Abstract
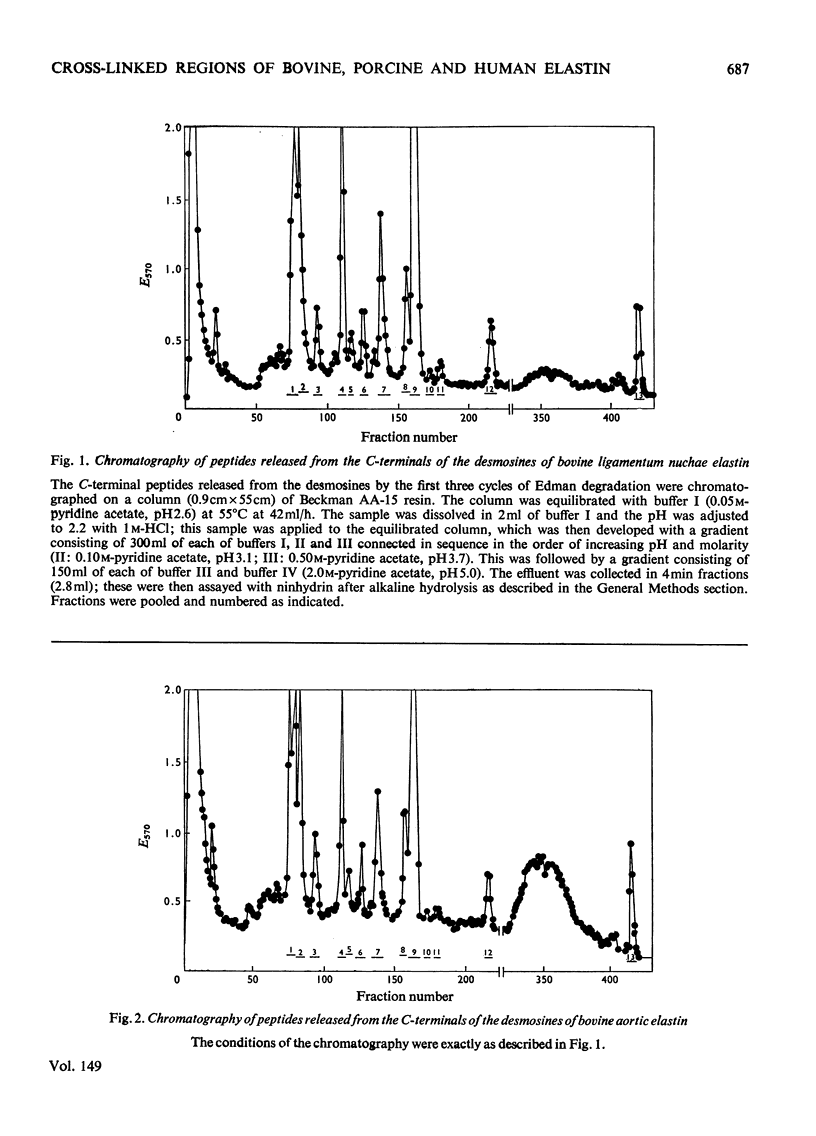
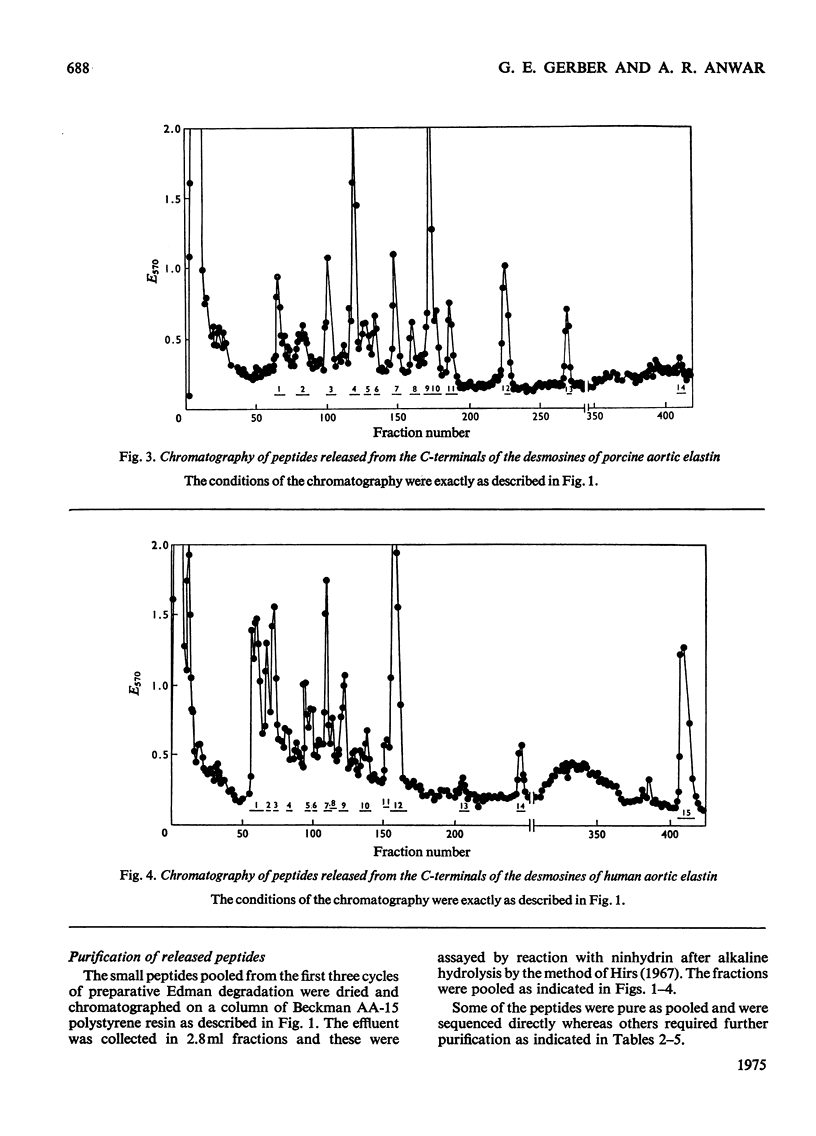
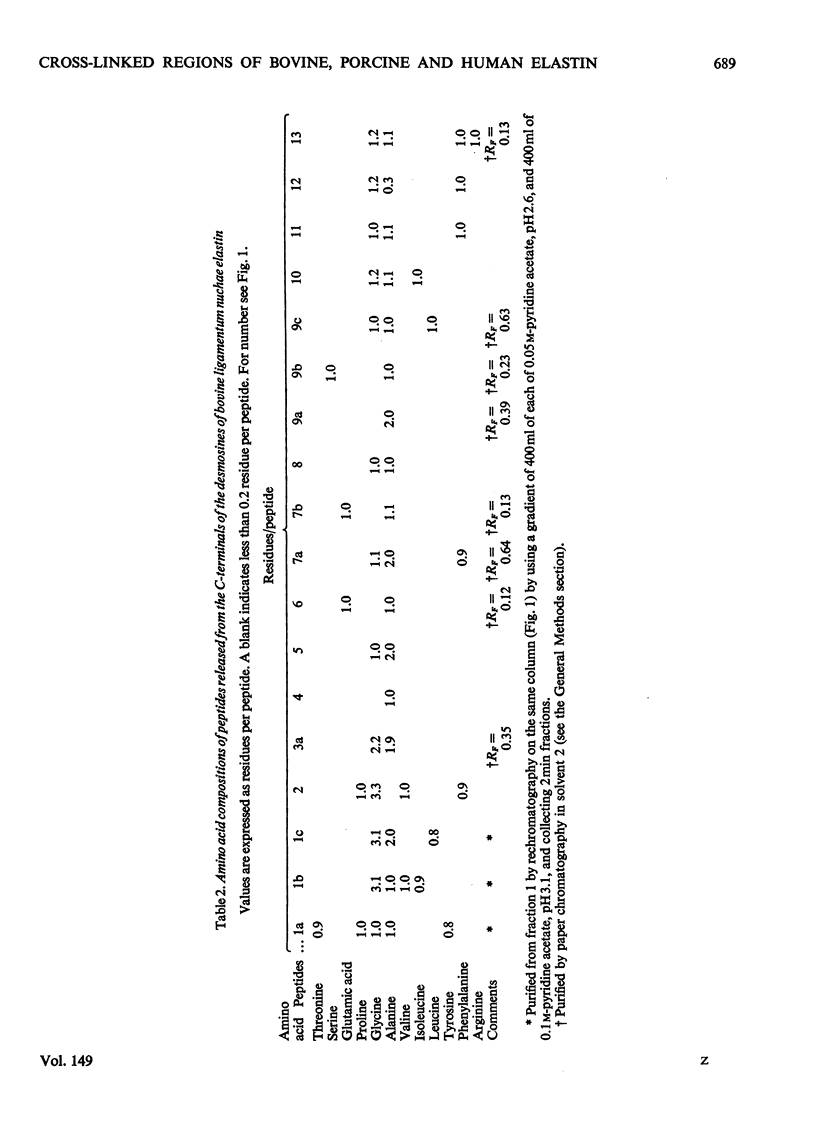
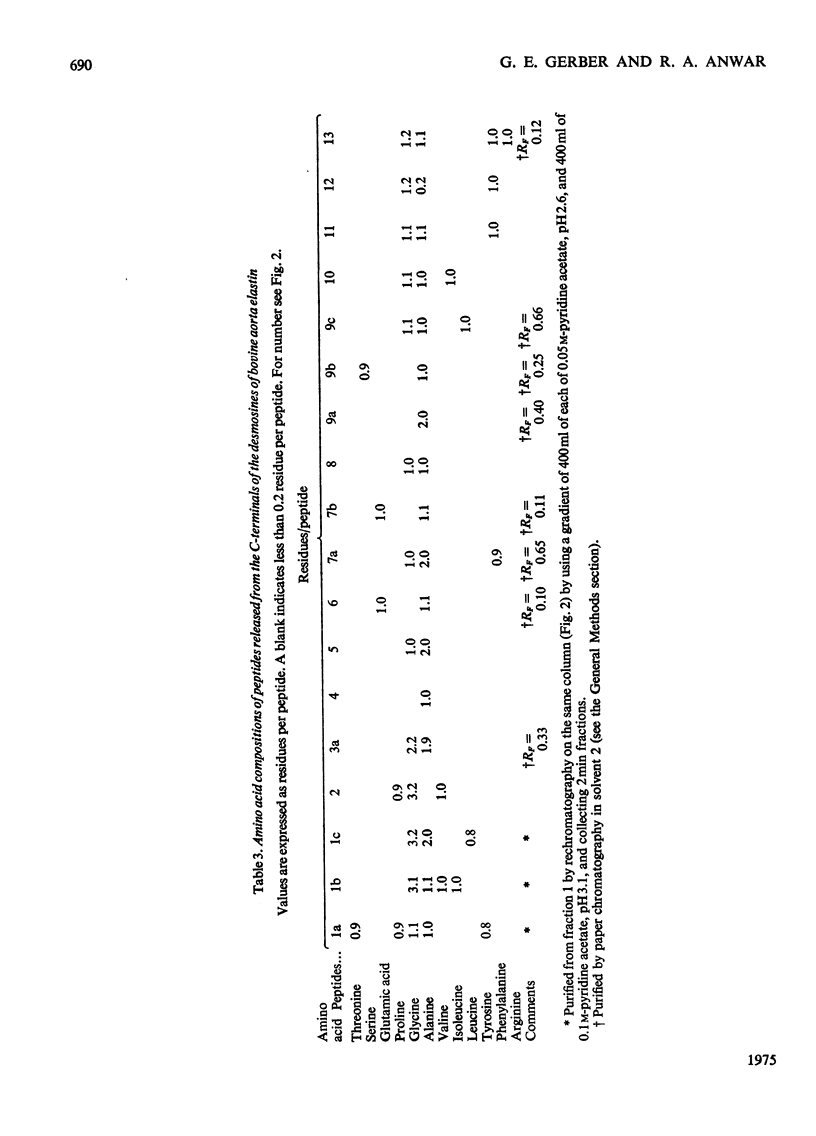
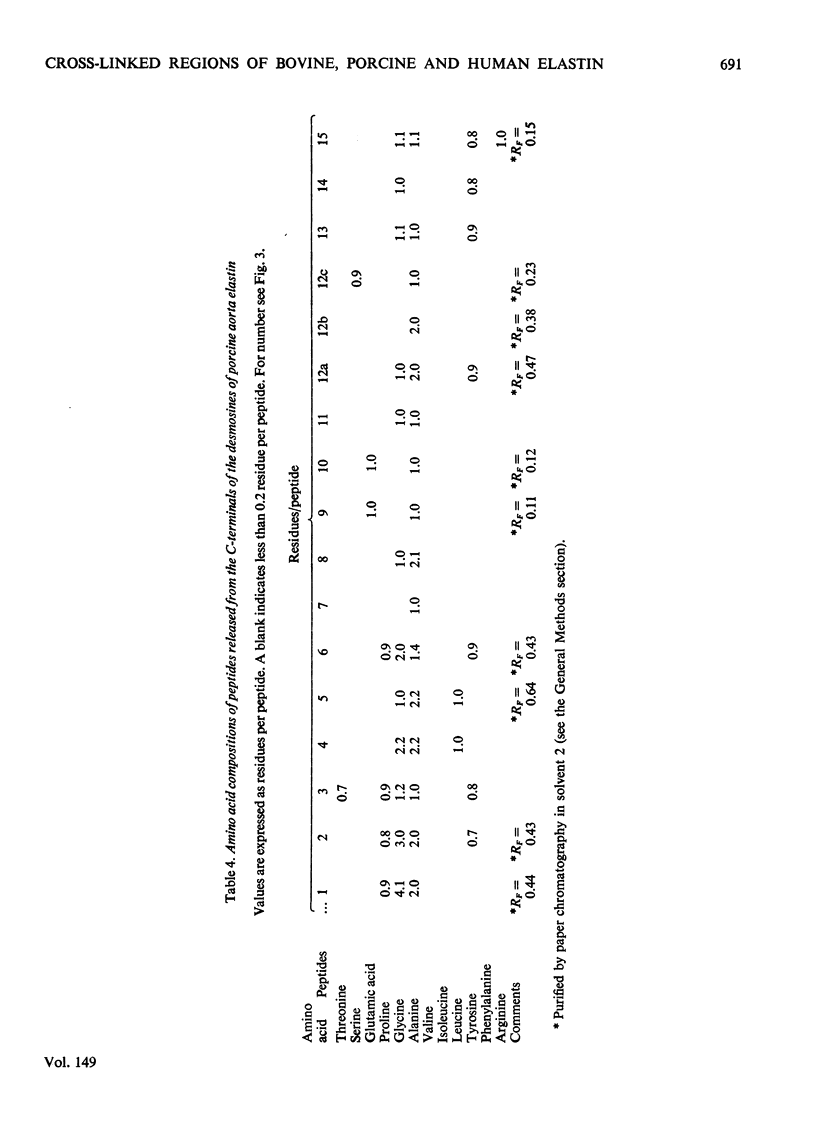
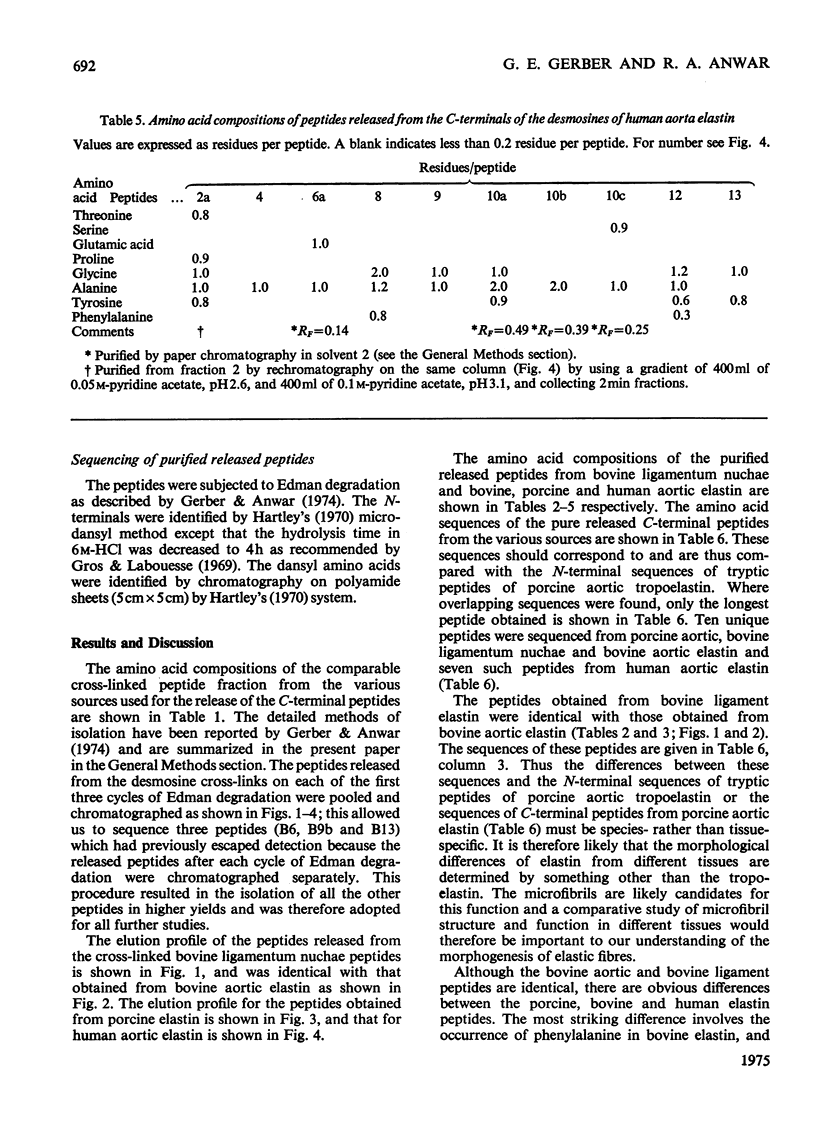
1. The preparative Edman degradation of desmosine-containing peptides permitted the isolation of peptides C-terminal to the desmosine cross-links in bovine, porcine and human aortic elastin as well as bovine ligamentum nuchae elastin. This identifies the lysines in the tropoelastin which give rise to the desmosine cross-links. 2. The sequences from bovine aortic elastin were identical with those obtained from bovine ligamentum nuchae elastin but differed from those obtained from the other species. The most striking difference involves the occurrence of phenylalanine in bovine elastin and tyrosine in porcine and human elastin C-terminal to the desmosine cross-links. 3. The sequences of the C-terminal peptides were found to fall into two distinct classes, one starting with hydrophobic residues, the other starting with alanine. It is proposed that thehydrophobic residue prevents the enzymic oxidative deamination of the adjacent lysine e-amino group and this then contributes the nitrogen to the pyridinium ring of the cross-links.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anwar R. A. Comparison of elastins from various sources. Can J Biochem. 1966 Jun;44(6):725–734. doi: 10.1139/o66-090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwar R. A., Oda G. The biosynthesis of desmosine and isodesmosine. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 25;241(20):4638–4641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRINK N. G., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Pancreatic elastase: purification, properties, and function. J Biol Chem. 1956 Oct;222(2):705–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davril M., Han K. K. Isolation and characterization of a highly cross-linked peptide from elastin of porcine aorta. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 1;43(3):331–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80673-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. A., Bruenger E., Gray W. R., Sandberg L. B. Isolation and amino acid sequences of tropoelastin peptides. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2876–2879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. A., Gray W. R., Franzblau C. Isolation and characterization of crosslinked peptides from elastin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 20;303(2):363–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90368-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. A., Rubin L., Kagan H. M., Franzblau C., Bruenger E., Sandberg L. B. Isolation and characterization of cross-linked peptides from elastin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6191–6196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber G. E., Anwar R. A. Structural studies on cross-linked regions of elastin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5200–5207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber G. E., Kemp G. D. Amino acid analysis of elastin--a rapid method. J Chromatogr. 1972 Sep 6;71(2):361–362. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)80697-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. R., Sandberg L. B., Foster J. A. Molecular model for elastin structure and function. Nature. 1973 Dec 21;246(5434):461–466. doi: 10.1038/246461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros C., Labouesse B. Study of the dansylation reaction of amino acids, peptides and proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):463–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEILMANN J., BARROLLIER J., WATZKE E. Beitrag zur Aminosäurebestimmung auf Papierchromatogrammen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1957;309(4-6):219–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley B. S. Strategy and tactics in protein chemistry. Biochem J. 1970 Oct;119(5):805–822. doi: 10.1042/bj1190805f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller S., Levi M. M., Mandl I. Antigenicity and chemical composition of an enzymatic digest of elastin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jul;132(2):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90399-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan A. S., Anwar R. A. The specificity of purified porcine pancreatic elastase. Biochem J. 1969 Aug;114(1):11–17. doi: 10.1042/bj1140011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARTRIDGE S. M., DAVIS H. F., ADAIR G. S. The chemistry of connective tissues. 2. Soluble proteins derived from partial hydrolysis of elastin. Biochem J. 1955 Sep;61(1):11–21. doi: 10.1042/bj0610011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge S. M., Elsden D. F., Thomas J., Dorfman A., Telser A., Ho P. L. Incorporation of labelled lysine into the desmosine cross-bridges in elastin. Nature. 1966 Jan 22;209(5021):399–400. doi: 10.1038/209399b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada W., Bowman A., Davis N. R., Anwar R. A. An approach to the study of the structure of desmosine and isodesmosine containing peptides isolated from the elastase digest of elastin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Oct 8;37(2):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90718-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


