Abstract
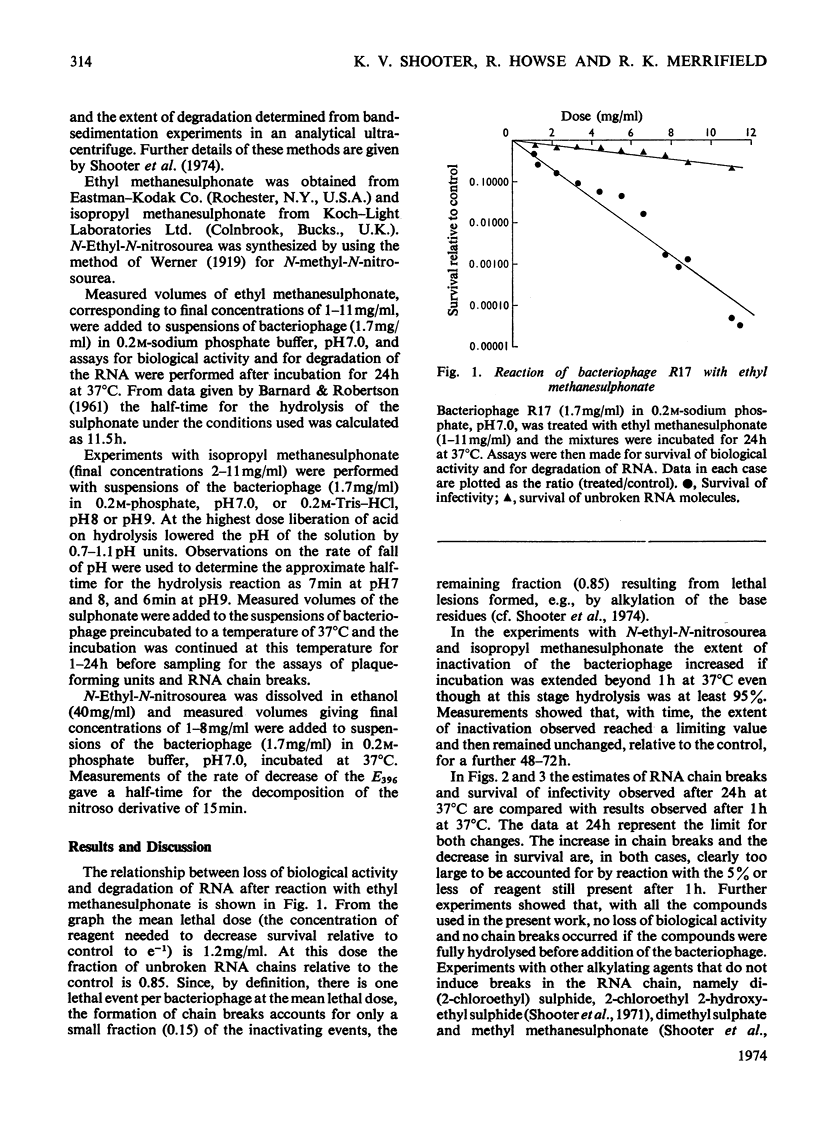
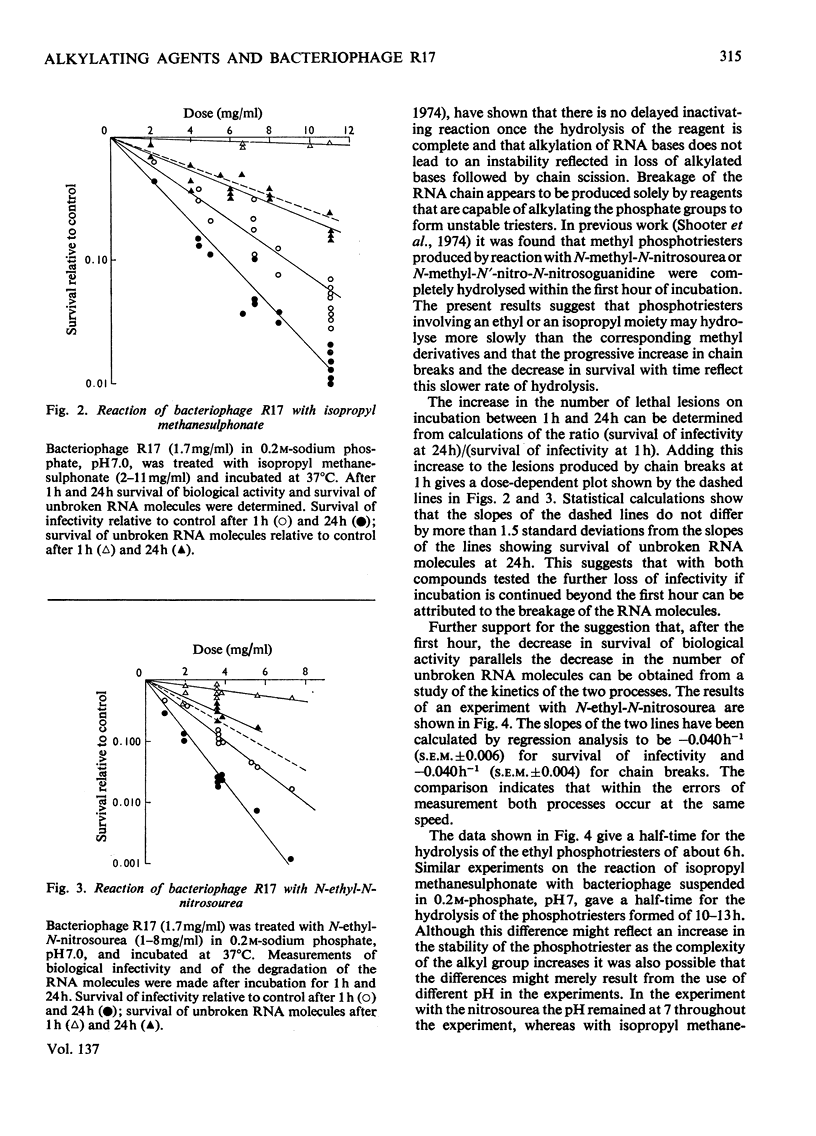
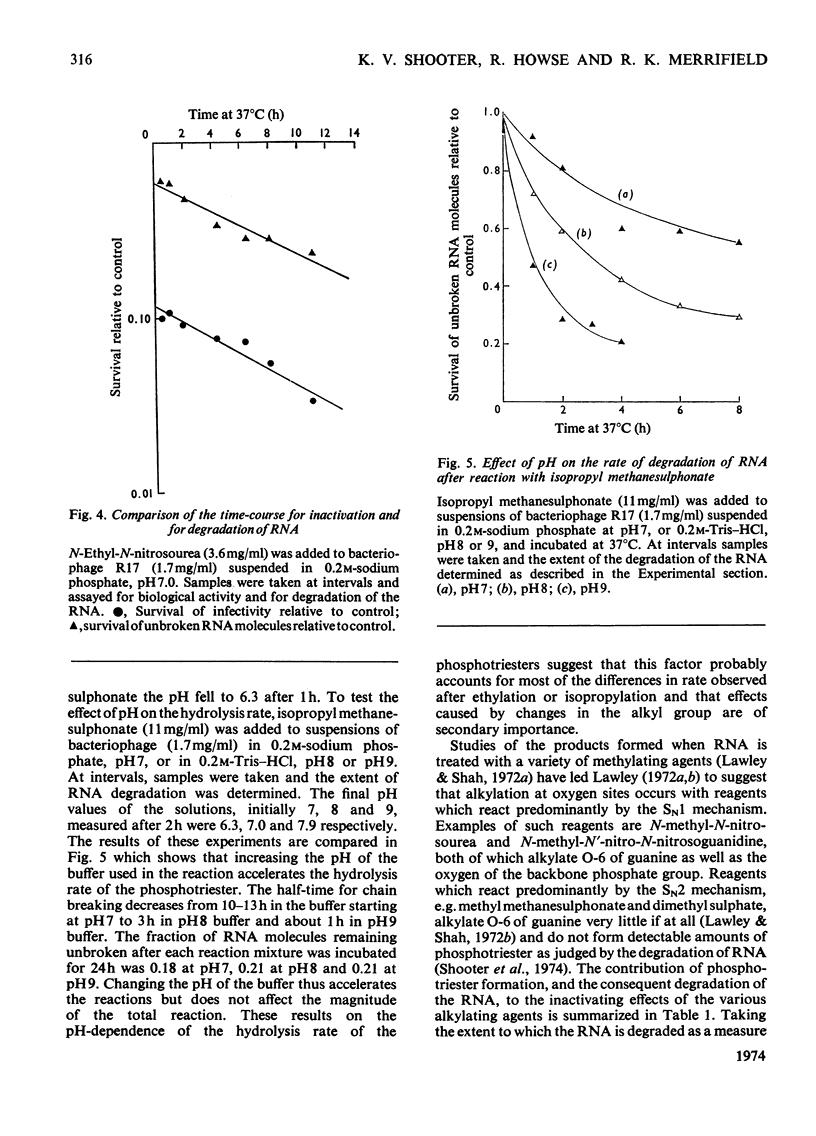
The extent of biological inactivation and of the degradation of the RNA after reaction of bacteriophage R17 with ethyl methanesulphonate, isopropyl methanesulphonate and N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea was studied. Formation of breaks in the RNA chain probably results from hydrolysis of phosphotriesters formed in the alkylation reactions. Near neutral pH the ethyl and isopropyl phosphotriesters are sufficiently stable for the kinetics of the hydrolysis reaction to be followed. Results indicate that the rate of hydrolysis increases rapidly as the pH is raised. The evidence shows that a phosphotriester group does not itself constitute a lethal lesion. The extent of phosphotriester formation by the different agents is discussed in terms of reaction mechanism.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWN D. M., TODD A. R. Nucleic acids. Annu Rev Biochem. 1955;24:311–338. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.24.070155.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannon P., Verly W. Alkylation of phosphates and stability of phosphate triesters in DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Nov 21;31(1):103–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02506.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freifelder D. Effect of NaCIO-4 on bacteriophage: release of DNA and evidence for population heterogeneity. Virology. 1966 Apr;28(4):742–750. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freifelder D. Mechanism of inactivation of coliphage T7 by x-rays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):128–134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawley P. D. Reaction of N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (MNUA) with 32P-labelled DNA: evidence for formation of phosphotriesters. Chem Biol Interact. 1973 Aug;7(2):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(73)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawley P. D., Shah S. A. Methylation of ribonucleic acid by the carcinogens dimethyl sulphate, N-methyl-N-nitrosourea and N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. Comparisons of chemical analyses at the nucleoside and base levels. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(1):117–132. doi: 10.1042/bj1280117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawley P. D., Shah S. A. Reaction of alkylating mutagens and carcinogens with nucleic acids: detection and estimation of a small extent of methylation at O-6 of guanine in DNA by methyl methanesulphonate in vitro. Chem Biol Interact. 1972 Sep;5(4):286–288. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(72)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawley P. D., Thatcher C. J. Methylation of deoxyribonucleic acid in cultured mammalian cells by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. The influence of cellular thiol concentrations on the extent of methylation and the 6-oxygen atom of guanine as a site of methylation. Biochem J. 1970 Feb;116(4):693–707. doi: 10.1042/bj1160693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhaese H. J., Boetker N. K. The molecular basis of mutagenesis by methyl and ethyl methanesulfonates. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jan 3;32(1):166–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shooter K. V., Edwards P. A., Lawley P. D. The action of mono- and di-functional sulphur mustards on the ribonucleic acid-containing bacteriophage mu2. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(3):829–840. doi: 10.1042/bj1250829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shooter K. V., Howse R., Shah S. A., Lawley P. D. The molecular basis for biological inactivation of nucleic acids. The action of methylating agents on the ribonucleic acid-containing bacteriophage R17. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;137(2):303–312. doi: 10.1042/bj1370303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


