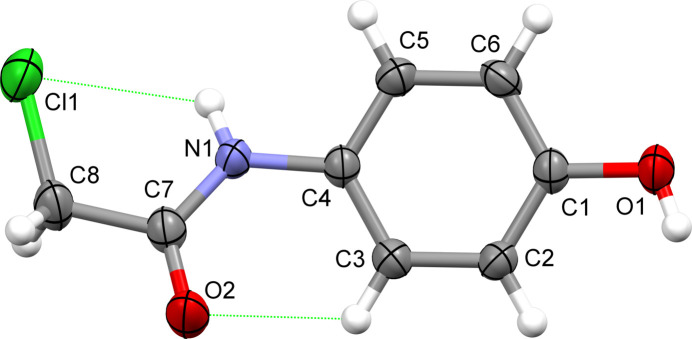
The title compound is significantly distorted from planarity, with a twist angle between the planes through the hydroxybenzene and acetamide groups being 23.5 (2)°. This conformation is supported by intramolecular C—H⋯O and N—H⋯Cl contacts. In the crystal, N—H⋯O hydrogen-bonding contacts between acetamide groups and O—H⋯O contacts between hydroxyl groups form tapes propagating parallel to [103].
Keywords: crystal structure, acetamide, hydrogen-bonding
Abstract
The title compound, C8H8ClNO2, is significantly distorted from planarity, with a twist angle between the planes through the hydroxybenzene and acetamide groups being 23.5 (2)°. This conformation is supported by intramolecular C—H⋯O and N—H⋯Cl contacts. In the crystal, N—H⋯O hydrogen-bonding contacts between acetamide groups and O—H⋯O contacts between hydroxyl groups form tapes propagating parallel to [103].
Structure description
N-arylacetamides are intermediates for the synthesis of medicinal, agrochemical and pharmaceutical compounds (Missioui et al., 2021 ▸). As part of our ongoing studies of these systems (Missioui et al., 2022 ▸), we now describe the synthesis and structure of the title compound, C8H8ClNO2.
The molecule, Fig. 1 ▸, is almost planar as indicated by a twist angle between the planes through the hydroxybenzene (C1–C6, O1) and acetamide (C7, C8, N1, O2) groups being 23.5 (2)°; the acetamide group has an anti conformation. The chloro substituent deviates only slightly from the plane of the acetamide group as indicated by the N1—C7—C8—Cl1 torsion angle of 15.4 (4)°.
Figure 1.
The molecule of 2-chloro-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide showing the atom-numbering scheme and displacement parameters at the 50% probability level. The intramolecular C—H⋯O and N—H⋯Cl contacts are shown as green dotted lines.
Two types of close intramolecular contacts occur within the molecule. The first contact is of the type C—H⋯O with a C3—H3⋯O2 angle of 116° and a C3⋯O2 distance of 2.873 (4) Å, Table 1 ▸. Similar contacts are observed in related structures including 2-chloro-N-(4-fluorophenyl)acetamide (Kang et al., 2008 ▸), 2-chloro-N-phenylacetamide (Gowda et al., 2008 ▸) and 2-chloro-N-(4-chlorophenyl)acetamide (Gowda et al., 2007 ▸). The second contact is of the type N—H⋯Cl and has a N1—H1⋯Cl1 angle of 115° and a N1⋯Cl1 distance of 2.999 (2) Å.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3—H3⋯O2 | 0.93 | 2.34 | 2.873 (4) | 116 |
| N1—H1⋯Cl1 | 0.86 | 2.53 | 2.999 (2) | 115 |
| N1—H1⋯O2i | 0.86 | 2.28 | 3.025 (3) | 145 |
| O1—H1A⋯O1ii | 0.82 | 2.06 | 2.8585 (17) | 166 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
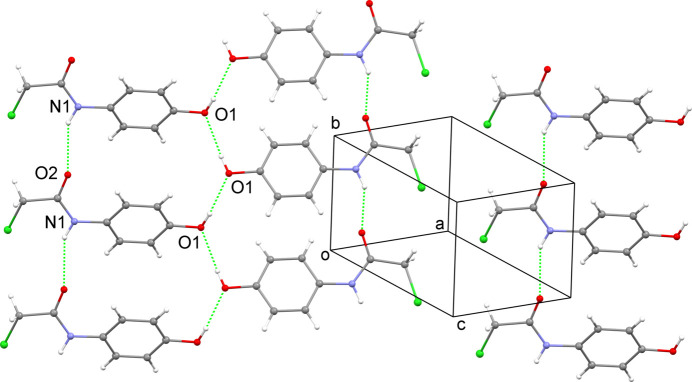
In the crystal, neighbouring molecules are linked by N—H⋯O hydrogen-bonding between translationally related acetamide groups with a N1—H1⋯O2i [symmetry code: (i) x, y − 1, z] angle of 145° and a N1⋯O2i distance of 3.025 (3) Å, Table 1 ▸, to form linear chains parallel to the b axis (Fig. 2 ▸). The molecules are also bridged by O—H⋯O contacts with a O1—H1A⋯O1ii [symmetry code: (ii) −x + 2, y +  , −z + 2] angle of 166° and an O1⋯O1ii distance of 2.8585 (17) Å which, by themselves assemble molecules along the 21 screw axis in the b-axis direction. The combined hydrogen-bonding interactions result in almost flat tapes of molecules parallel to [
, −z + 2] angle of 166° and an O1⋯O1ii distance of 2.8585 (17) Å which, by themselves assemble molecules along the 21 screw axis in the b-axis direction. The combined hydrogen-bonding interactions result in almost flat tapes of molecules parallel to [ 03].
03].
Figure 2.
A segment of the packing in the crystal of 2-chloro-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide showing the intermolecular N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds as green dotted lines.
Synthesis and crystallization
4-Aminophenol (1 mmol) was dissolved in pure acetic acid (30 ml) and placed in an ice-bath. Subsequently, chloroacetyl chloride (1.2 mmol) was added portion-wise under stirring. At the end of the reaction, a solution of sodium acetate (25 ml) was added, and a solid precipitate formed after 30 min of stirring at room temperature. The resulting solid was filtered, washed with cold water, dried and recrystallized from its ethanol solution to yield the title compound as colourless crystals.
Yield = 89%, colour:colourless, m.p. = 413–415 K. FT–IR (ATR, ν, cm−1): 3385 (OH), 3200 (NH), 1640 (C=O). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ p.p.m. 4.21 (s, 2H, CH2), 6.76–7.34 (m, 4H, Ar—H), 9.20 (s, 1H, OH), 10.23 (s, 1H, NH). 13C NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6): 43.42 (CH2); 117.68, 122.20, 131.50, 132.63, 153.68 (C—Ar); 164.76 (C=O). HRMS (ESI): calculated for C8H8ClNO2 [M - H]+ 186.0224, found 186.0328.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C8H8ClNO2 |
| M r | 185.60 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21 |
| Temperature (K) | 296 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 6.5088 (6), 5.1758 (5), 12.2175 (14) |
| β (°) | 101.649 (10) |
| V (Å3) | 403.11 (7) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.43 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.45 × 0.20 × 0.07 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | SuperNova, Dual, Cu at home/near, Atlas |
| Absorption correction | Gaussian (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2023 ▸) |
| Tmin, Tmax | 0.642, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 3642, 1902, 1487 |
| R int | 0.028 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.697 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)], wR(F2), S | 0.039, 0.081, 1.06 |
| No. of reflections | 1902 |
| No. of parameters | 110 |
| No. of restraints | 1 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.16, −0.19 |
| Absolute structure | Flack x determined using 510 quotients [(I+)−(I−)]/[(I+)+(I−)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) |
| Absolute structure parameter | 0.11 (5) |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314624010150/tk4111sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314624010150/tk4111Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314624010150/tk4111Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2392239
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
YR is thankful to the National Center for Scientific and Technical Research of Morocco (CNRST) for its continuous support. The contributions of the authors are as follows: conceptualization, YR; methodology, AA; investigation, AEMAA and IAEH; writing (original draft), AEMAA; writing (review and editing of the manuscript), YR; formal analysis, YR and BMK; supervision, YR; crystal structure determination, BMK.
full crystallographic data
2-Chloro-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide . Crystal data
| C8H8ClNO2 | F(000) = 192 |
| Mr = 185.60 | Dx = 1.529 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 6.5088 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 1576 reflections |
| b = 5.1758 (5) Å | θ = 3.9–28.2° |
| c = 12.2175 (14) Å | µ = 0.43 mm−1 |
| β = 101.649 (10)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 403.11 (7) Å3 | Plate, colourless |
| Z = 2 | 0.45 × 0.20 × 0.07 mm |
2-Chloro-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide . Data collection
| SuperNova, Dual, Cu at home/near, Atlas diffractometer | 1487 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| ω scans | Rint = 0.028 |
| Absorption correction: gaussian (CrysAlis Pro; Rigaku OD, 2023) | θmax = 29.7°, θmin = 3.3° |
| Tmin = 0.642, Tmax = 1.000 | h = −8→8 |
| 3642 measured reflections | k = −7→7 |
| 1902 independent reflections | l = −16→13 |
2-Chloro-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.039 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0294P)2 + 0.0021P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.081 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.06 | Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3 |
| 1902 reflections | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
| 110 parameters | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 510 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure parameter: 0.11 (5) |
2-Chloro-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
2-Chloro-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.7301 (4) | 0.3699 (6) | 0.8980 (2) | 0.0311 (7) | |
| C2 | 0.5982 (4) | 0.5654 (6) | 0.9179 (3) | 0.0334 (7) | |
| H2 | 0.645995 | 0.688449 | 0.972562 | 0.040* | |
| C3 | 0.3940 (5) | 0.5786 (6) | 0.8563 (3) | 0.0337 (7) | |
| H3 | 0.305127 | 0.710757 | 0.869335 | 0.040* | |
| C4 | 0.3236 (4) | 0.3932 (6) | 0.7754 (2) | 0.0290 (7) | |
| C5 | 0.4562 (5) | 0.1964 (6) | 0.7575 (3) | 0.0335 (8) | |
| H5 | 0.408280 | 0.070786 | 0.703994 | 0.040* | |
| C6 | 0.6593 (5) | 0.1844 (6) | 0.8184 (3) | 0.0348 (8) | |
| H6 | 0.747984 | 0.051642 | 0.805778 | 0.042* | |
| C7 | −0.0065 (5) | 0.6041 (7) | 0.6835 (3) | 0.0349 (7) | |
| C8 | −0.2181 (5) | 0.5695 (7) | 0.6051 (3) | 0.0442 (9) | |
| H8A | −0.238963 | 0.713348 | 0.553173 | 0.053* | |
| H8B | −0.326264 | 0.580067 | 0.649112 | 0.053* | |
| N1 | 0.1164 (3) | 0.3959 (5) | 0.7083 (2) | 0.0331 (6) | |
| H1 | 0.065971 | 0.250333 | 0.681401 | 0.040* | |
| O1 | 0.9342 (3) | 0.3507 (4) | 0.9570 (2) | 0.0433 (6) | |
| H1A | 0.967245 | 0.484830 | 0.991810 | 0.065* | |
| O2 | 0.0363 (3) | 0.8215 (4) | 0.7186 (2) | 0.0500 (6) | |
| Cl1 | −0.25580 (12) | 0.27889 (19) | 0.52655 (7) | 0.0555 (3) |
2-Chloro-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0250 (14) | 0.0296 (17) | 0.0360 (17) | −0.0017 (13) | −0.0002 (12) | 0.0054 (14) |
| C2 | 0.0334 (17) | 0.0289 (17) | 0.0344 (17) | −0.0011 (14) | −0.0014 (13) | −0.0042 (14) |
| C3 | 0.0304 (16) | 0.0303 (17) | 0.0383 (18) | 0.0034 (14) | 0.0022 (13) | −0.0025 (14) |
| C4 | 0.0251 (15) | 0.0268 (15) | 0.0329 (16) | −0.0010 (13) | 0.0006 (12) | 0.0036 (13) |
| C5 | 0.0326 (16) | 0.0266 (17) | 0.0386 (18) | −0.0022 (13) | 0.0007 (13) | −0.0037 (13) |
| C6 | 0.0293 (15) | 0.0254 (16) | 0.050 (2) | 0.0063 (12) | 0.0079 (14) | −0.0008 (14) |
| C7 | 0.0279 (16) | 0.0337 (18) | 0.0412 (18) | 0.0000 (14) | 0.0022 (13) | 0.0041 (15) |
| C8 | 0.0340 (17) | 0.0336 (19) | 0.058 (2) | 0.0014 (15) | −0.0066 (15) | 0.0046 (17) |
| N1 | 0.0279 (13) | 0.0259 (13) | 0.0407 (15) | −0.0005 (11) | −0.0047 (11) | −0.0030 (12) |
| O1 | 0.0293 (10) | 0.0387 (15) | 0.0545 (14) | 0.0005 (10) | −0.0093 (9) | −0.0015 (12) |
| O2 | 0.0407 (12) | 0.0297 (14) | 0.0705 (16) | 0.0019 (11) | −0.0105 (11) | −0.0033 (12) |
| Cl1 | 0.0505 (5) | 0.0519 (5) | 0.0530 (5) | −0.0009 (5) | −0.0155 (4) | −0.0056 (5) |
2-Chloro-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C6 | 1.378 (4) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.379 (4) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| C1—O1 | 1.381 (3) | C7—O2 | 1.216 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.391 (4) | C7—N1 | 1.340 (4) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C7—C8 | 1.520 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.387 (4) | C8—Cl1 | 1.774 (4) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C8—H8A | 0.9700 |
| C4—C5 | 1.381 (4) | C8—H8B | 0.9700 |
| C4—N1 | 1.430 (3) | N1—H1 | 0.8600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.382 (4) | O1—H1A | 0.8200 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 120.3 (3) | C1—C6—H6 | 120.1 |
| C6—C1—O1 | 117.8 (3) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.1 |
| C2—C1—O1 | 121.9 (3) | O2—C7—N1 | 125.5 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 120.1 (3) | O2—C7—C8 | 116.4 (3) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.9 | N1—C7—C8 | 118.1 (3) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.9 | C7—C8—Cl1 | 116.7 (2) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.6 (3) | C7—C8—H8A | 108.1 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.2 | Cl1—C8—H8A | 108.1 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.2 | C7—C8—H8B | 108.1 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.8 (3) | Cl1—C8—H8B | 108.1 |
| C5—C4—N1 | 117.6 (3) | H8A—C8—H8B | 107.3 |
| C3—C4—N1 | 122.6 (3) | C7—N1—C4 | 126.0 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.6 (3) | C7—N1—H1 | 117.0 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.7 | C4—N1—H1 | 117.0 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.7 | C1—O1—H1A | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 119.7 (3) | ||
| N1—C7—C8—Cl1 | −15.4 (4) |
2-Chloro-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C3—H3···O2 | 0.93 | 2.34 | 2.873 (4) | 116 |
| N1—H1···Cl1 | 0.86 | 2.53 | 2.999 (2) | 115 |
| N1—H1···O2i | 0.86 | 2.28 | 3.025 (3) | 145 |
| O1—H1A···O1ii | 0.82 | 2.06 | 2.8585 (17) | 166 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y−1, z; (ii) −x+2, y+1/2, −z+2.
References
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst.45, 849–854.
- Gowda, B. T., Foro, S. & Fuess, H. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o4488.
- Gowda, B. T., Kožíšek, J., Tokarčík, M. & Fuess, H. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kang, S., Zeng, H., Li, H. & Wang, H. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Sovago, I., Cottrell, S. J., Galek, P. T. A., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Platings, M., Shields, G. P., Stevens, J. S., Towler, M. & Wood, P. A. (2020). J. Appl. Cryst.53, 226–235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Missioui, M., Guerrab, W., Nchioua, I., El Moutaouakil Ala Allah, A., Kalonji Mubengayi, C., Alsubari, A., Mague, J. T. & Ramli, Y. (2022). Acta Cryst. E78, 687–690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Missioui, M., Mortada, S., Guerrab, W., Serdaroğlu, G., Kaya, S., Mague, J. T., Essassi, E. M., Faouzi, M. E. A. & Ramli, Y. (2021). J. Mol. Struct.1239, 130484.
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Rigaku OD (2023). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314624010150/tk4111sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314624010150/tk4111Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314624010150/tk4111Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2392239
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report