Abstract
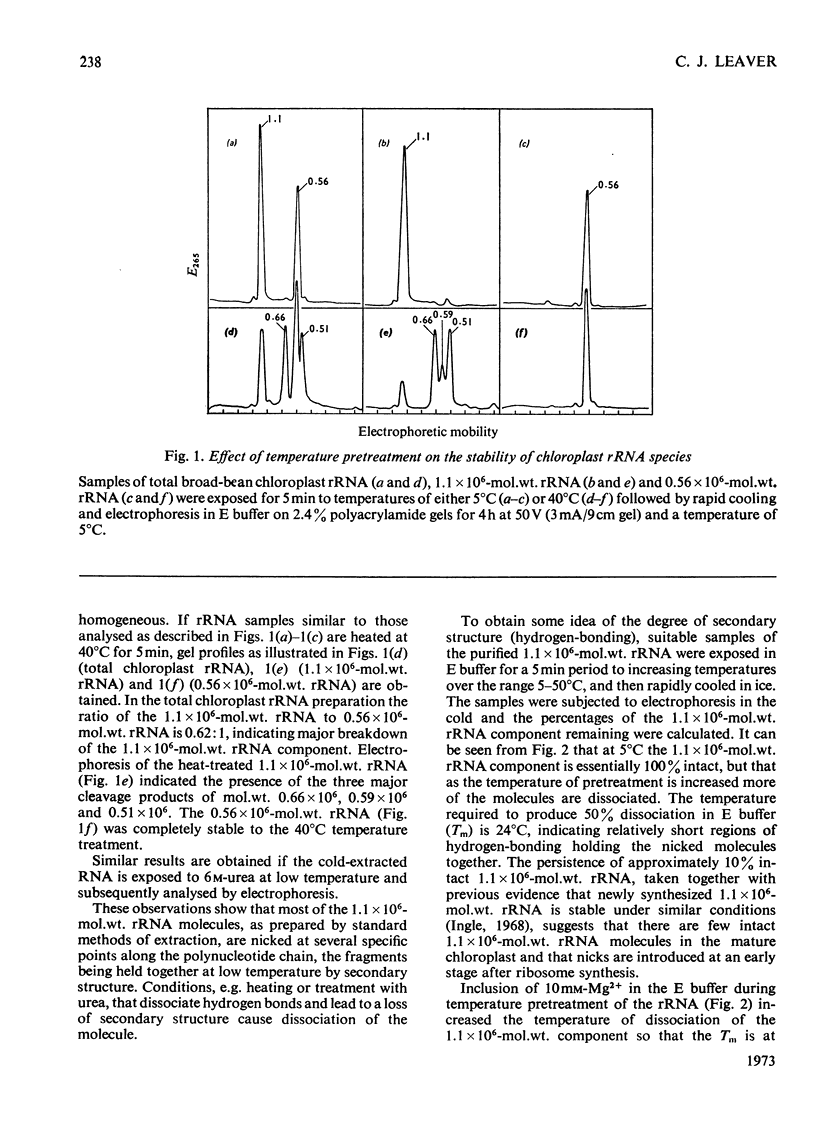
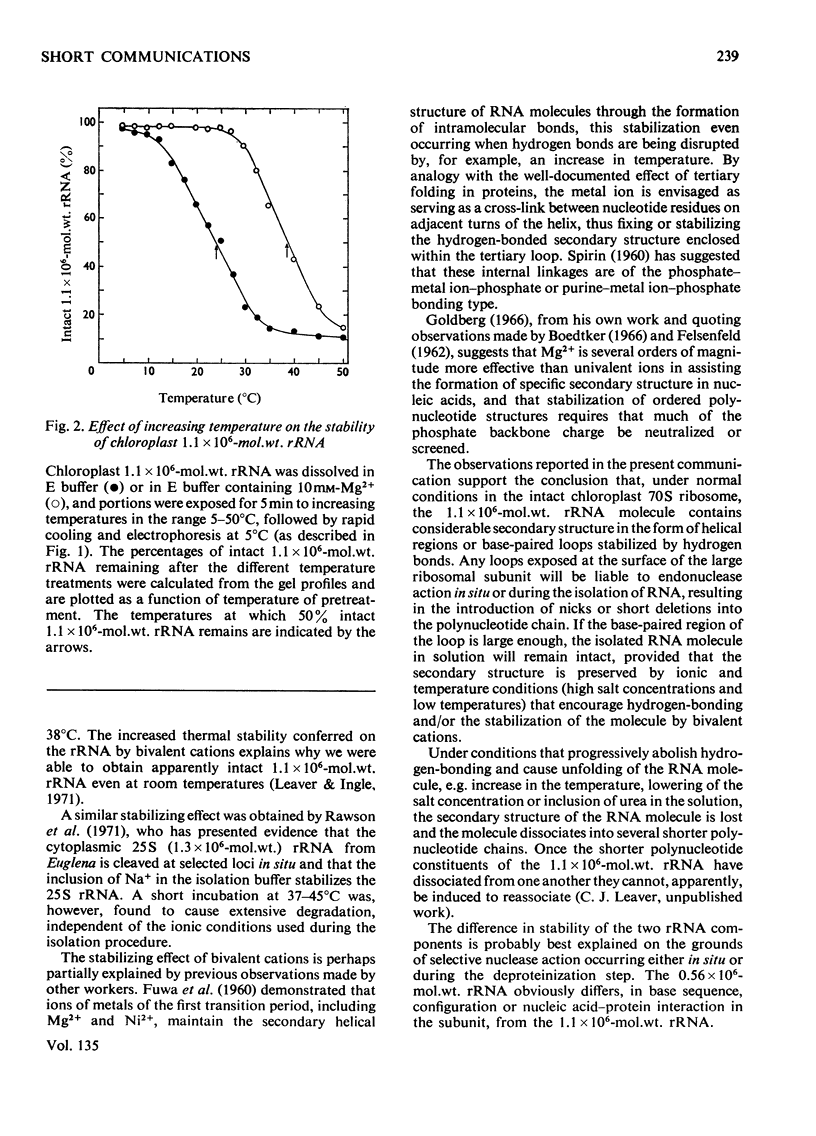
The majority of chloroplast 1.1×106-mol.wt. rRNA molecules are nicked at specific points in the polynucleotide chain, the molecules being kept intact at low temperatures by their secondary structure. Conditions that break hydrogen bonds and lead to loss of secondary structure cause dissociation of the molecule.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fuwa K., Wacker W. E., Druyan R., Bartholomay A. F., Vallee B. L. NUCLEIC ACIDS AND METALS, II: TRANSITION METALS AS DETERMINANTS OF THE CONFORMATION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACIDS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Oct;46(10):1298–1307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.10.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. Magnesium binding by Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Feb;15(2):663–673. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80134-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingle J. Synthesis and Stability of Chloroplast Ribosomal-RNA's. Plant Physiol. 1968 Sep;43(9):1448–1454. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.9.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leaver C. J., Ingle J. The molecular integrity of chloroplast ribosomal ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(2):235–243. doi: 10.1042/bj1230235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawson J. R., Crouse E. J., Stutz E. The integrity of the 25-S ribosomal RNA from Euglena gracilis 87-S ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 24;246(3):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90788-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



