Abstract
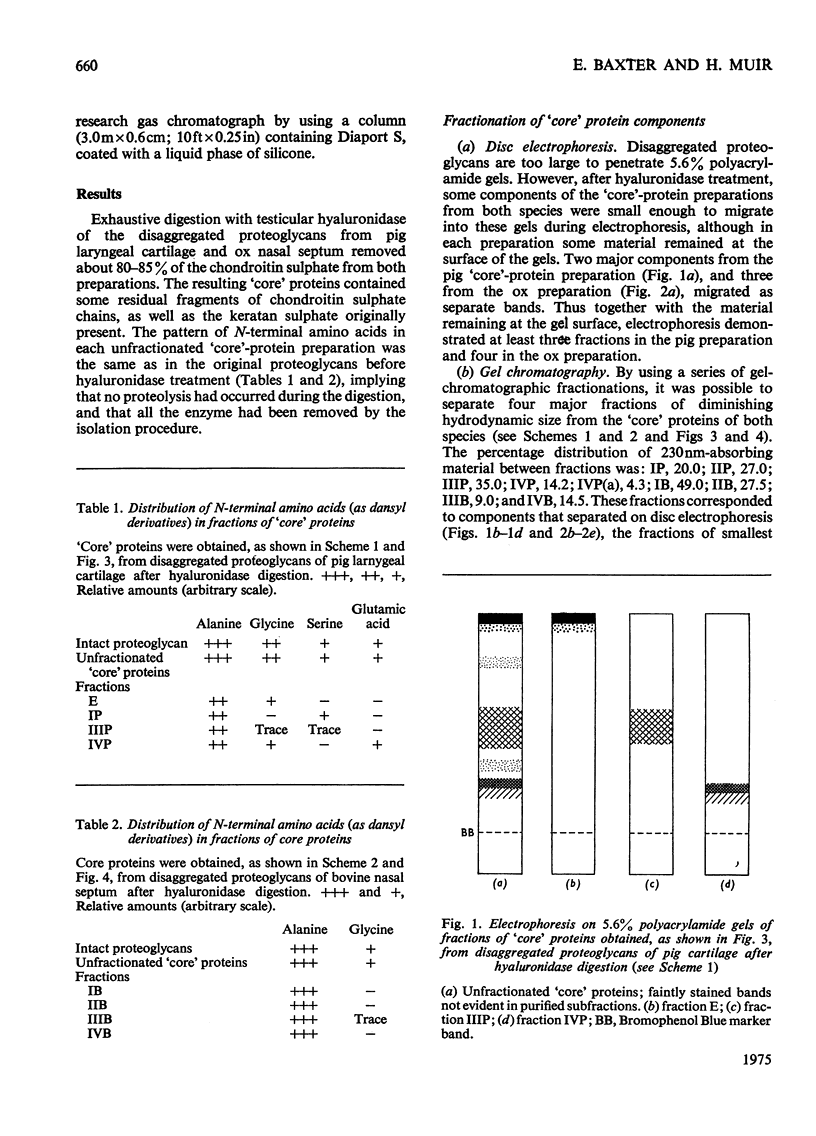
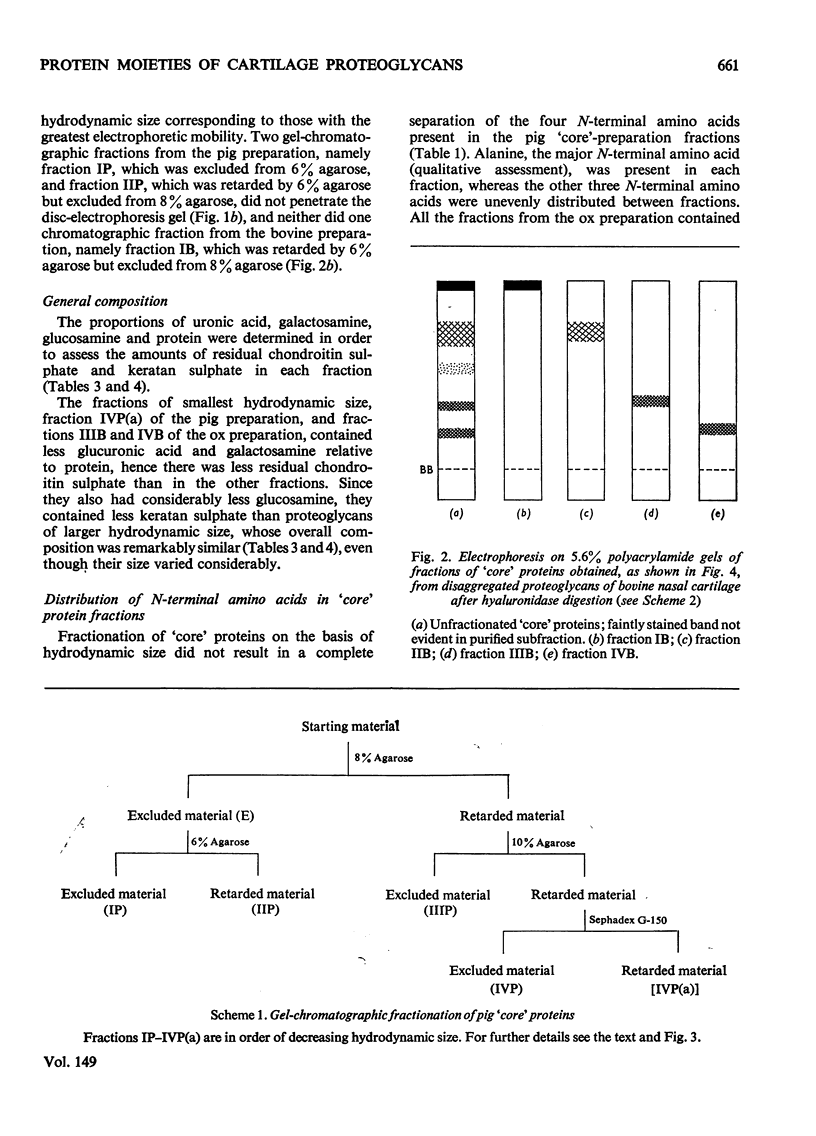
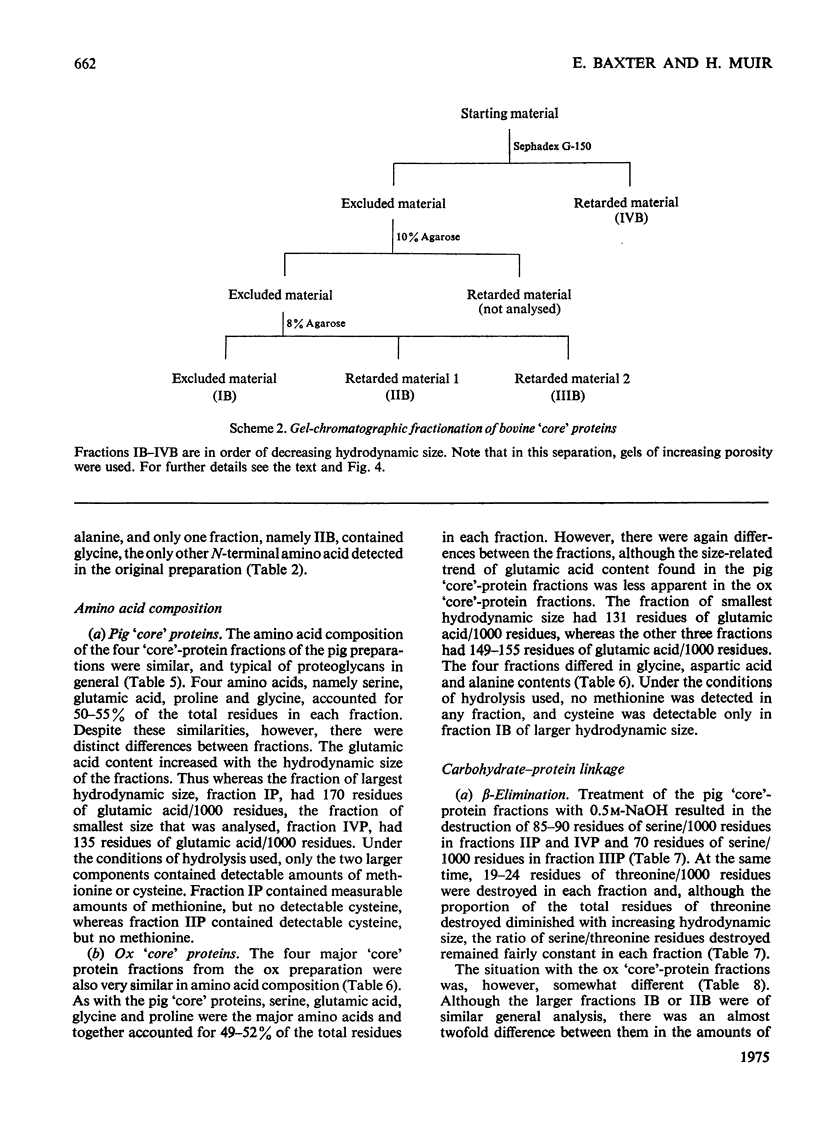
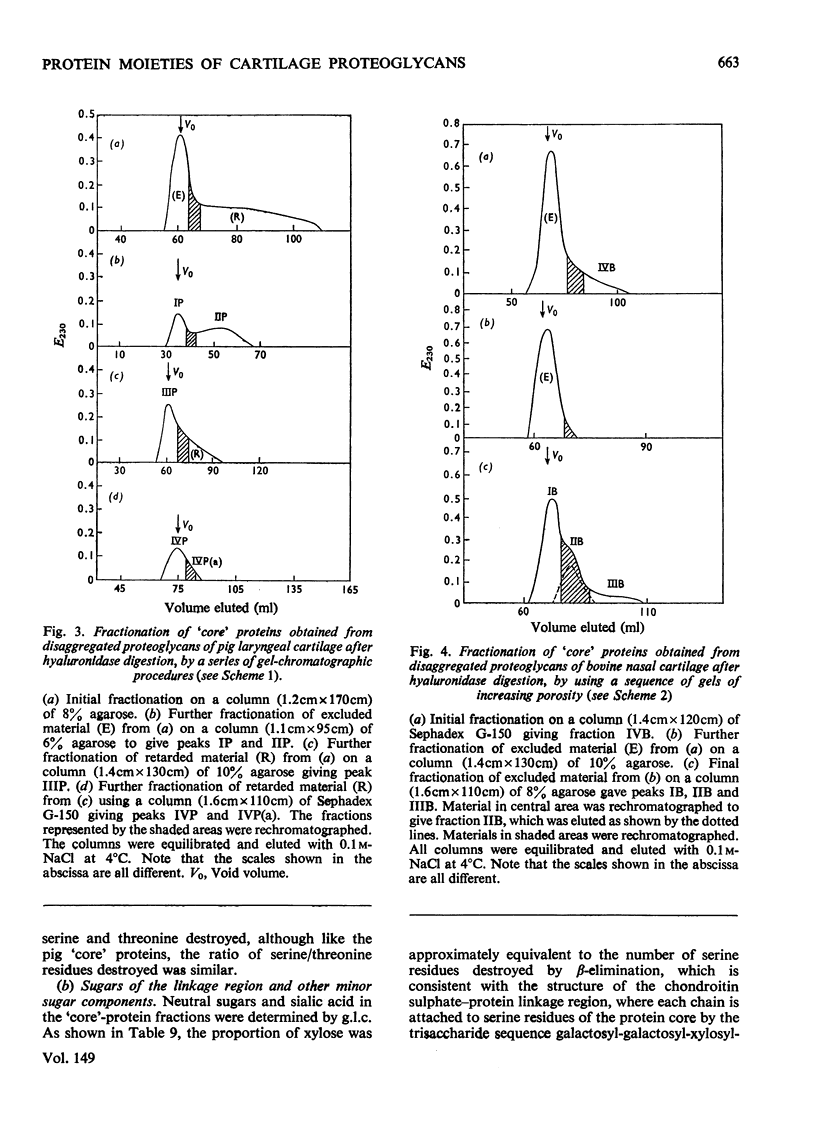
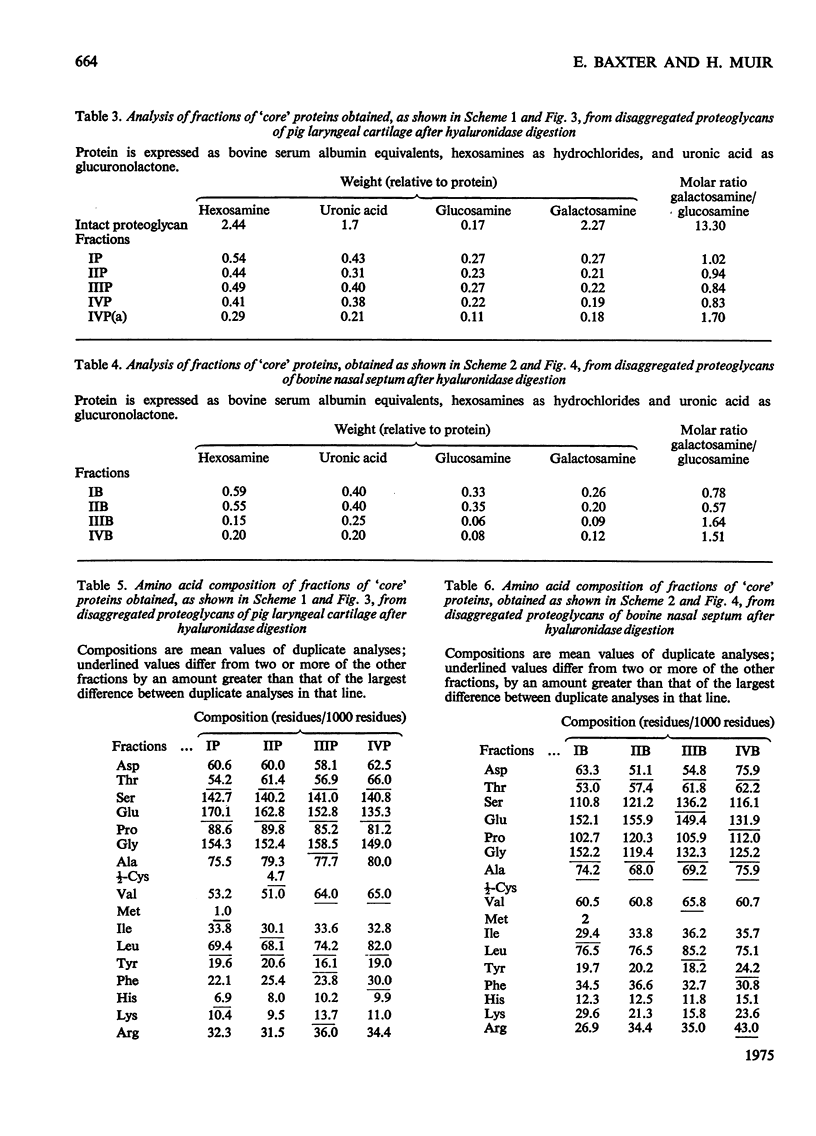
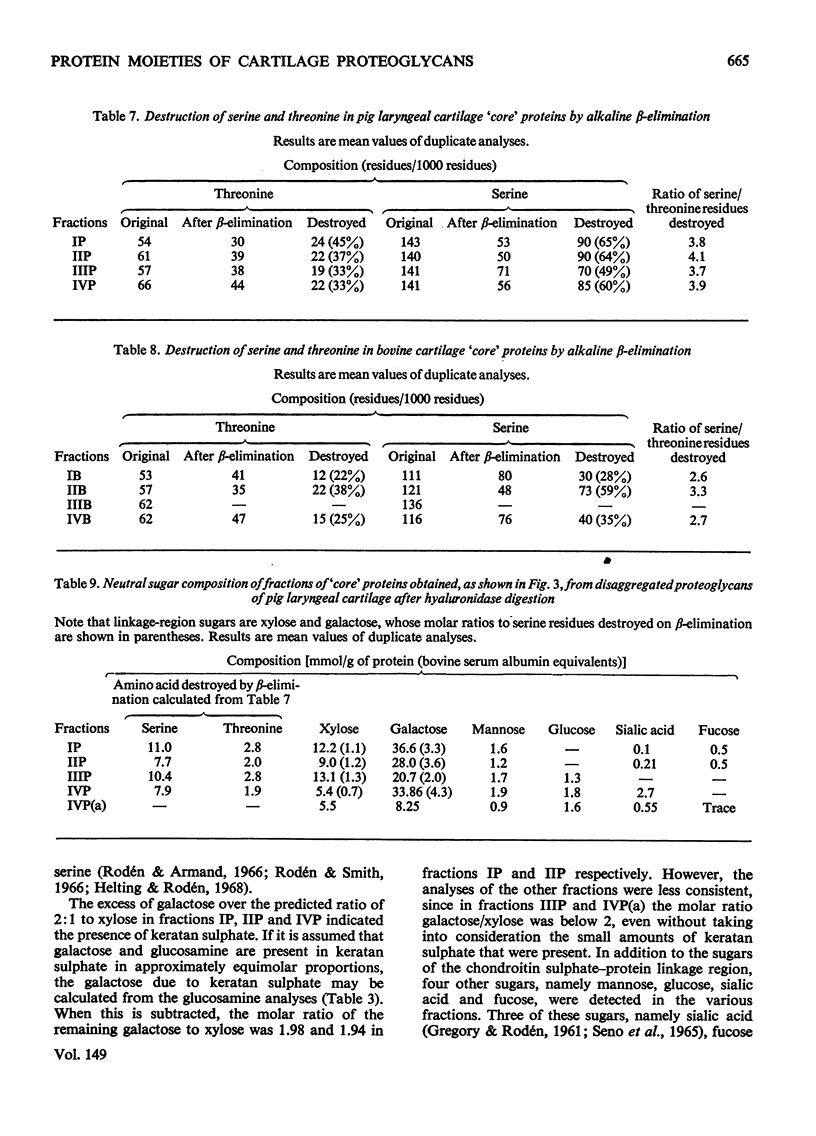
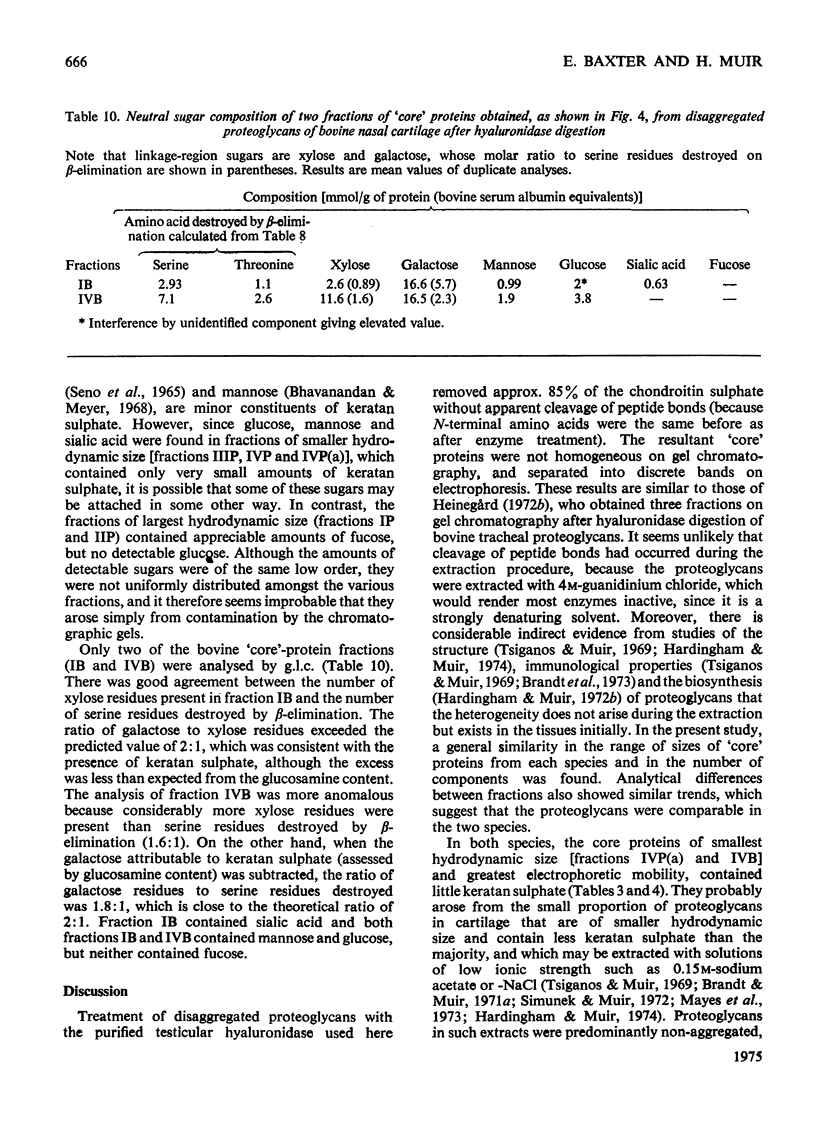
Proteoglycans extracted with 4M-guanidinium chloride from pig laryngeal cartilage and bovine nasal septum were purified by density-gradient centrifugation in CsCl under 'associative' followed by 'dissociative' conditions [Hascall & Sajdera (1969) J. Biol. Chem. 244, 2384-2396]. Proteoglycans were then digested exhaustively with testicular hyaluronidase, which removed about 80% of the chondroitin sulphate. The hyaluronidase was purified until no proteolytic activity was detectable under the conditions used for digestion. The resulting 'core' proteins of both species were fractionated by a sequence of gel-chromatographic procedures which gave four major fractions of decreasing hydrodynamic size. Those that on electrophoresis penetrated 5.6% (w/v) polyacrylamide gels migrated as discrete bands whose mobility increased with decreasing hydrodynamic size. The unfractionated 'core' proteins had the same N-terminal amino acids as the intact proteoglycan, suggesting that no peptide bonds had been cleaved during hyaluronidase digestion. Alanine predominated as the N-terminal residue in all the fractions of both species. Fractions were analysed for amino acid, amino sugar, uronic acid and neutral sugar compositions. In pig 'core' proteins, the glutamic acid content increased significantly with hydrodynamic size, but in bovine 'core' proteins this trend was less marked. Significant differences in amino acid composition between fractions suggested that in each species there was more than one variety of proteoglycan. The molar proportions of xylose to serine destroyed on alkaline beta-elimination were equivalent in most fractions, indicating that the serine residues destroyed were attached to the terminal xylose of chondroitin sulphate chains. The ratio of serine residues to threonine residues destroyed on beta-elimination, was similar in all fractions of both species. Since the fractions of smallest hydrodynamic size contained less keratan sulphate than those of larger size, it implies that in the former the keratan sulphate chains were shorter than in the latter.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON B., HOFFMAN P., MEYER K. THE O-SERINE LINKAGE IN PEPTIDES OF CHONDROITIN 4- OR 6-SULFATE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:156–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter E., Muir H. The antigenicity of cartilage proteoglycans: the relationship of the antigenic determinants present in Smith degraded and intact proteoglycans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 15;279(2):276–281. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhavanandan V. P., Meyer K. Studies on keratosulfates. Methylation, desulfation, and acid hydrolysis studies on old human rib cartilage keratosulfate. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 10;243(5):1052–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borders C. L., Jr, Raftery M. A. Purification and partial characterization of testicular hyaluronidase. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3756–3762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt K. D., Muir H. Characterization of protein-polysaccharides of articular cartilage from mature and immature pigs. Biochem J. 1969 Oct;114(4):871–876. doi: 10.1042/bj1140871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt K. D., Muir H. Heterogeneity of protein-polysaccharides of porcine articular cartilage. The chondroitin sulphate proteins associaterd with collagen. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;123(5):747–755. doi: 10.1042/bj1230747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt K. D., Muir H. Heterogeneity of protein-polysaccharides of porcine articular cartilage. The sequential extraction of chondroitin sulphate-proteins with iso-osmotic neutral sodium acetate. Biochem J. 1971 Jan;121(2):261–270. doi: 10.1042/bj1210261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt K. D., Tsiganos C. P., Muir H. Immunological relationships between proteoglycans of different hydrodynamic size from articular cartilage of foetal and mature pigs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 14;320(2):453–468. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90326-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray B. A., Lieberman R., Meyer K. Structure of human skeletal keratosulfate. The linkage region. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 25;242(14):3373–3380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrambach A., Reisfeld R. A., Wyckoff M., Zaccari J. A procedure for rapid and sensitive staining of protein fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clamp J. R., Dawson G., Hough L. The simultaneous estimation of 6-deoxy-L-galactose (L-fucose), D-mannose, D-galactose, 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucose (N-acetyl-D-glucosamine) and N-acetylneuraminic acid (sialic acid) in glycopeptides and glycoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Nov 28;148(2):342–349. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Biosynthesis of proteoglycans in cartilage slices. Fractionation by gel chromatography and equilibrium density-gradient centrifugation. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(4):791–803. doi: 10.1042/bj1260791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Hyaluronic acid in cartilage and proteoglycan aggregation. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):565–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1390565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. The specific interaction of hyaluronic acid with cartillage proteoglycans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 15;279(2):401–405. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Heinegård D. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. I. The role of hyaluronic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4232–4241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Heinegård D. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. II. Oligosaccharide competitors of the proteoglycan-hyaluronic acid interaction. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4242–4249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Riolo R. L. Characteristics of the protein-keratan sulfate core and of keratan sulfate prepared from bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4529–4538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Riolo R. L., Hayward J., Jr, Reynolds C. C. Treatment of bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycan with chondroitinases from Flavobacterium heparinum and Proteus vulgaris. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4521–4528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Sajdera S. W. Physical properties and polydispersity of proteoglycan from bovine nasal cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):4920–4930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Sajdera S. W. Proteinpolysaccharide complex from bovine nasal cartilage. The function of glycoprotein in the formation of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2384–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D. Extraction, fractionation and characterization of proteoglycans from bovine tracheal cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 28;285(1):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90190-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Hascall V. C. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. 3. Characteristics of the proteins isolated from trypsin digests of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4250–4256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D. Hyaluronidase digestion and alkaline treatment of bovine tracheal cartilage proteoglycans. Isolation and characterisation of different keratan sulfate proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 28;285(1):193–207. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90191-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helting T., Rodén L. The carbohydrate-protein linkage region of chondroitin 6-sulfate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 23;170(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P., Mashburn T. A., Jr, Meyer K. Proteinpolysaccharide of bovine cartilage. II. The relation of keratan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 10;242(17):3805–3809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATHEWS M. B., LOZAITYTE I. Sodium chondroitin sulfate-protein complexes of cartilage. I. Molecular weight and shape. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Mar;74(1):158–174. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90210-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUIR H. The nature of the link between protein and carbohydrate of a chondroitin sulphate complex from hyaline cartilage. Biochem J. 1958 Jun;69(2):195–204. doi: 10.1042/bj0690195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashburn T. A., Jr, Hoffman P. Comparative fractionation studies of cartilage proteinpolysaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6497–6506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayes R. W., Mason R. M., Griffin D. C. The composition of cartilage proteoglycans. An investigation using high- and low-inonic-strength extraction procedures. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;131(3):541–553. doi: 10.1042/bj1310541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir H., Jacobs S. Protein-polysaccharides of pig laryngeal cartilage. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):367–374. doi: 10.1042/bj1030367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARTRIDGE S. M., DAVIS H. F., ADAIR G. S. The chemistry of connective tissues. 6. The constitution of the chondroitin sulphate-protein complex in cartilage. Biochem J. 1961 Apr;79:15–26. doi: 10.1042/bj0790015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrini V. Electrophoretic heterogeneity of proteinpolysaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 25;244(6):1540–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodén L., Armand G. Structure of the chondroitin 4-sulfate-protein linkage region. Isolation and characterization of the disaccharide 3-O-beta-D-glucuronosyl-D-galactose. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 10;241(1):65–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodén L., Smith R. Structure of the neutral trisaccharide of the chondroitin 4-sulfate-protein linkage region. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 25;241(24):5949–5954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L. C., Pal S., Beale R. J. Proteoglycans from bovine proximal humeral articular cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3681–3690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Pal S., Beale R., Schubert M. A comparison of proteinpolysaccharides of bovine nasal cartilage isolated and fractionated by different methods. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 25;245(16):4112–4122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SENO N., MEYER K., ANDERSON B., HOFFMAN P. VARIATIONS IN KERATOSULFATES. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1005–1010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajdera S. W., Hascall V. C. Proteinpolysaccharide complex from bovine nasal cartilage. A comparison of low and high shear extraction procedures. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 10;244(1):77–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Fracassini A., Peters T. J., Floreani L. The protein-polysaccharide complex of bovine nasal cartilage. Studies on the protein core. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):569–575. doi: 10.1042/bj1050569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simůnek Z., Muir H. Changes in the protein-polysaccharides of pig articular cartilage during prenatal life, development and old age. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):515–523. doi: 10.1042/bj1260515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda N., Seno N. Sialic acid in the keratan sulfate fraction from whale cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 12;208(2):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiganos C. P., Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Proteoglycans of cartilage: an assessment of their structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 16;229(2):529–534. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90216-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiganos C. P., Muir H. Studies on protein-polysaccharides from pig laryngeal cartilage. Heterogeneity, fractionation and characterization. Biochem J. 1969 Aug;113(5):885–894. doi: 10.1042/bj1130885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods K. R., Wang K. T. Separation of dansyl-amino acids by polyamide layer chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 21;133(2):369–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


