Abstract
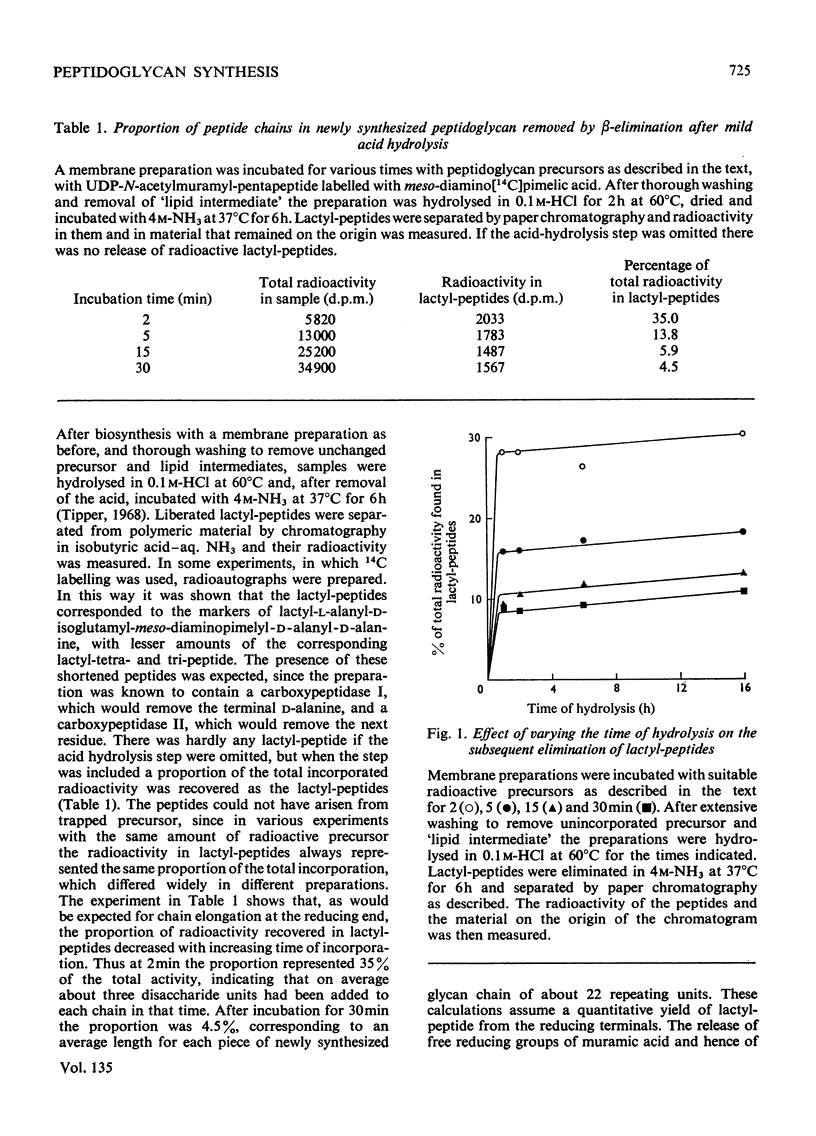
A cell-free membrane preparation from a poorly lytic mutant of Bacillus licheniformis was used to synthesize radioactive peptidoglycan. The product was apparently un-cross-linked. When UDP-N-acetyl[14C]glucosamine was used and the final peptidoglycan subjected to Smith degradation, no radioactive glycerol was found. On the other hand, when peptidoglycan labelled with meso-diamino[14C]pimelic acid was first hydrolysed in 0.1m-HCl at 60°C for 2h and then subjected to alkaline conditions, radioactive lactyl-peptides were eliminated. The proportion of radioactive lactyl-peptide decreased with increasing time of incorporation. It is concluded that the glycan chains grow by extension at their reducing ends while remaining attached by some linkage labile to mild acid, such as a glycosyl link to undecaprenol pyrophosphate.
Full text
PDF



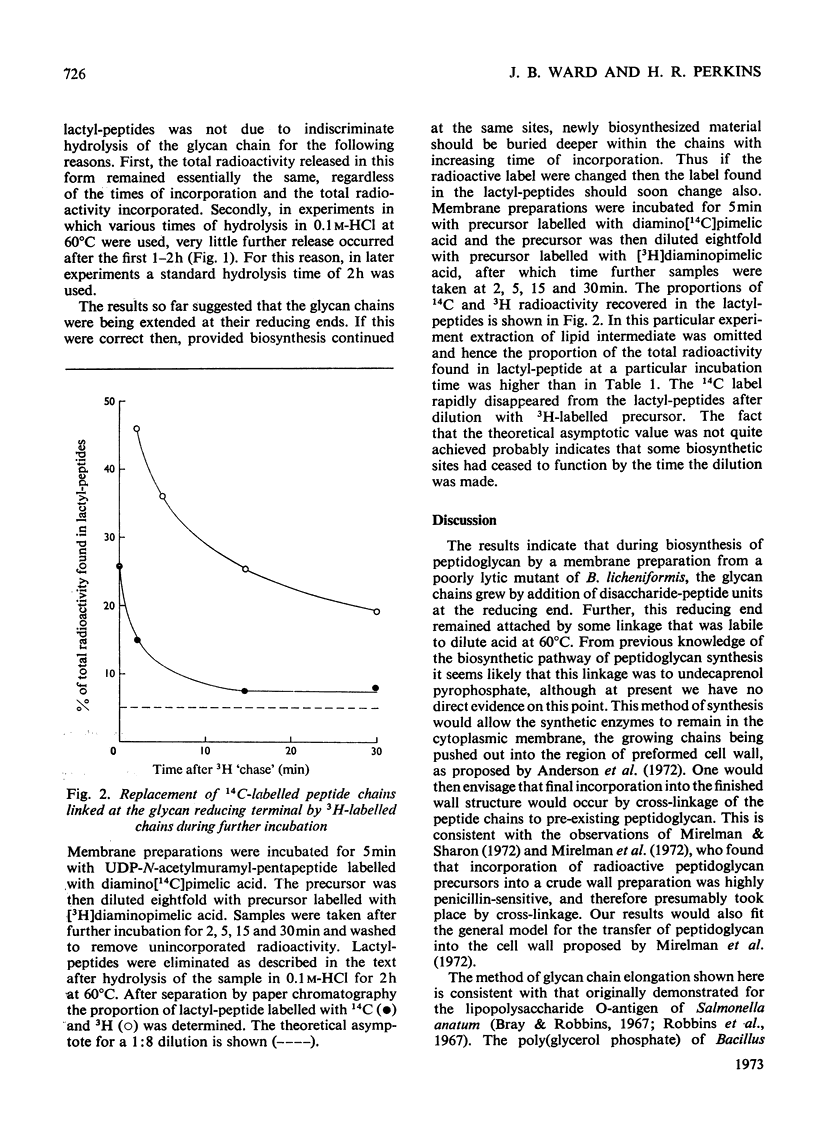


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON J. S., MATSUHASHI M., HASKIN M. A., STROMINGER J. L. LIPID-PHOSPHOACETYLMURAMYL-PENTAPEPTIDE AND LIPID-PHOSPHODISACCHARIDE-PENTAPEPTIDE: PRESUMED MEMBRANE TRANSPORT INTERMEDIATES IN CELL WALL SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Apr;53:881–889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.4.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. S., Matsuhashi M., Haskin M. A., Strominger J. L. Biosythesis of the peptidoglycan of bacterial cell walls. II. Phospholipid carriers in the reaction sequence. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 10;242(13):3180–3190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. G., Hussey H., Baddiley J. The mechanism of wall synthesis in bacteria. The organization of enzymes and isoprenoid phosphates in the membrane. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):11–25. doi: 10.1042/bj1270011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D., Robbins P. W. The direction of chain growth in Salmonella anatum O-antigen biosynthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Aug 7;28(3):334–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90314-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee A. N., Ward J. B., Perkins H. R. Synthesis of mucopeptide by L-form membranes. Nature. 1967 Jun 24;214(5095):1311–1314. doi: 10.1038/2141311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Wyrick P. B., Ward J. B., Rogers H. J. Effect of phosphate limitation on the morphology and wall composition of Bacillus licheniformis and its phosphoglucomutase-deficient mutants. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):969–984. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.969-984.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C., Rogers H. J. Autolytic enzymes in growth of bacteria. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):272–273. doi: 10.1038/229272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett A. J. The effect of magnesium ion deprivation on the synthesis of mucopeptide and its precursors in Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(3):419–430. doi: 10.1042/bj1150419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M., Bricas E., Leyh-Bouille M., Lache M., Shockman G. D. The peptide N alpha-(L-alanyl-D-isoglutaminyl)-N epsilon-(D-isoasparaginyl)-L-lysyl-D-alanine and the disaccharide N-acetylglucosaminyl-beta-1,4-N-acetylmuramic acid in cell wall peptidoglycan of Streptococcus faecalis strain ATCC 9790. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2607–2619. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. Biosynthesis of the wall teichoic acid in Bacillus licheniformis. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):27–37. doi: 10.1042/bj1270027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Strominger J. L., Sweeley C. C. Structure of a lipid intermediate in cell wall peptidoglycan synthesis: a derivative of a C55 isoprenoid alcohol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1878–1884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussey H., Brooks D., Baddiley J. Direction of chain extension during the biosynthesis of teichoic acids in bacterial cell walls. Nature. 1969 Feb 15;221(5181):665–666. doi: 10.1038/221665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANCZURA E., PERKINS H. R., ROGERS H. J. Teichuronic acid: a mucopolysaccharide present in wall preparations from vegetative cells of Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1961 Jul;80:82–93. doi: 10.1042/bj0800082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leyh-Bouille M., Nakel M., Frère J. M., Johnson K., Ghuysen J. M., Nieto M., Perkins H. R. Penicillin-sensitive DD-carboxypeptidases from Streptomyces strains R39 and K11. Biochemistry. 1972 Mar 28;11(7):1290–1298. doi: 10.1021/bi00757a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Bracha R., Sharon N. Role of the penicillin-sensitive transpeptidation reaction in attachment of newly synthesized peptidoglycan to cell walls of Micrococcus luteus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3355–3359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Sharon N. Biosynthesis of peptidoglycan by a cell wall preparation of Staphylococcus aureus and its inhibition by penicillin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 10;46(5):1909–1917. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P. E. Peptidoglycan synthesis in bacilli. II. Characteristics of protoplast membrane preparations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 18;237(2):255–272. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90316-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins P. W., Bray D., Dankert B. M., Wright A. Direction of chain growth in polysaccharide synthesis. Science. 1967 Dec 22;158(3808):1536–1542. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3808.1536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., THRENN R. H. Accumulation of a uridine nucleotide in Staphylococcus aureus as the consequence of lysine deprivation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Nov;36:83–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRUVE W. G., NEUHAUS F. C. EVIDENCE FOR AN INITIAL ACCEPTOR OF UDP-NAC-MURAMYL-PENTAPEPTIDE IN THE SYNTHESIS OF BACTERIAL MUCOPEPTIDE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 4;18:6–12. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90873-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siewert G., Strominger J. L. Bacitracin: an inhibitor of the dephosphorylation of lipid pyrophosphate, an intermediate in the biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan of bacterial cell walls. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):767–773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strominger J. L., Izaki K., Matsuhashi M., Tipper D. J. Peptidoglycan transpeptidase and D-alanine carboxypeptidase: penicillin-sensitive enzymatic reactions. Fed Proc. 1967 Jan-Feb;26(1):9–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struve W. G., Sinha R. K., Neuhaus F. C. On the initial stage in peptidoglycan synthesis. Phospho-N-acetylmuramyl-pentapeptide translocase (uridine monophosphate). Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):82–93. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. B., Perkins H. R. The purification and properties of two staphylolytic enzymes from Streptomyces griseus. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(1):69–76. doi: 10.1042/bj1060069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. B. The chain length of the glycans in bacterial cell walls. Biochem J. 1973 Jun;133(2):395–398. doi: 10.1042/bj1330395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A., Dankert M., Fennessey P., Robbins P. W. Characterization of a polyisoprenoid compound functional in O-antigen biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1798–1803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A., Dankert M., Robbins P. W. Evidence for an intermediate stage in the biosynthesis of the Salmonella O-antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):235–241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


