Abstract
1. In addition to poly(ribitol phosphate) the walls of a bacteriophage-resistant mutant of Staphylococcus aureus H contain glycerol phosphate residues that are not removed on digestion with trypsin or extraction with phenol. 2. The glycerol phosphate is present in a chain, containing three or four glycerol phosphate residues, which is covalently attached to the peptidoglycan through a phosphodiester linkage to muramic acid; this linkage is readily hydrolysed by dilute alkali. 3. The degradative studies described suggest that the poly(ribitol phosphate) chains of the wall teichoic acid may be attached to the wall by linkage to this glycerol phosphate oligomer.
Full text
PDF
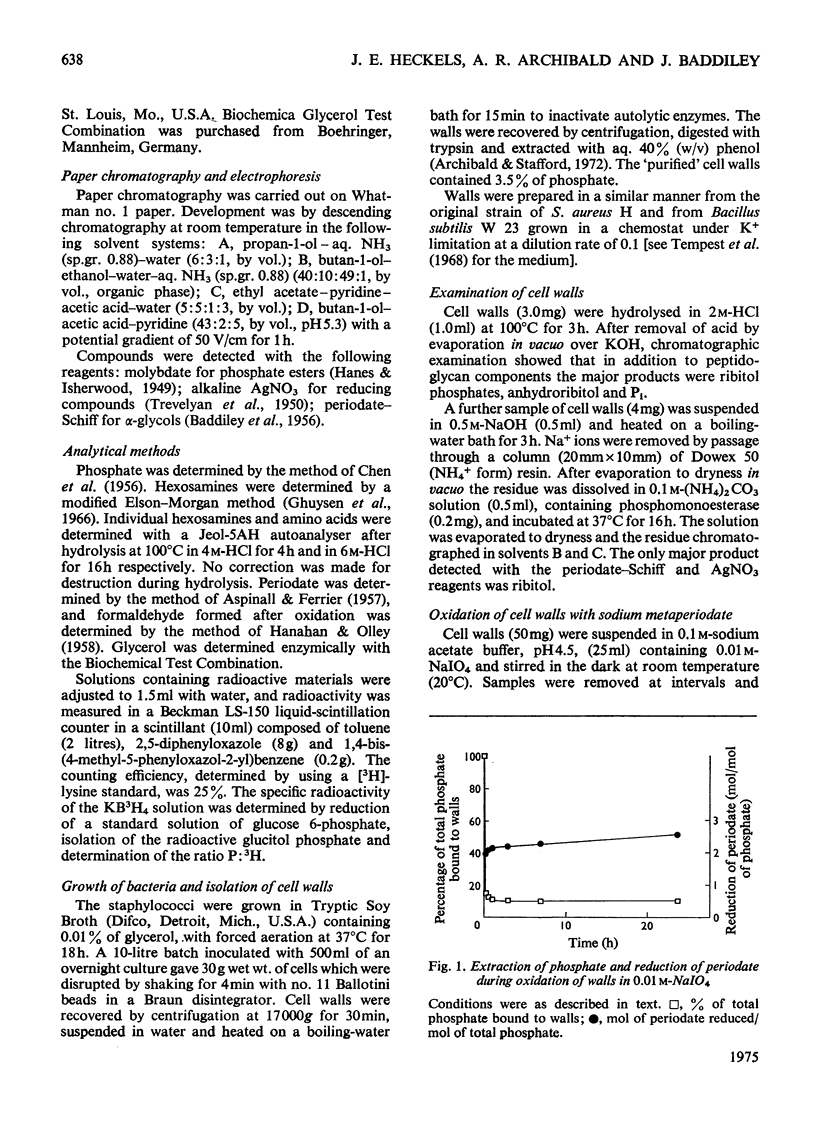
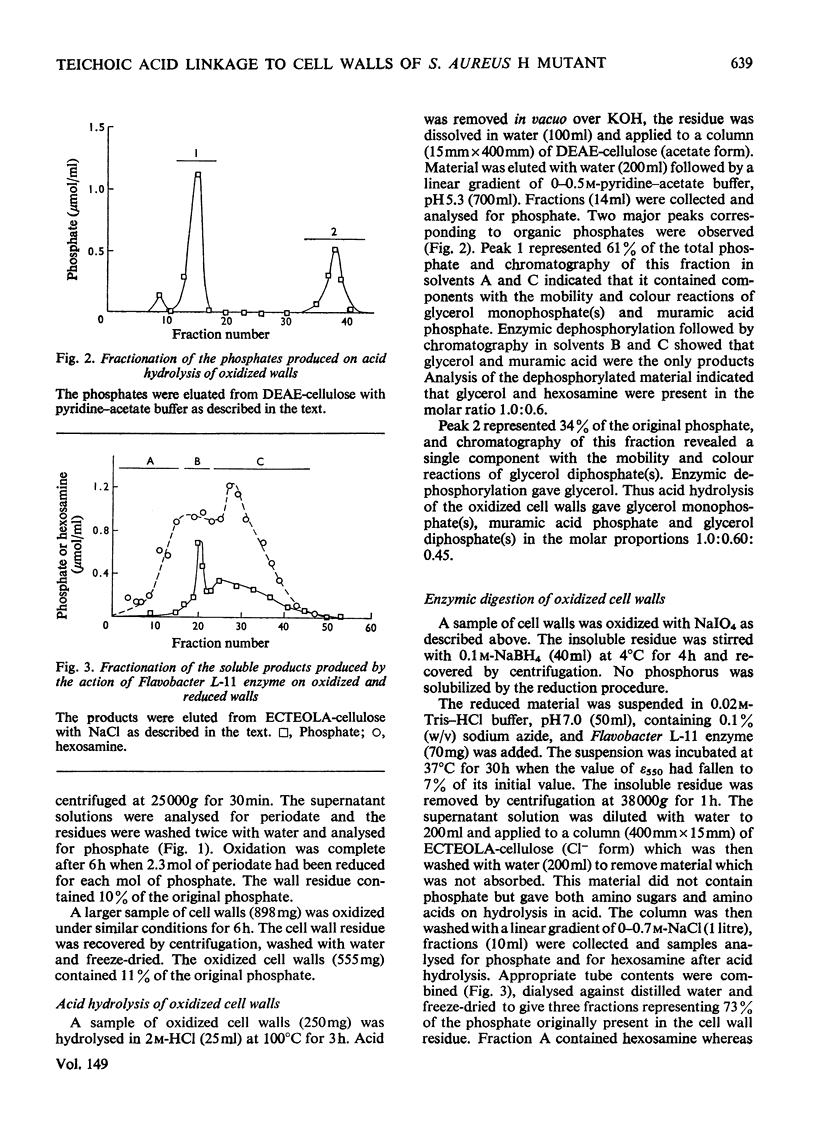
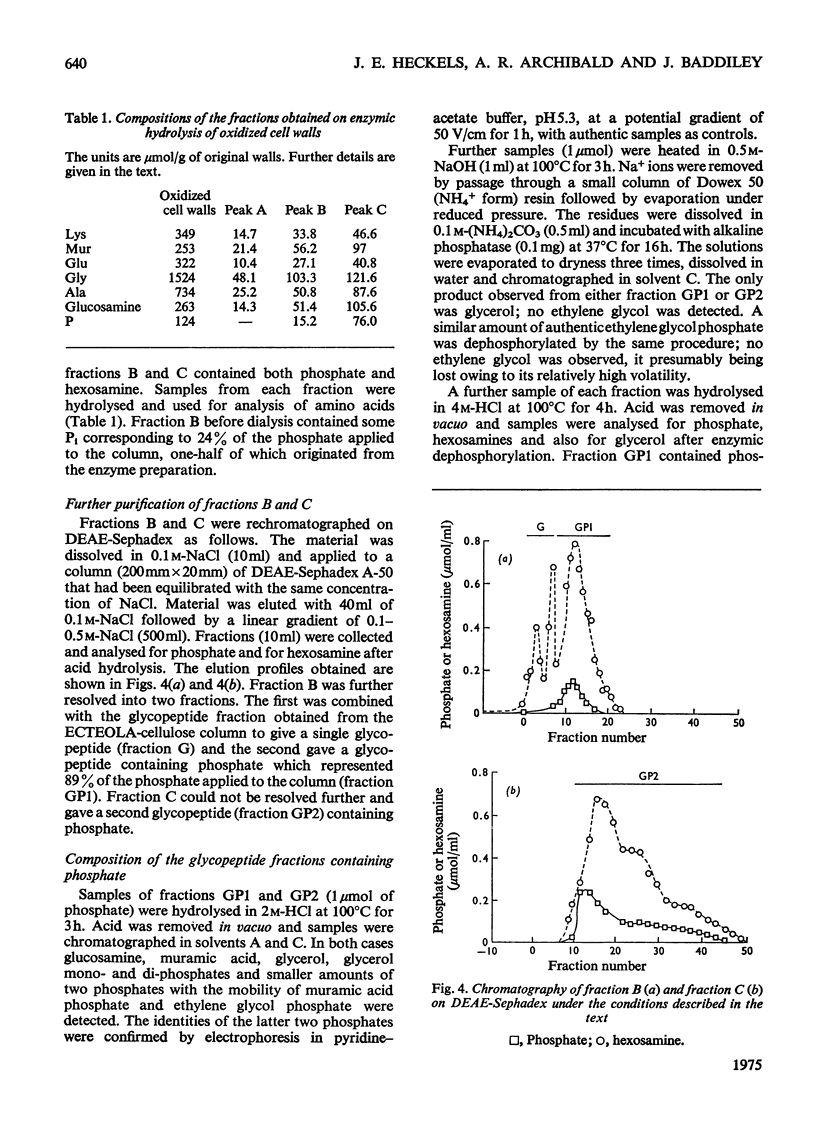
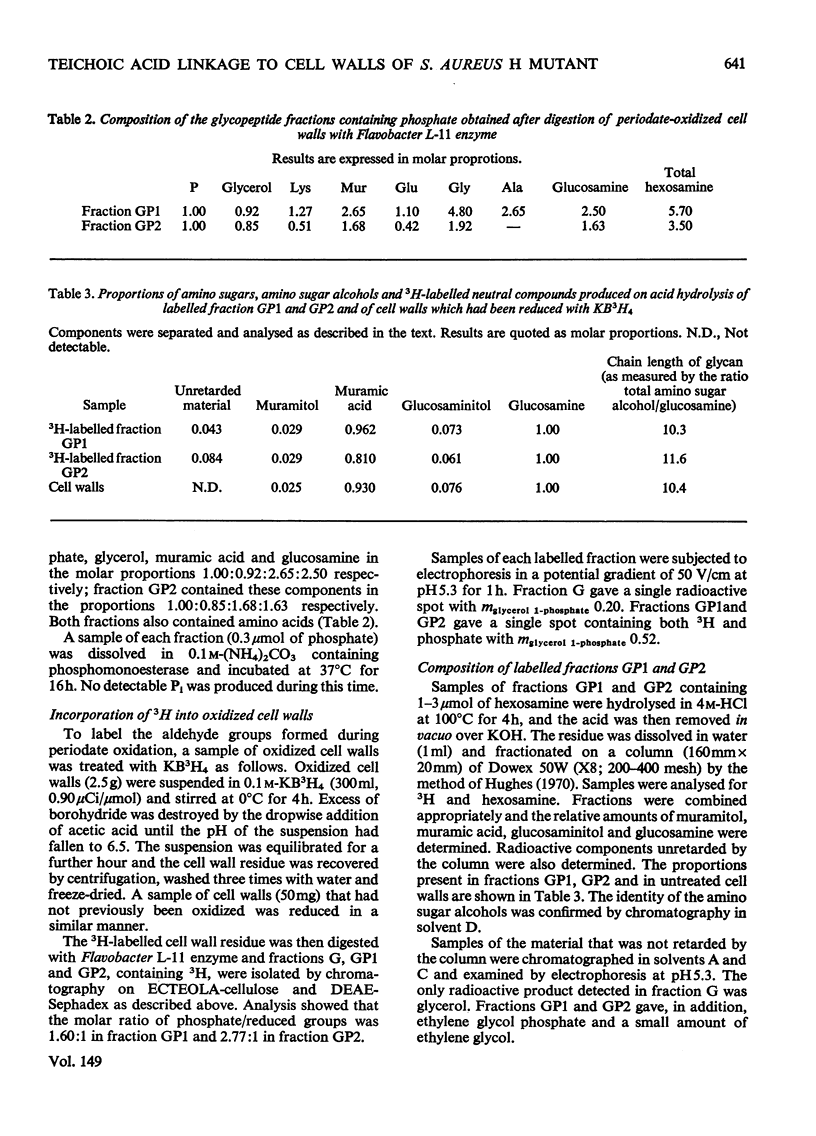




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archibald A. R., Baddiley J., Heckels J. E., Heptinstall S. Further studies on the glycerol teichoic acid of walls of Staphylococcus lactis I3. Location of the phosphodiester groups and their susceptibility to hydrolysis with alkali. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):353–359. doi: 10.1042/bj1250353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald A. R., Stafford G. H. A polymer of N-acetylglucosamine 1-phosphate in the wall of Staphylococcus lactis 2102. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(3):681–690. doi: 10.1042/bj1300681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BADDILEY J., BUCHANAN J. G., HARDY F. E., MARTIN R. O., RAJBHANDARY U. L., SANDERSON A. R. The structure of the ribitol teichoic acid of Staphylococcus aureus H. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 16;52:406–407. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90699-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BADDILEY J., BUCHANAN J. G., MARTIN R. O., RAJBHANDARY U. L. Teichoic acid from the walls of Staphylococcus aureus H. 2. Location of phosphate and alanine residues. Biochem J. 1962 Oct;85:49–56. doi: 10.1042/bj0850049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BADDILEY J., BUCHANAN J. G., RAJBHANDARY U. L., SANDERSON A. R. Teichoic acid from the walls of Staphylococcus aureus H. Structure of the N-acetylglucosaminyl-ribitol residues. Biochem J. 1962 Mar;82:439–448. doi: 10.1042/bj0820439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler F., Glaser L. The synthesis of polyribitol phosphate. I. Purification of polyribitol phosphate polymerase and lipoteichoic acid carrier. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2684–2689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GHUYSEN J. M., TIPPER D. J., STROMINGER J. L. STRUCTURE OF THE CELL WALL OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS, STRAIN COPENHAGEN. IV. THE TEICHOIC ACID-GLYCOPEPTIDE COMPLEX. Biochemistry. 1965 Mar;4:474–485. doi: 10.1021/bi00879a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant W. D., Wicken A. J. Muramic acid phosphate and the linkage of teichoic acid to peptidoglycan in Bacillus stearothermophilus cell walls. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jul 26;32(2):122–128. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90356-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANAHAN D. J., OLLEY J. N. Chemical nature of monophosphoinositides. J Biol Chem. 1958 Apr;231(2):813–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANES C. S., ISHERWOOD F. A. Separation of the phosphoric esters on the filter paper chromatogram. Nature. 1949 Dec 31;164(4183):1107-12, illust. doi: 10.1038/1641107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J. B., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. The molecular structure of bacterial walls. The size of ribitol teichoic acids and the nature of their linkage to glycosaminopeptides. Biochem J. 1965 Dec;97(3):723–730. doi: 10.1042/bj0970723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymann H., Manniello J. M., Barkulis S. S. Structure of streptococcal cell walls. V. Phosphate esters in the walls of group A Streptococcus pyogenes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Feb 21;26(4):486–491. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90574-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C. The cell wall of Bacillus licheniformis N.C.T.C. 6346. Linkage between the teichuronic acid and mucopeptide components. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(3):431–439. doi: 10.1042/bj1170431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Strominger J. L. Structure of the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureaus. IX. Mechanism of hydrolysis by the L11 enzyme. Biochemistry. 1968 Aug;7(8):2745–2761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Hall E. A. The linkage between the polysaccharide and mucopeptide components of the cell wall of Lactobacillus casei. Biochem J. 1965 Aug;96(2):302–309. doi: 10.1042/bj0960302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Holmwood K. J. Structure of the cell wall of Lactobacilli. Role of muramic acid phosphate in Lactobacillus fermenti. Biochem J. 1968 Jul;108(3):363–368. doi: 10.1042/bj1080363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T. Y., Gotschlich E. C. Muramic acid phosphate as a component of the mucopeptide of Gram-positive bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 10;242(3):471–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz E., Ghuysen J. M., Heymann H. Cell walls of Streptococcus pyogenes, type 14. C polysaccharide-peptidoglycan and G polysaccharide-peptidoglycan complexes. Biochemistry. 1967 Dec;6(12):3659–3670. doi: 10.1021/bi00864a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., GHUYSEN J. M. ON THE LINKAGE BETWEEN TEICHOIC ACID AND THE GLYCOPEPTIDE IN THE CELL WALL OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Aug 14;12:418–424. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest D. W., Dicks J. W., Ellwood D. C. Influence of growth condition on the concentration of potassium in Bacillus subtilis var. niger and its possible relationship to cellular ribonucleic acid, teichoic acid and teichuronic acid. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj1060237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


