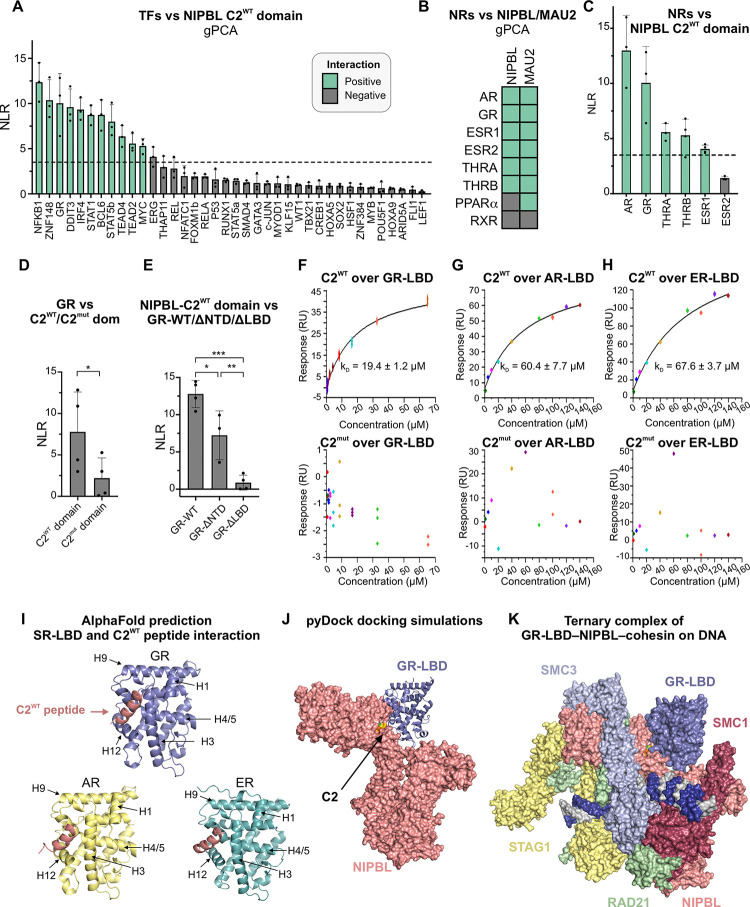
Figure 3: SR-LBDs interact with NIPBL through C2.
(A) NLRs of the NIPBL-C2WT domain against indicated TFs. Green = positive and black = negative interactions. (B) Heatmap of interactions between NIPBL/MAU2 and NRs detected by gPCA. (C-E) NLRs for (C) NIPBL-C2WT domain against the NRs that scored positively against NIPBL-WT; (D) GR against NIPBL-C2WT/C2mut domains; *p<0.05 (paired t-test); (E) NIPBL-C2WT domain vs GR-WT, GR lacking its NTD (GR-ΔNTD), or its LBD (GR-ΔLBD), *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 (one-way ANOVA and Tukey test for multiple comparisons). Error bars in panels A-E represent the standard deviation across measurements. (F-H) SPR sensorgrams for indicated human (h) SR-LBDs against human NIPBL-C2WT (top) and C2mut (bottom) peptides. (I) AlphaFold2-Multimer predictions for the interaction between hNIPBL-C2WT peptide (salmon) and the LBDs of hGR, hAR, and hER. (J) Docking prediction for the hGR-LBD (blue) with the structured portion of hNIPBL (salmon). (K) Superposition of the pyDock prediction of the NIPBL-GR-LBD structure with the cryo-EM structure of the NIPBL-cohesin-DNA complex23. See also, Figure S3.