Abstract
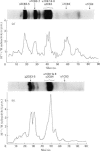
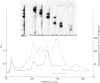
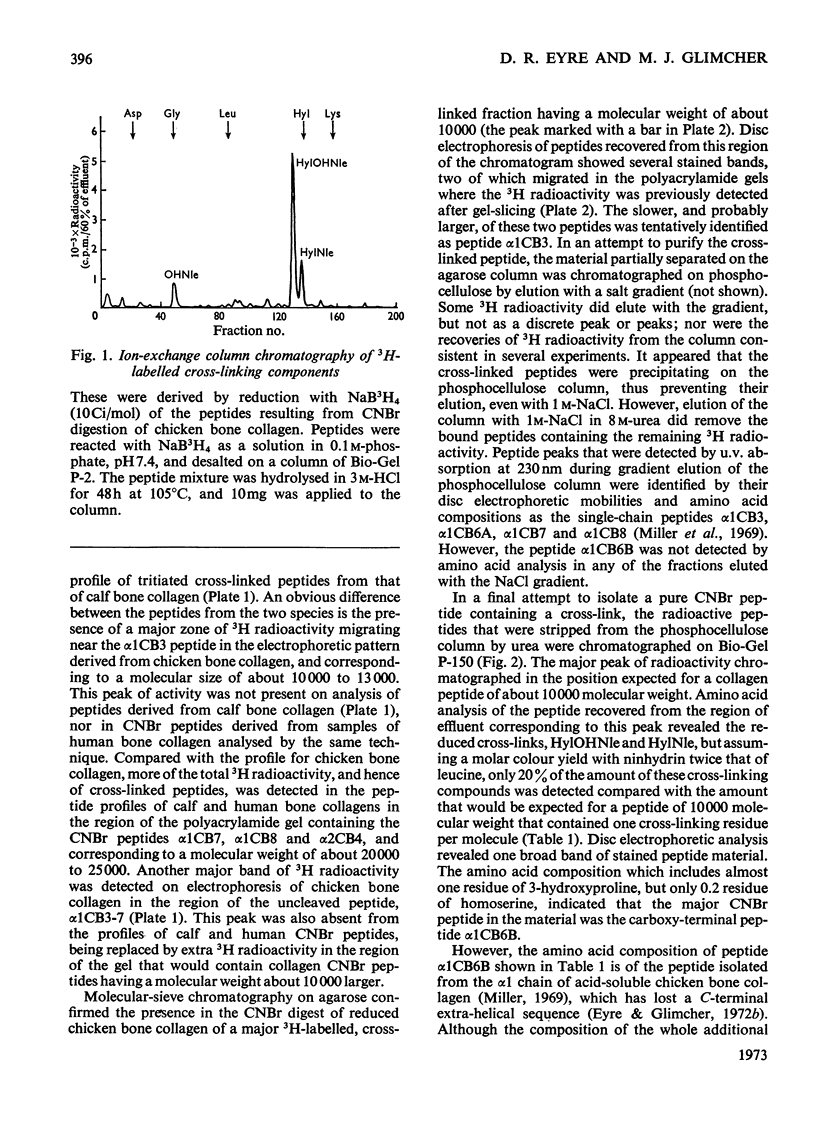
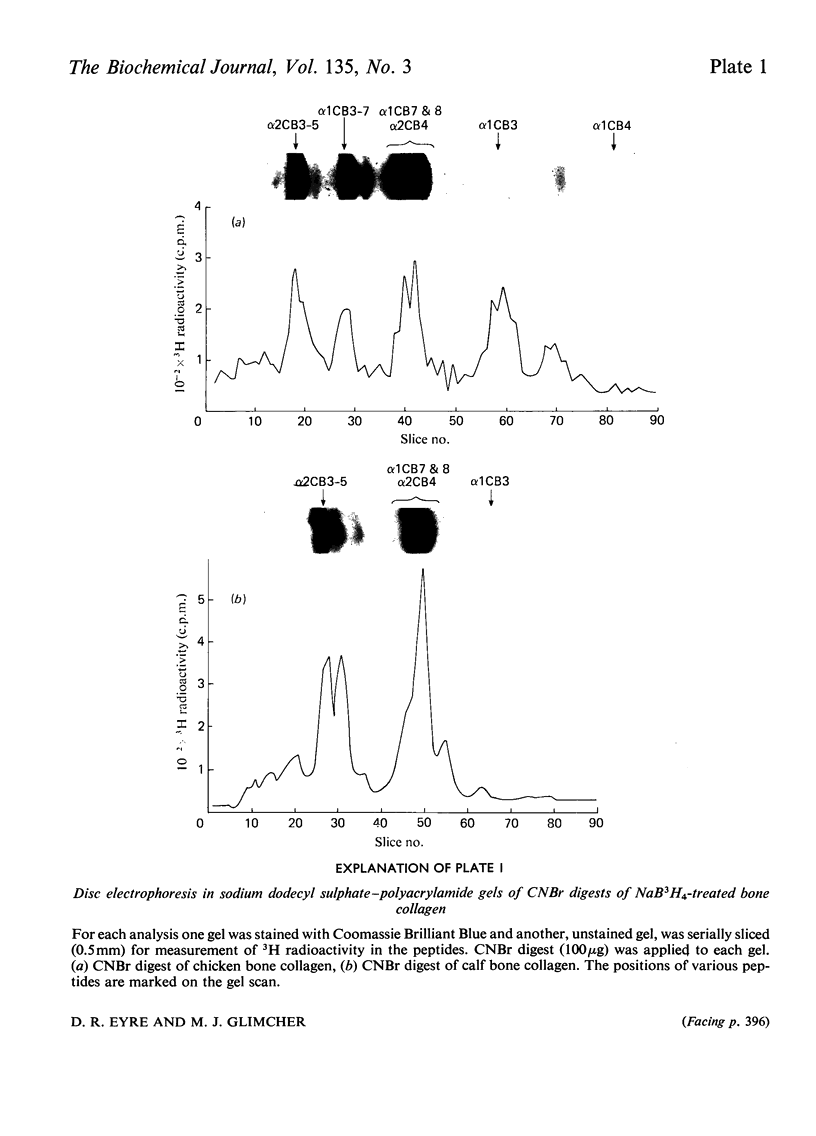
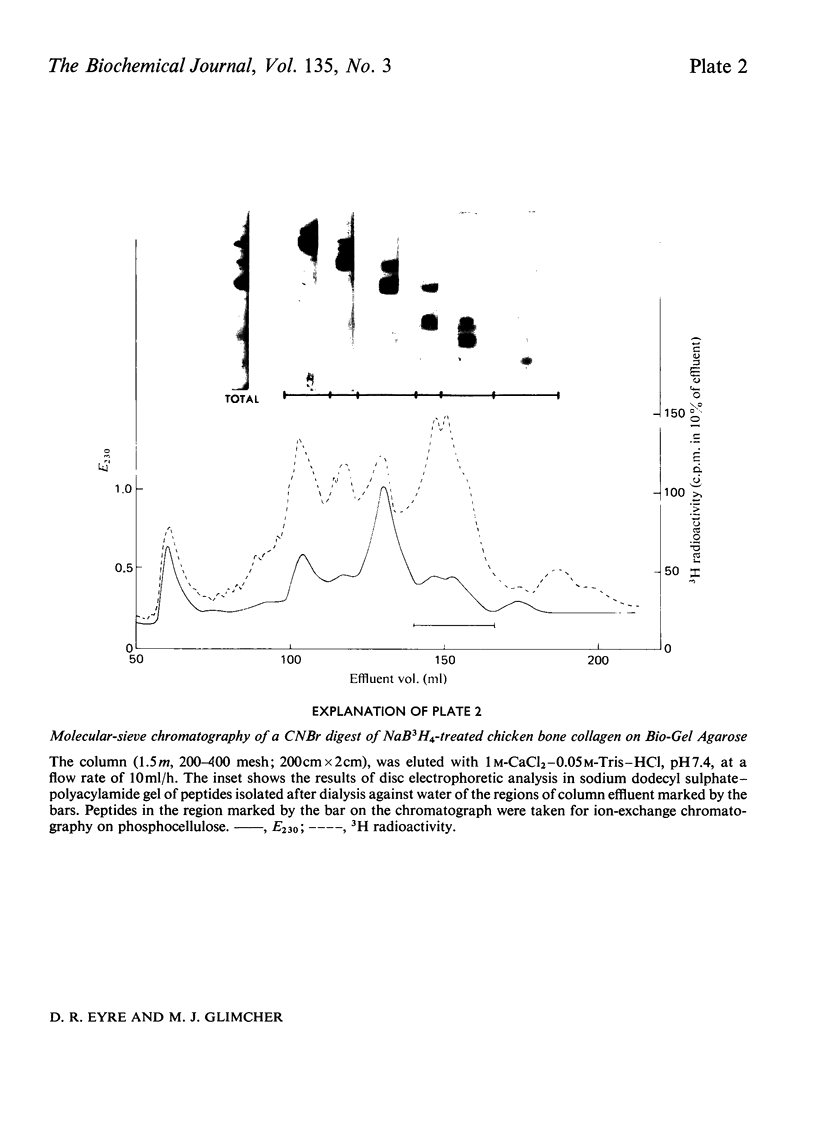
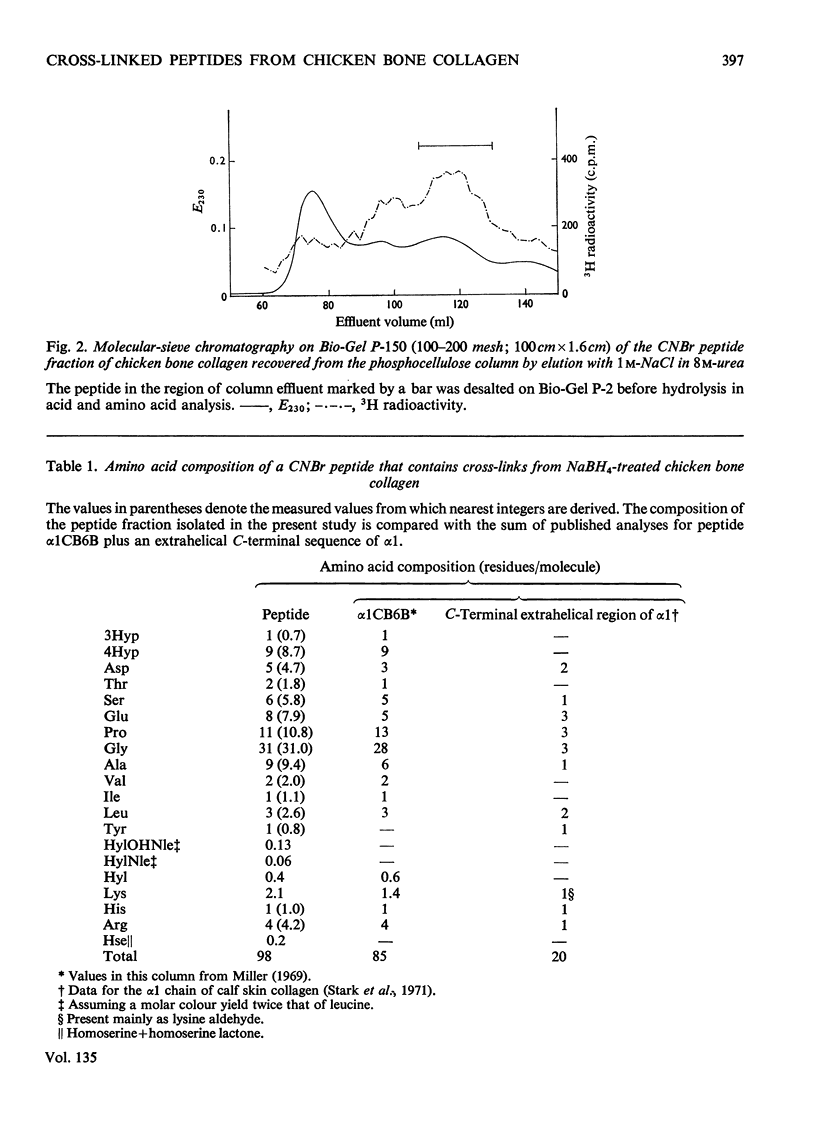
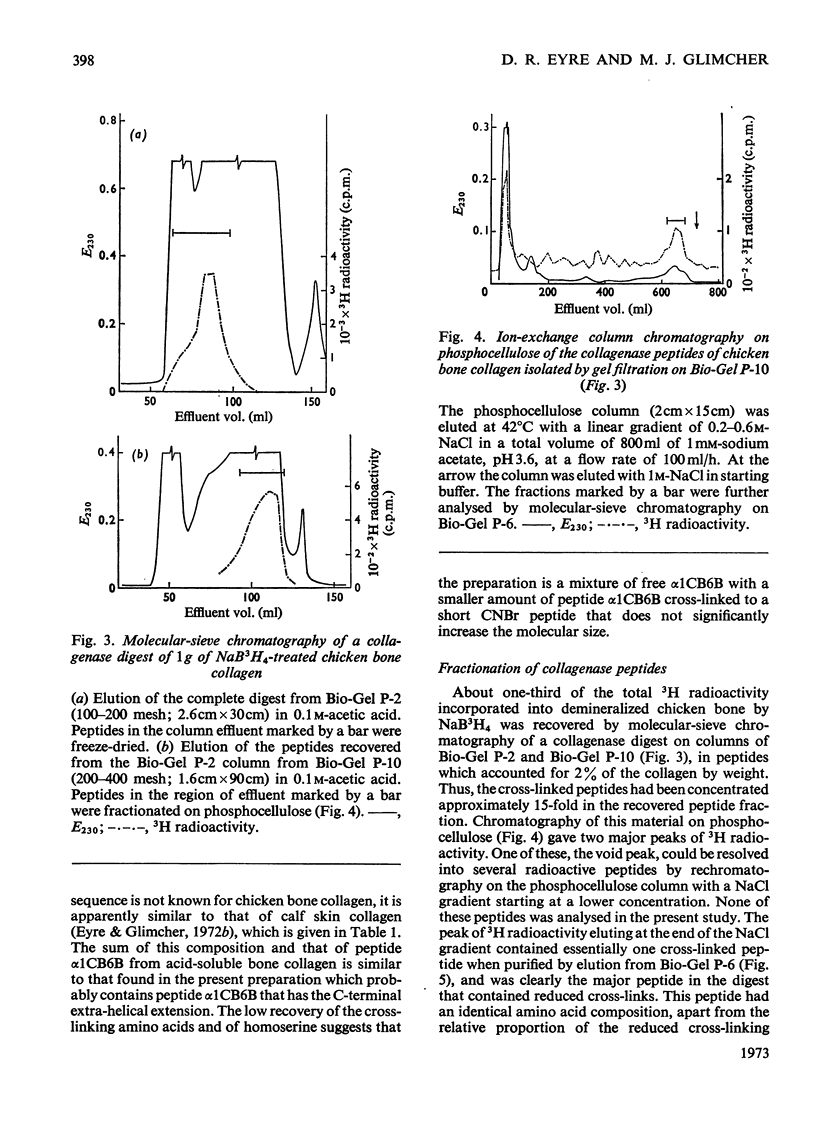
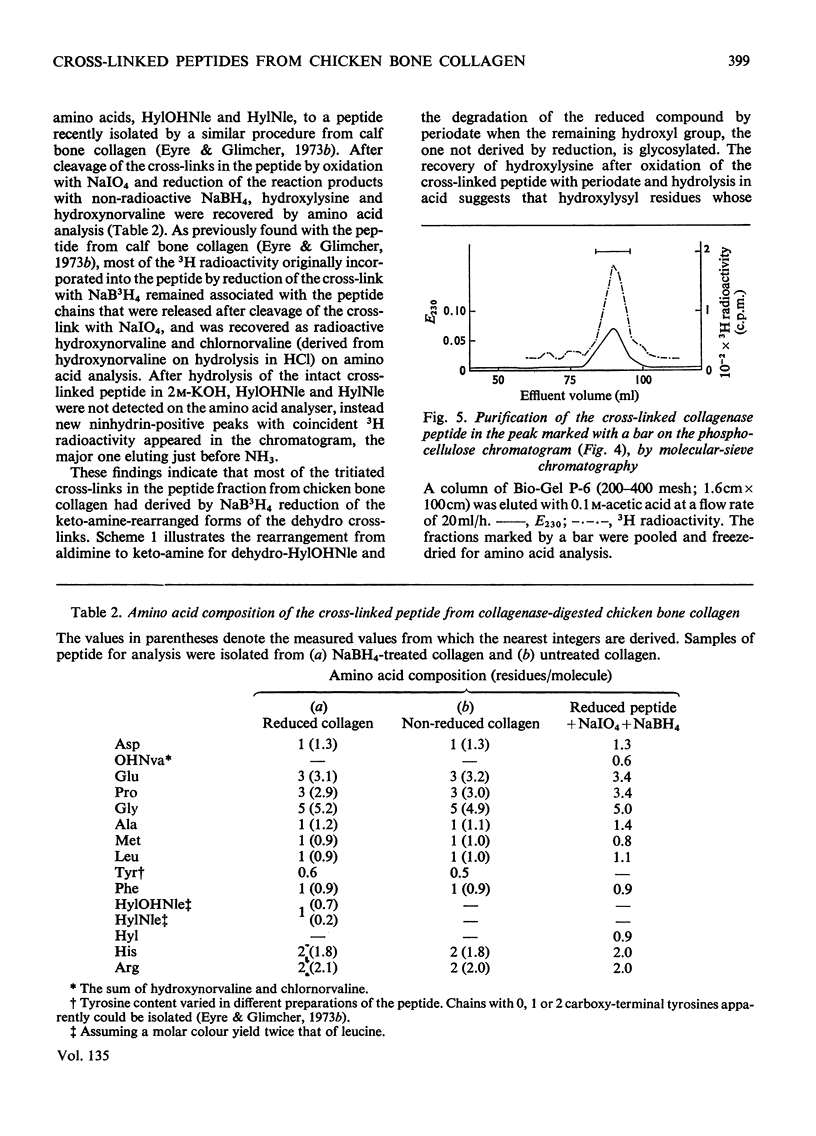
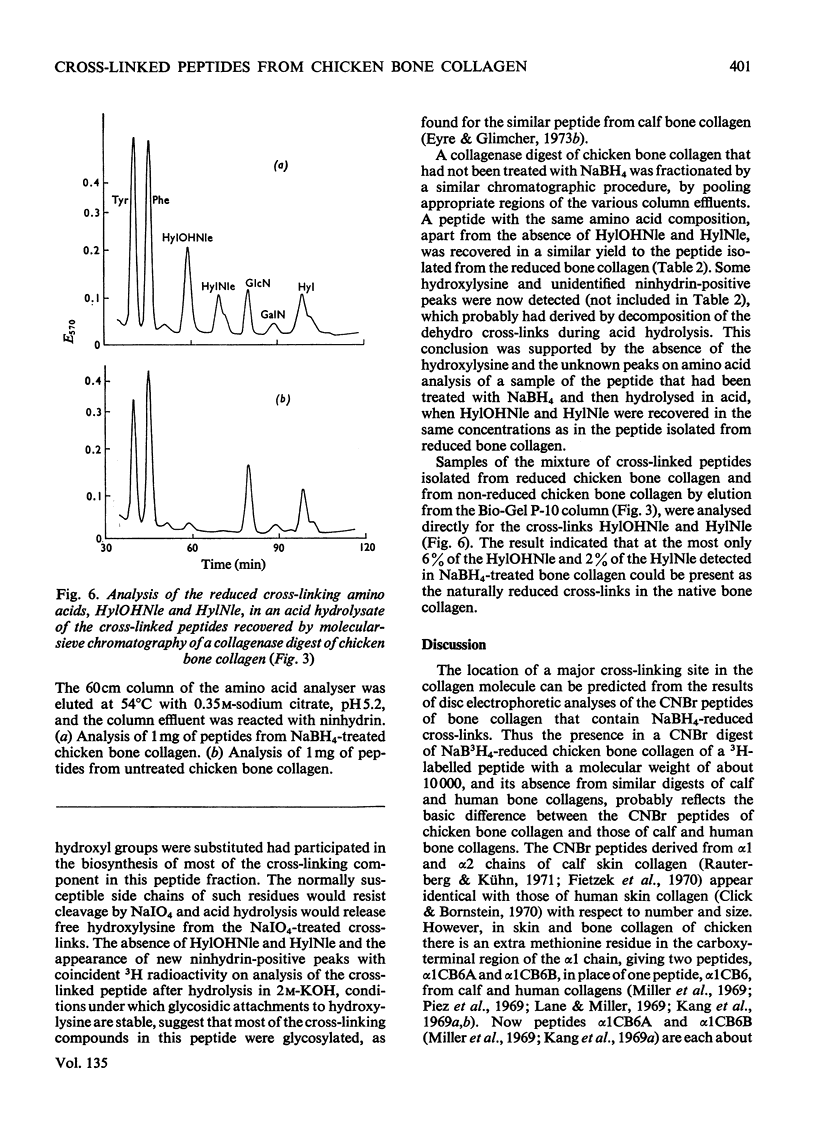
Cross-linked peptides were isolated from chicken bone collagen that had been digested with CNBr or with bacterial collagenase. Analyses of 3H radioactivity in disc electrophoretic profiles of the CNBr peptides from bone collagens that had been treated with NaB3H indicated that a major site of intermolecular cross-linking in chicken bone collagen is located between the carboxy-terminal region of an α1 chain and a small CNBr peptide, probably situated near the amino-terminus of an α1 or α2 chain in an adjacent collagen molecule. A small amount of this cross-linked CNBr peptide was isolated from a CNBr digest of chicken bone collagen by column chromatography. Amino acid analysis showed that the CNBr peptide, α1CB6B, the carboxy-terminal peptide of the α1 chain, was the major CNBr peptide in the preparation, and the reduced cross-linking components were identified as hydroxylysinohydroxynorleucine (HylOHNle), with a smaller amount of hydroxylysinonorleucine (HylNle). However, the composition and the low recovery of the cross-linking amino acids suggested that the preparation was a mixture of CNBr peptides α1CB6B and α1CB6B cross-linked to a small CNBr peptide whose identity could not be determined. A small cross-linked peptide was isolated from chicken bone collagen that had been reduced with NaB3H4 and digested with bacterial collagenase. This peptide was the major cross-linked peptide in the digest and contained a stoicheiometric amount of the reduced cross-linking compounds. A peptide which had the same amino acid composition, but contained the cross-linking compounds in their reducible forms, was isolated from a collagenase digest of chicken bone collagen that had not been treated with NaBH4. The absence of the reduced cross-links from this peptide indicates that, at least for the cross-linking site from which the peptide derives, natural reduction is not a significant pathway for biosynthesis of stable cross-links. However, most of the reducible cross-linking component in the peptide appeared to stabilize in the bone collagen by rearrangement from aldimine to ketoamine form.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey A. J., Peach C. M., Fowler L. J. Chemistry of the collagen cross-links. Isolation and characterization of two intermediate intermolecular cross-links in collagen. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(5):819–831. doi: 10.1042/bj1170819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey A. J., Shimokomaki M. S. Age related changes in the reducible cross-links of collagen. FEBS Lett. 1971 Aug 1;16(2):86–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80338-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey Allen J. Comparative studies on the nature of the cross-links stabilizing the collagen fibres of invertebrates, cyclostomes and elasmobranchs. FEBS Lett. 1971 Oct 15;18(1):154–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80433-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Click E. M., Bornstein P. Isolation and characterization of the cyanogen bromide peptides from the alpha 1 and alpha 2 chains of human skin collagen. Biochemistry. 1970 Nov 24;9(24):4699–4706. doi: 10.1021/bi00826a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. R., Bailey A. J. Chemical synthesis of the reduced form of an intermolecular crosslink of collagen: a re-evaluation of the structure of syndesine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Dec 17;45(6):1416–1422. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Glimcher M. J. Analysis of a crosslinked peptide from calf bone collagen: evidence that hydroxylysyl glycoside participates in the crosslink. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):663–671. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90764-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Glimcher M. J. Comparative biochemistry of collagen crosslinks: reducible bonds in invertebrate collagens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 28;243(3):525–529. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90027-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Glimcher M. J. Evidence for a previously undetected sequence at the carboxyterminus of the 1 chain of chicken bone collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Aug 7;48(3):720–727. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90408-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Glimcher M. J. Evidence for intramolecular crosslinks in chicken bone collagen: the isolation of peptides containing allysine aldol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 25;295(1):301–307. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90097-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Glimcher M. J. Reducible crosslinks in hydroxylysine-deficient collagens of a heritable disorder of connective tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2594–2598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fietzek P. P., Münch M., Breitkreutz D., Kühn K. Isolation and characterization of the cyanogen bromide peptides from the alpha2 chain of calf skin collagen. FEBS Lett. 1970 Aug 17;9(4):229–231. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80362-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H., Timpl R. Characterization of collagen peptides by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jun;41(2):510–516. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallop P. M., Blumenfeld O. O., Seifter S. Structure and metabolism of connective 801 tissue proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:617–672. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang A. H., Igarashi S., Gross J. Characterization of the cyanogen bromide peptides from the alpha-2 chain of chick skin collagen. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3200–3204. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang A. H., Piez K. A., Gross J. Characterization of the cyanogen bromide peptides from the alpha 1 chain of chick skin collagen. Biochemistry. 1969 Apr;8(4):1506–1514. doi: 10.1021/bi00832a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang A. H. Studies on the location of intermolecular cross-links in collagen. Isolation of a CNBr peptide containing -hydroxylysinonorleucine. Biochemistry. 1972 May 9;11(10):1828–1835. doi: 10.1021/bi00760a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane J. M., Miller E. J. Isolation and characterization of the peptides derived from the alpha 2 chain of chick bone collagen after cyanogen bromide cleavage. Biochemistry. 1969 May;8(5):2134–2139. doi: 10.1021/bi00833a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechanic G., Gallop P. M., Tanzer M. L. The nature of crosslinking in collagens from mineralized tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov 5;45(3):644–653. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90465-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Biochemical studies on the structure of chick bone collagen. Fed Proc. 1969 Nov-Dec;28(6):1839–1845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Lane J. M., Piez K. A. Isolation and characterization of the peptides derived from the alpha-1 chain of chick bone collagen after cyanogen bromide cleavage. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):30–39. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piez K. A., Miller E. J., Lane J. M., Butler W. T. The order of the CNBr peptides from the alpha-1 chain of collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Nov 20;37(5):801–805. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90962-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauterberg J., Fietzek P., Rexrodt F., Becker U., Stark M., Kühn K. The amino acid sequence of the carboxyterminal nonhelical cross link region of the alpha 1 chain of calf skin collagen. FEBS Lett. 1972 Mar;21(1):75–79. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80167-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauterberg J., Kühn K. Acid soluble calf skin collagen. Characterization of the peptides obtained by cyanogen bromide cleavage of its alpha-1-chain. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Apr;19(3):398–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01329.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M., Rauterberg J., Kühn K. Evidence for a non-helical region at the carboxyl terminus of the collagen molecule. FEBS Lett. 1971 Feb 19;13(2):101–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80209-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer M. L. Cross-linking of collagen. Science. 1973 May 11;180(4086):561–566. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4086.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer M. L., Housley T., Berube L., Fairweather R., Franzblau C., Gallop P. M. Structure of two histidine-containing crosslinks from collagen. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):393–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W., Piez K. A. The chemistry and structure of collagen. Adv Protein Chem. 1971;25:243–352. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpin D., Veis A. Differences between CNBr peptides of soluble and insoluble bovine collagens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Aug 20;44(4):804–812. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90782-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuust J., Lane J. M., Fietzek P. P., Miller E. J., Piez K. A. The order of the CNBr peptides from the alpha 2 chain of collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Feb 20;38(4):703–708. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90638-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Gratzer W. B. Limitations of the detergent-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis method for molecular weight determination of proteins. J Chromatogr. 1971 Apr 22;57(1):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(71)80013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]