Abstract
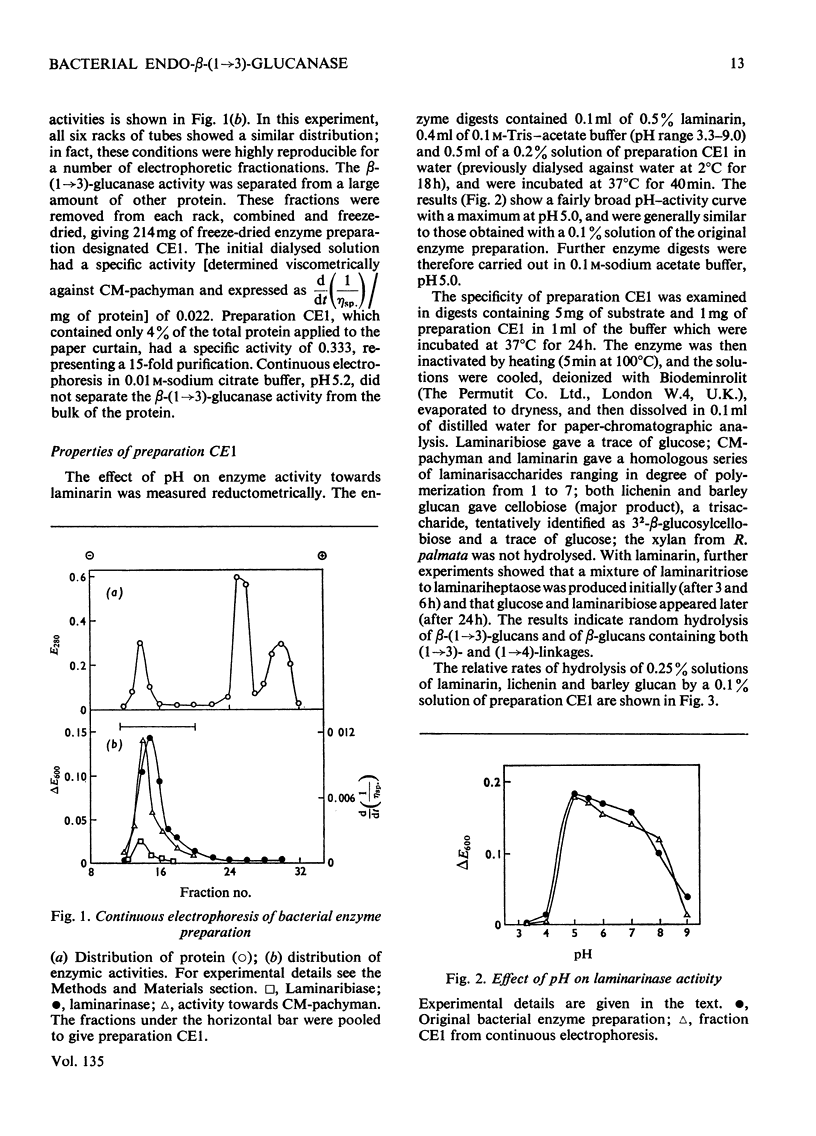
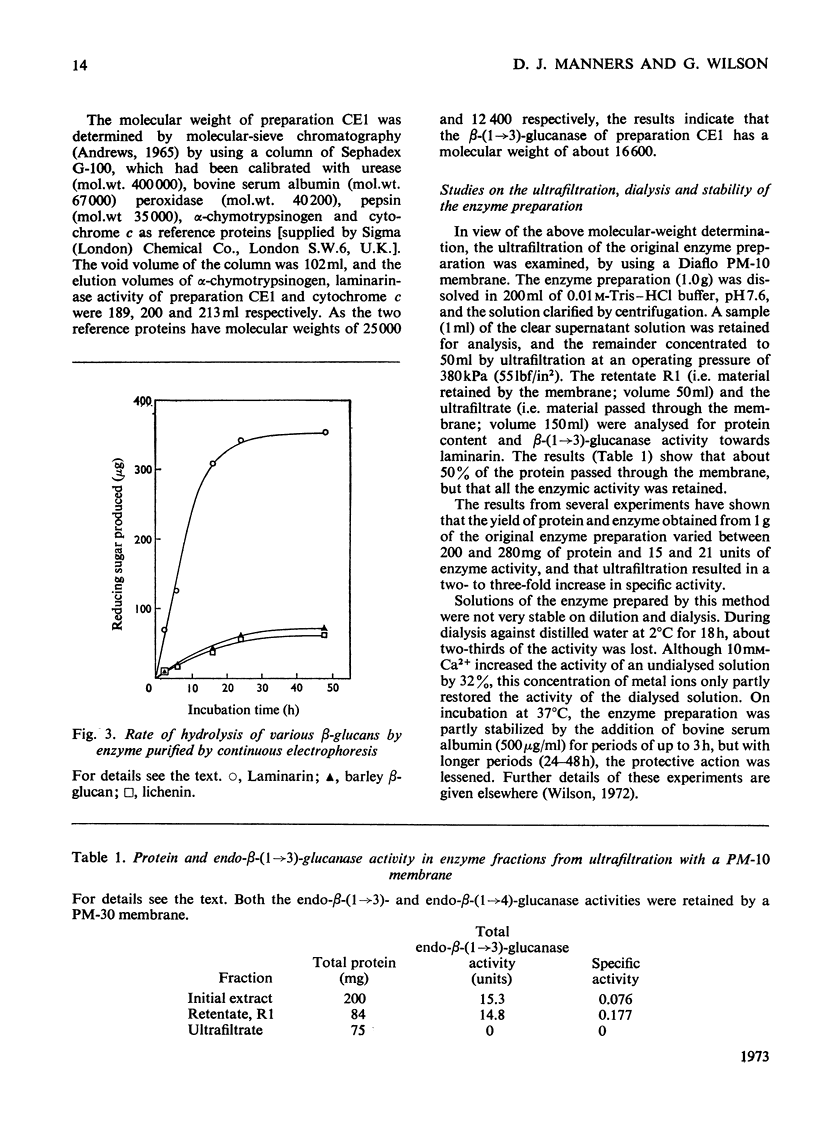
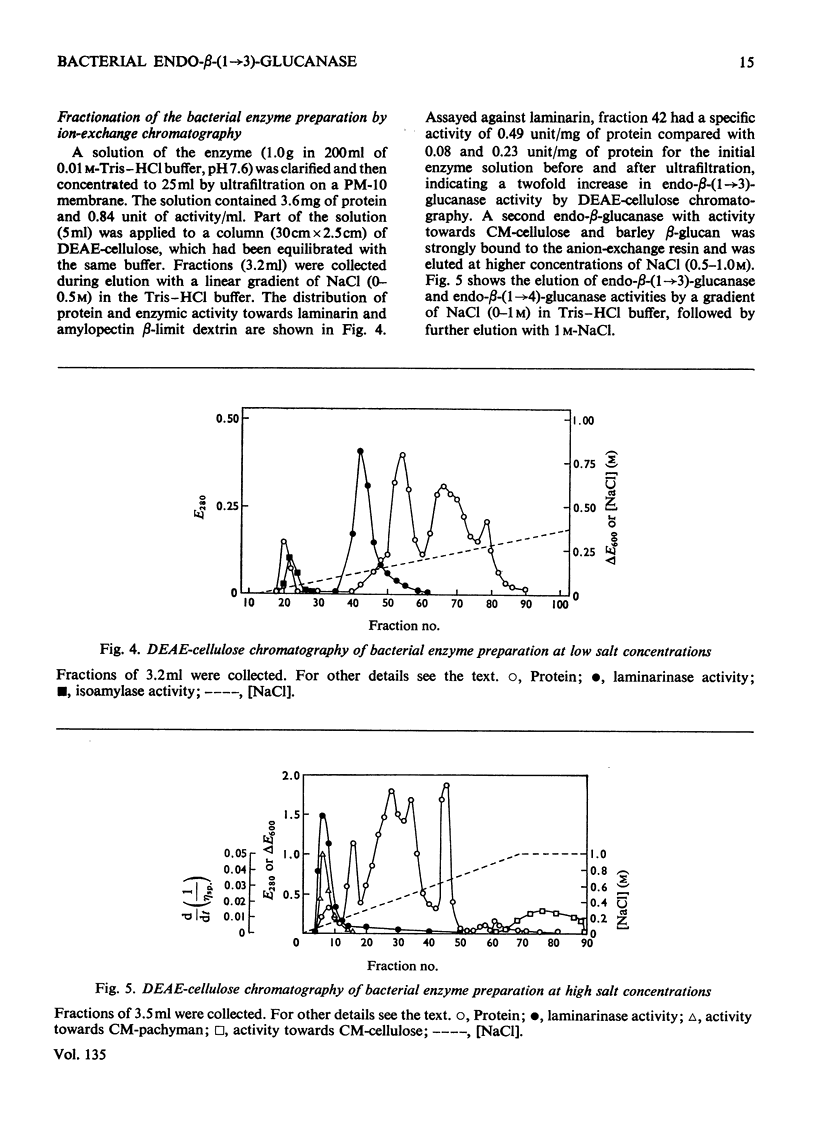
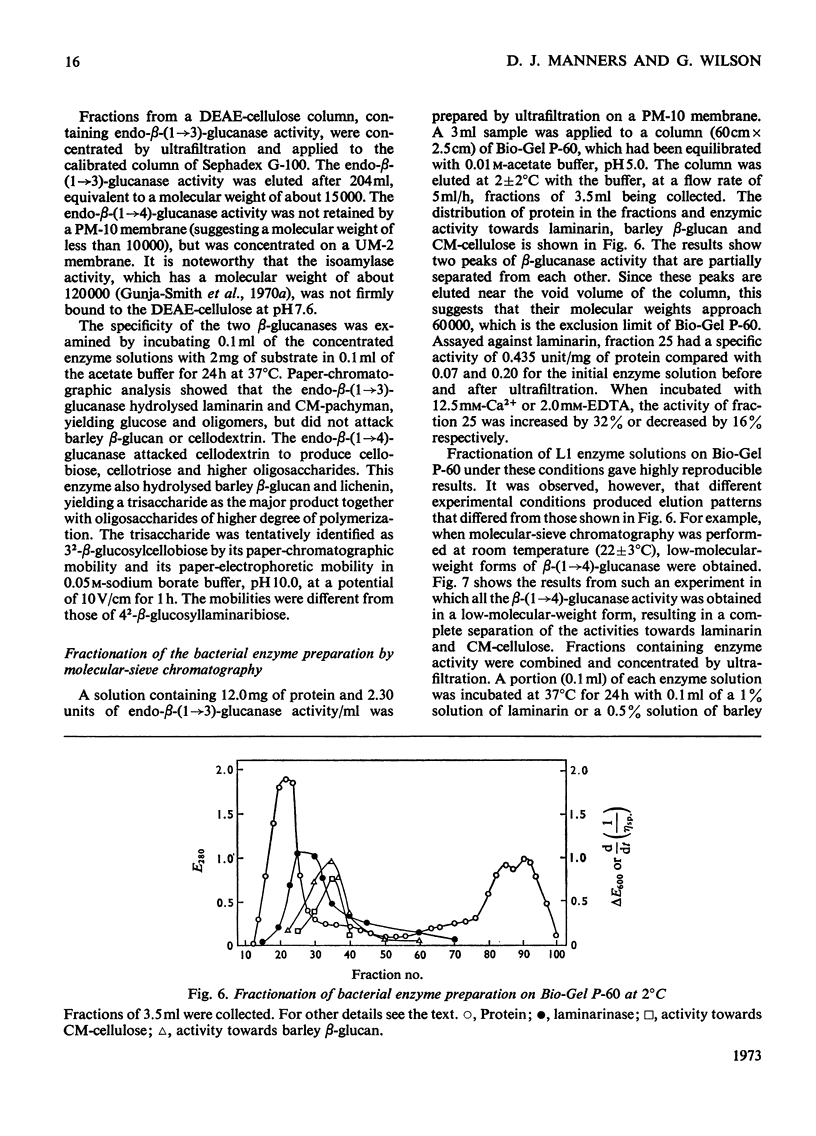
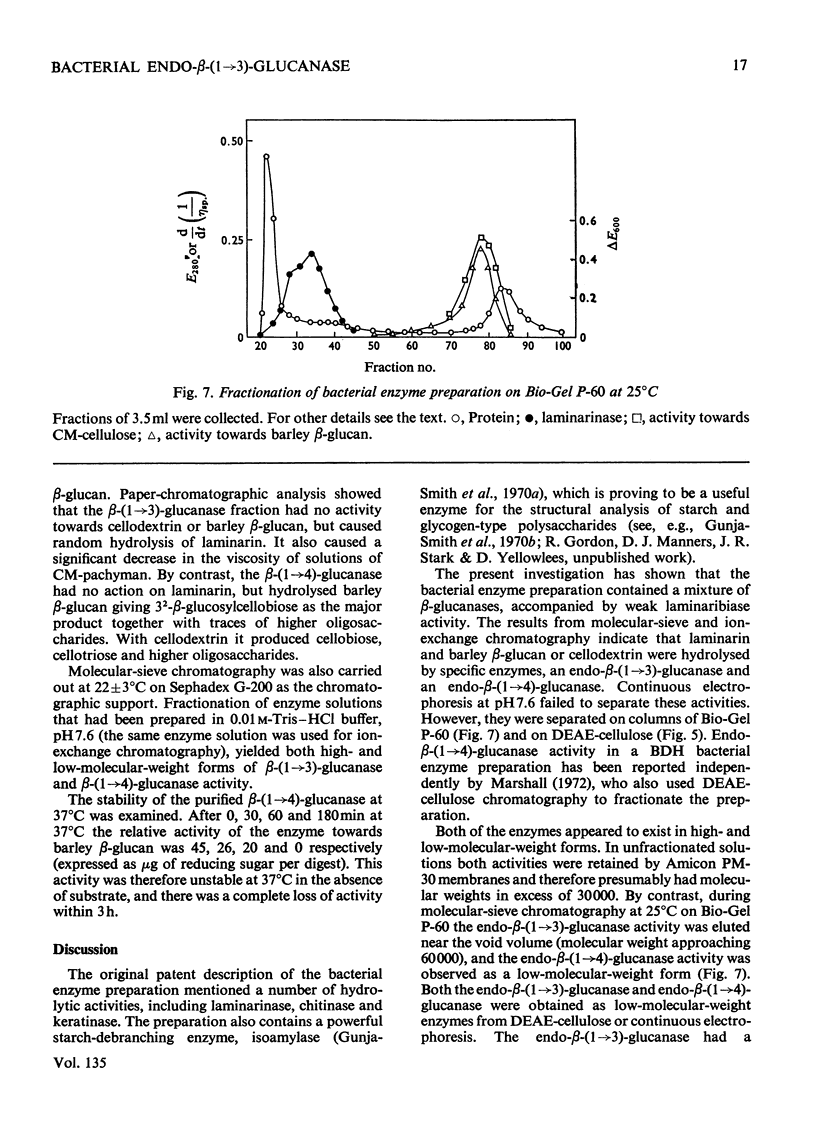
A commercial enzyme preparation, originally obtained from a Flavobacterium(Cytophaga), was fractionated by continuous electrophoresis, giving a protein fraction which hydrolysed laminarin, carboxymethylpachyman, barley β-glucan, lichenin and cellodextrin in random fashion. This enzymic activity was not very stable. Ion-exchange chromatography and molecular-sieve chromatography on Bio-Gel P-60 showed that this activity was due to two specific β-glucanases, an endo-β-(1→3)-glucanase and an endo-β-(1→4)-glucanase. The two enzymes occur in both high- and low-molecular-weight forms, the latter endo-β-(1→3)-glucanase having a molecular weight of about 16000.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisele B., Rasched I. R., Wallenfels K. Molecular characterization of pullulanase from Aerobacter aerogenes. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Mar 15;26(1):62–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming M., Manners D. J., Masson A. J. The enzymic degradation of laminarin. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):32P–33P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunja-Smith Z., Marshall J. J., Mercier C., Smith E. E., Whelan W. J. A revision of the Meyer-Bernfeld model of glycogen and amylopectin. FEBS Lett. 1970 Dec 28;12(2):101–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80573-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunja-Smith Z., Marshall J. J., Smith E. E., Whelan W. J. A glycogen-debranching enzyme from Cytophaga. FEBS Lett. 1970 Dec 28;12(2):96–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80572-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins R. P., Young L. Biochemical studies of toxic agents. Metabolic ring-fission of cis- and trans-acenaphthene-1,2-diol. Biochem J. 1966 Jan;98(1):19–24. doi: 10.1042/bj0980019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. J. Facile purification of a -glucan hydrolase by chromatography on DEAE-cellulose. J Chromatogr. 1972 Sep 6;71(2):367–369. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)80699-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell T. G., Hendrie M. S., Shewan J. M. The taxonomy, differentiation and identification of Cytophaga species. J Appl Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;32(1):40–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1969.tb02187.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMOGYI M. Notes on sugar determination. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


