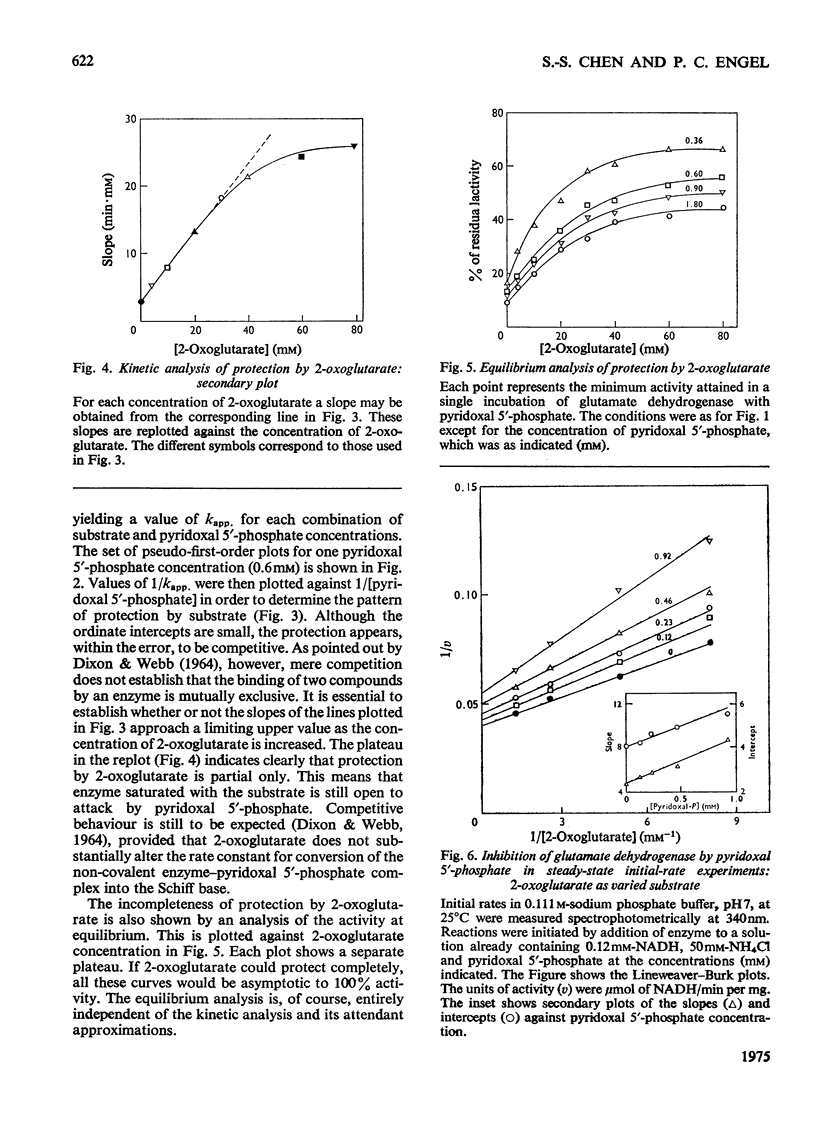
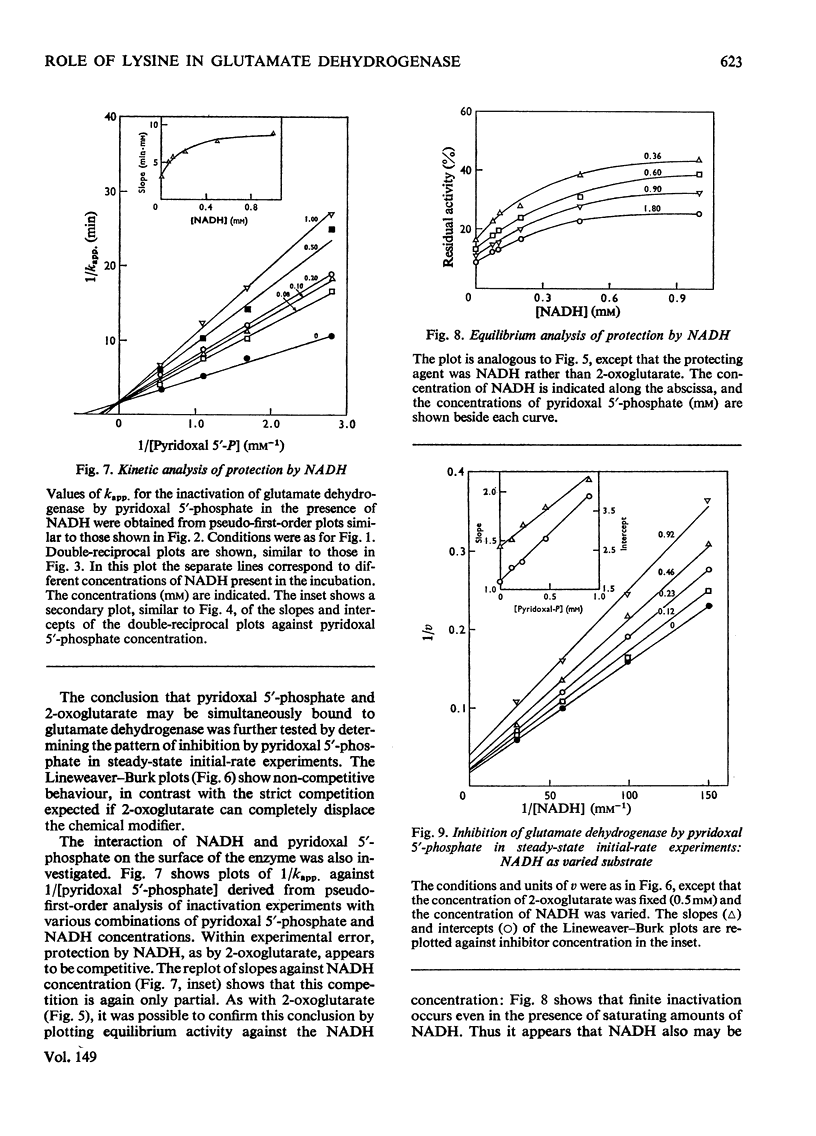
The time-course of inactivation of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase by pyridoxal 5'-phosphate was studied in the presence of varied amounts of 2-oxoglutarate or NADH. Pseudo-first-order analysis reveals that the protection by both these compounds is competitive with respect to the chemical modifier. The competition is only partial, however: saturation with either NADH or 2-oxoglutarate decreases the rate constant for inactivation to a finite minimum and not to zero. Similarly, the plot of activity at equilibrium as a function of the concentration of the protecting substrate or coenzyme reveals that neither NADH nor 2-oxoglutarate protects completely against inactivation. In initial-rate experiments, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, used as an instantaneous inhibitor rather than a long-term inactivator, displayed non-competitive inhibition with respect to both 2-oxoglutarate and NADH. These results clearly indicate that, although there is mutual hindrance between the binding to the enzyme of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, on the one hand, and 2-oxoglutarate or NADH on the other, binding is not mutually exclusive. These findings are discussed in terms of the two-step mechanism for inactivation by pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. It is concluded that lysine-126 cannot be solely responsible for binding either the substrate or the coenzyme, but could be essential for the catalytic step.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B. M., Anderson C. D., Churchich J. E. Inhibition of glutamic dehydrogenase by pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. Biochemistry. 1966 Sep;5(9):2893–2900. doi: 10.1021/bi00873a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal K. M., Smith E. L. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-specific glutamate dehydrogenase of Neurospora. I. Isolation, subunits, amino acid composition, sulfhydryl groups, and identification of a lysine residue reactive with pyridoxal phosphate and N-ethylmaleimide. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6002–6008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A., Culver J. M., Fisher H. F. Mechanism of inactivation of L-glutamate dehydrogenase by pyridoxal and pyridoxal phosphate. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 23;12(22):4367–4373. doi: 10.1021/bi00746a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. S., Engel P. C. Inactivation of nicotinamide--adenine dinucleotide-linked dehydrogenases by pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. Biochem Soc Trans. 1975;3(1):80–82. doi: 10.1042/bst0030080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. S., Engel P. C. The equilibrium position of the reaction of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase with pyridoxal5'-phosphate. A demonstration that covalent modification with this reagent completely abolishes catalytic activity. Biochem J. 1975 May;147(2):351–358. doi: 10.1042/bj1470351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S., Engel P. C. Protection of glutamate dehydrogenase by nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide against reversible inactivation by pyridoxal 5'-phosphate as a sensitive indicator of conformational change induced by substrates and substrate analogues. Biochem J. 1974 Dec;143(3):569–574. doi: 10.1042/bj1430569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffee C. J., Bradshaw R. A., Goldin B. R., Frieden C. Identification of the sites of modification of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase reacted with trinitrobenzenesulfonate. Biochemistry. 1971 Sep 14;10(19):3516–3526. doi: 10.1021/bi00795a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross D. G., McGregor L. L., Fisher H. F. The binding of -ketoglutarate in a binary complex and in a ternary complex with NADP + by L-glutamate dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 10;289(1):28–36. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W., Hucho F., Sund H. Studies of glutamate dehydrogenase. Modification with 5-diazo-1H-tetrazole and glyoxal. Importance of two different amino groups for the binding of 2-oxoglutarate and NADH. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jan 3;32(1):76–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02581.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel P. C., Dalziel K. Kinetic studies of glutamate dehydrogenase. The reductive amination of 2-oxoglutarate. Biochem J. 1970 Jul;118(3):409–419. doi: 10.1042/bj1180409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER H. F. The mechanism of the glutamic dehydrogenase reaction. I. The molecularity of the first complex formed. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1830–1834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forcina B. G., Ferri G., Zapponi M. C., Ronchi S. Identification of lysines reactive with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate in glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jun 29;20(4):535–540. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin B. R., Frieden C. The effect of pyridoxal phosphate modification on the catalytic and regulatory properties of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2139–2144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook J. J., Roberts P. A., Wallis R. B. The site at which 4-iodoacetamidosalicylate reacts with glutamate dehydrogenases. Biochem J. 1973 May;133(1):165–171. doi: 10.1042/bj1330165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm A. D., Radda G. K. Allosteric transitions of glutamate dehydrogenase. Nature. 1968 Aug 31;219(5157):947–949. doi: 10.1038/219947a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm A. D., Radda G. K. The reaction of glutamate dehydrogenase with 4-iodoacetamido salicylic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Sep;15(3):555–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon K., Piszkiewicz D., Smith E. L. Glutamate dehydrogenase: amino-acid sequence of the bovine enzyme and comparison with that from chicken liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1380–1383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piszkiewicz D., Landon M., Smith E. L. Bovine glutamate dehydrogenase. Loss of allosteric inhibition by guanosine triphosphate and nitration of tyrosine-412. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1324–1329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piszkiewicz D., Landon M., Smith E. L. Bovine liver flutamate dehydrogenase. Sequence of a hexadecapeptide containing a lysyl residue reactive with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 25;245(10):2622–2626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piszkiewicz D., Smith E. L. Bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase. Equilibria and kinetics of inactivation by pyridoxal. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4538–4544. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price N. C., Radda G. K. Desensitization of glutamate dehydrogenase by reaction of tyrosne residues. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(2):419–427. doi: 10.1042/bj1140419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. L., Landon M., Piszkiewicz D., Brattin W. J., Langley T. J., Melamed M. D. Bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase: tentative amino acid sequence; identification of a reactive lysine; nitration of a specific tyrosine and loss of allosteric inhibition by guanosine triphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):724–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veronese F. M., Piszkiewicz D., Smith E. L. Inactivation of bovine glutamate dehydrogenase by carbamyl phosphate and cyanate. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):754–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis R. B., Holbrook J. J. The effect of modifying lysine-126 on the physical, catalytic and regulatory properties of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1973 May;133(1):173–182. doi: 10.1042/bj1330173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wootton J. C., Chambers G. K., Taylor J. G., Fincham J. R. Amino-acid sequence homologies between the NADP-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase of Neurospora and the bovine enzyme. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 10;241(106):42–43. doi: 10.1038/newbio241042a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


