Abstract
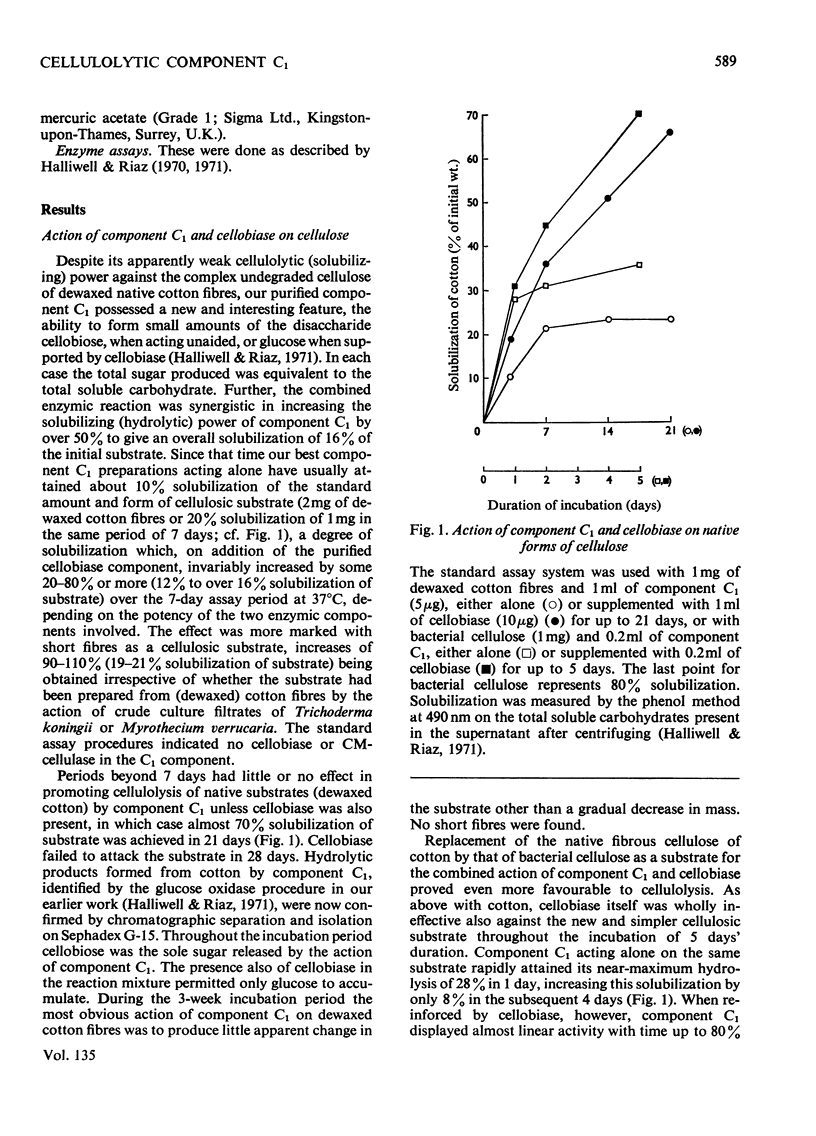
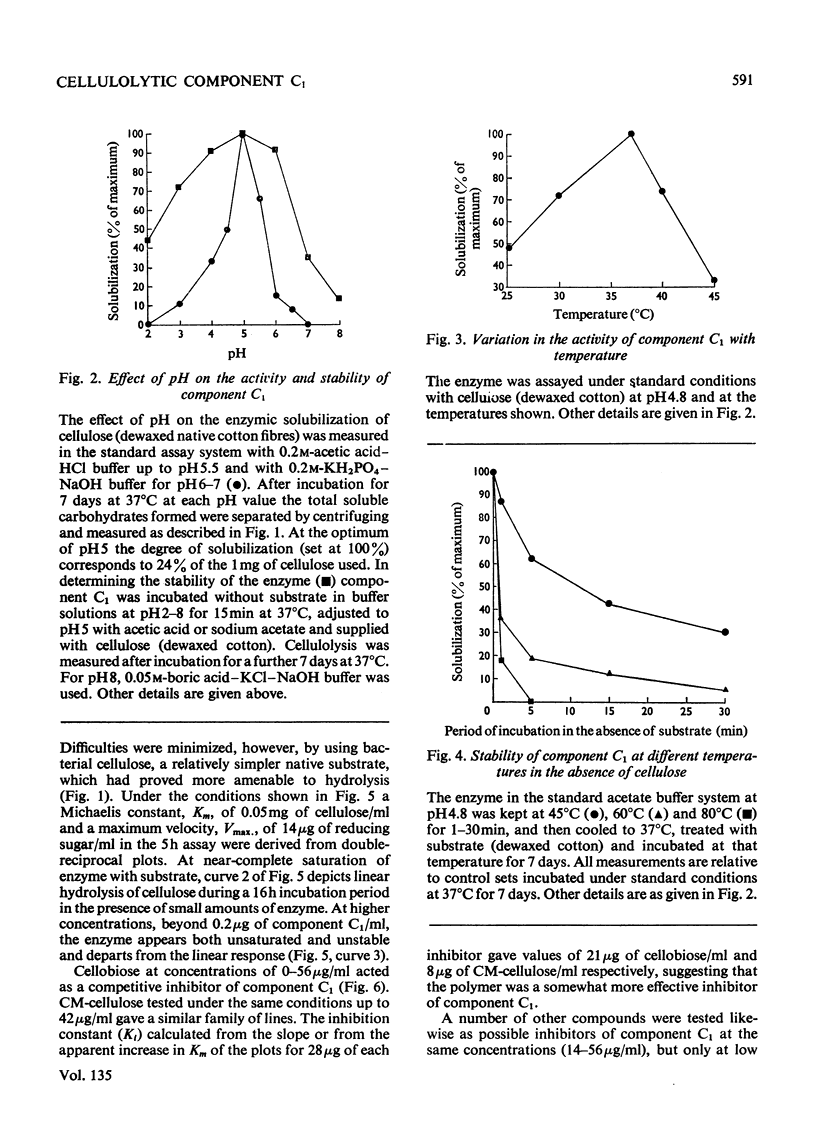
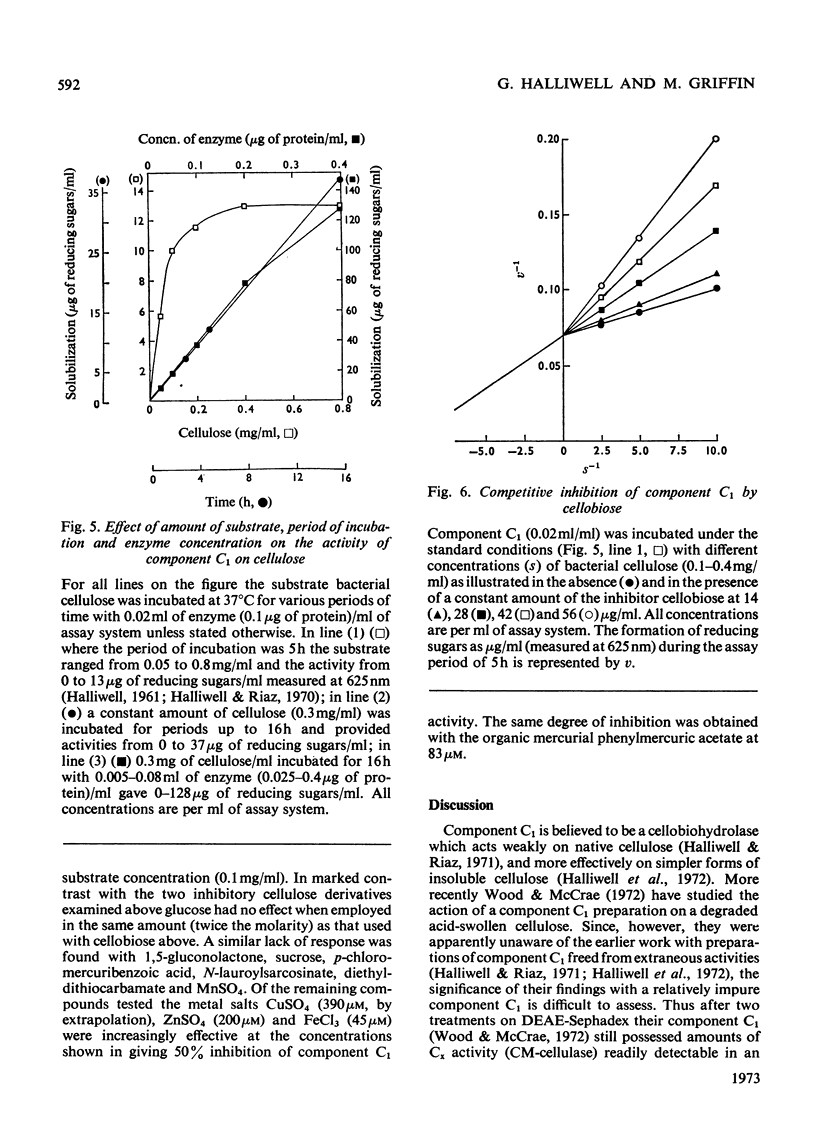
1. A purified cellulolytic component C1 was isolated free from associated activities of the cellulase complex and shown to act as a β-1,4-glucan cellobiohydrolase on both simple and complex forms of native cellulose. 2. The enzyme releases terminal cellobiose units from cellulose, its extent of action being determined principally by the product and by the nature of the substrate. 3. Component Cx of the cellulase system is not required for the action of component C1 (cellobiohydrolase). The enzyme synergizes extensively with cellobiase in extending the hydrolysis of native and of less-complex forms of cellulose to at least 70% with the liberation of glucose. 4. The cellobiohydrolase is relatively unstable, with an optimum at pH5 and a Km of 0.05mg/ml. The enzyme is inhibited by its product, from which it is released by cellobiase. 5. Of other compounds tested against the cellobiohydrolase the metal ions Cu2+, Zn2+, phenylmercuric and Fe3+ are increasingly effective inhibitors. Glucose has no action at concentrations found inhibitory with cellobiose. 6. The relationship of the enzyme to the entire cellulase complex is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HALLIWELL G. HYDROLYSIS OF FIBROUS COTTON AND REPRECIPITATED CELLULOSE BY CELLULOLYTIC ENZYMES FROM SOIL MICRO-ORGANISMS. Biochem J. 1965 Apr;95:270–281. doi: 10.1042/bj0950270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIWELL G. The action of cellulolytic enzymes from Myrothecium verrucaria. Biochem J. 1961 Apr;79:185–192. doi: 10.1042/bj0790185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESTRIN S., SCHRAMM M. Synthesis of cellulose by Acetobacter xylinum. II. Preparation of freeze-dried cells capable of polymerizing glucose to cellulose. Biochem J. 1954 Oct;58(2):345–352. doi: 10.1042/bj0580345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell G., Riaz M. Interactions between components of the cellulase complex of Trichoderma koningii on native substrates. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;78(4):295–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00412270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell G., Riaz M. The formation of short fibres from native cellulose by components of Trichoderma koningii cellulase. Biochem J. 1970 Jan;116(1):35–42. doi: 10.1042/bj1160035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell G. Solubilization of native and derived forms of cellulose by cell-free microbial enzymes. Biochem J. 1966 Aug;100(2):315–320. doi: 10.1042/bj1000315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REESE E. T., SIU R. G. H., LEVINSON H. S. The biological degradation of soluble cellulose derivatives and its relationship to the mechanism of cellulose hydrolysis. J Bacteriol. 1950 Apr;59(4):485–497. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.4.485-497.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby K., Maitland C. C. The cellulase of Trichoderma viride. Separation of the components involved in the solubilization of cotton. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):716–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1040716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITAKER D. R. Purification of Myrothecium verrucaria cellulase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Apr;43(2):253–268. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood T. M. Cellulolytic enzyme system of Trichoderma koningii. Separation of components attacking native cotton. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(2):217–227. doi: 10.1042/bj1090217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood T. M., McCrae S. I. The purification and properties of the C 1 component of Trichoderma koningii cellulase. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1183–1192. doi: 10.1042/bj1281183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


